Inbound call routing menus, auto attendants, and IVR systems help customers navigate a business phone system, allowing callers to get the assistance they need without involving a live agent.
But lengthy and overly complicated menus can irritate your customers–especially those who already know the agent, department, or extension they want to dial.
Direct Inward Dialing puts an end to the frustrations of automated call menus, creating a more immediate connection by routing calls to a particular phone within your company’s network.
This article covers the ins and outs of direct inward dialing, discussing what it is, how it works, how to get it, and the business benefits DID provides.
- DID Overview
- What is a DID Number?
- How DID Works
- DID vs DOD
- The Benefits of DID
- Get a DID Number
- FAQs
What is Direct Inward Dialing?
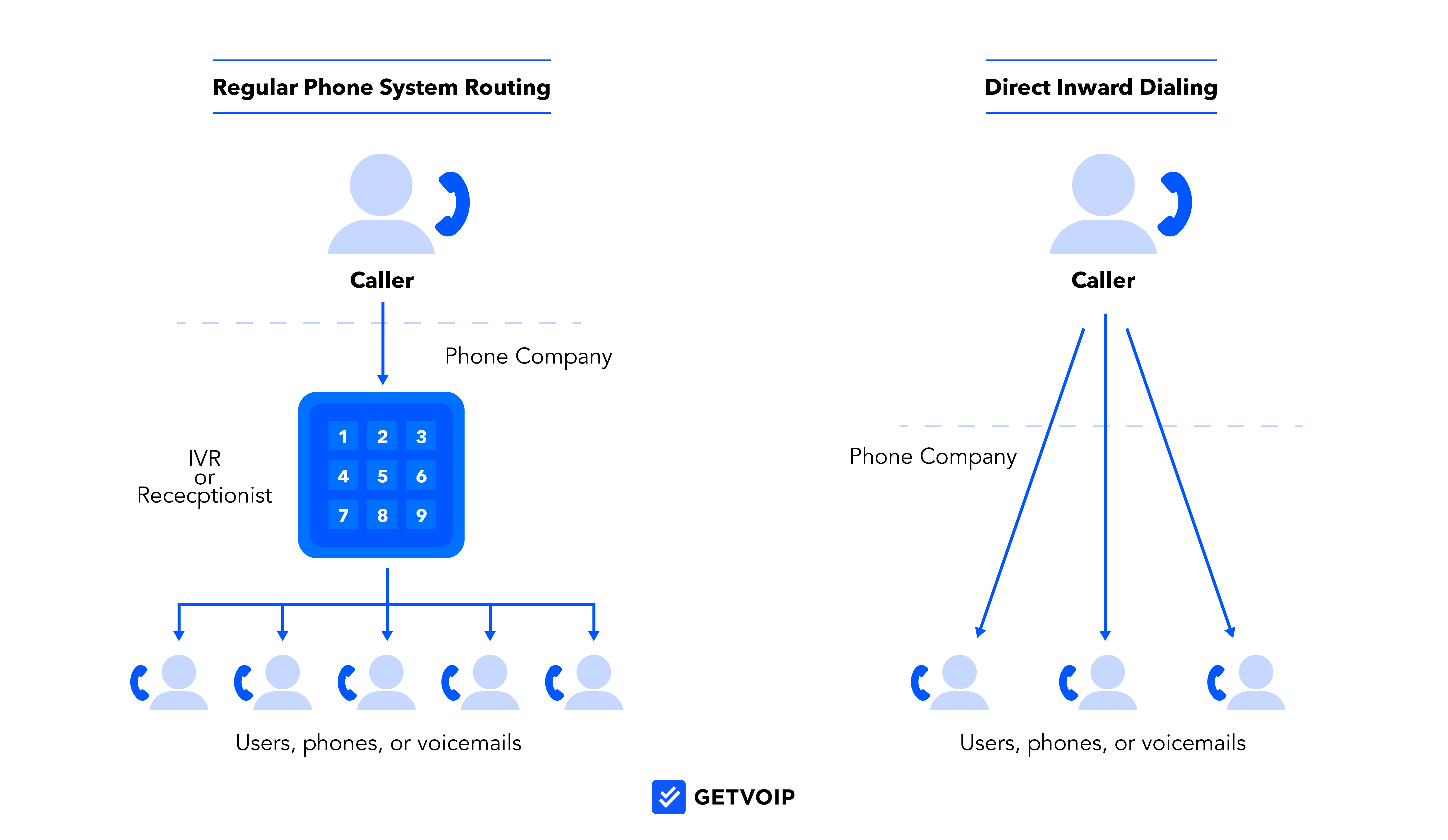
Direct inward dialing (DID) is a phone system feature that connects inbound calls directly with a specific user, extension, or voicemail rather than going through an automated routing menu or recepsionist.
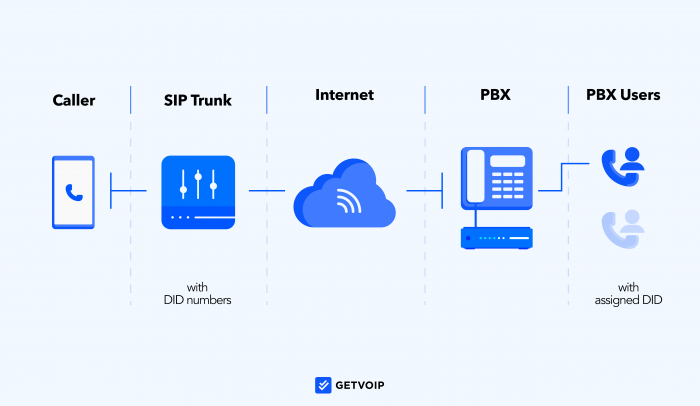
Businesses access direct inward dialing by leasing business phone numbers from a service provider, then assigning these DID numbers to particular users, queues, or ring groups.
Both cloud-based PBX and traditional landline PBX providers offer DID, but the setup process varies depending on whether your phone system uses VoIP or PSTN.
What is a DID Number?
A DID number is any business phone number that routes directly to a specific phone or user within the company phone network, bypassing IVR menus and self-service routing systems.
If your company uses a landline PBX phone system, your phone provider can assign you local numbers based on your building’s address.
Alternatively, with a cloud-based or hosted PBX system from a VoIP or UCaaS provider, you can purchase local, toll-free, and vanity numbers from anywhere in the world–then assign them to team members.
How Does Direct Inward Dialing Work?
When a user calls a direct inward dial number, the phone system provider routes the call directly to the associated user or phone. This call routing is achieved via either cloud-based VoIP or landline-wired PRI.
DID’s data transmission method depends on your company’s phone system type:
- Cloud-based VoIP system
- SIP trunking with an onsite PBX system
- Traditional public-switched telephone network (PSTN)
- Fax
Direct Inward Dialing with Cloud-Hosted VoIP
With cloud-hosted VoIP and UCaaS, your virtual phone provider handles the SIP trunking needed to receive all incoming calls, whether via PSTN or VoIP. Your provider then virtually routes these calls to the appropriate DID number.
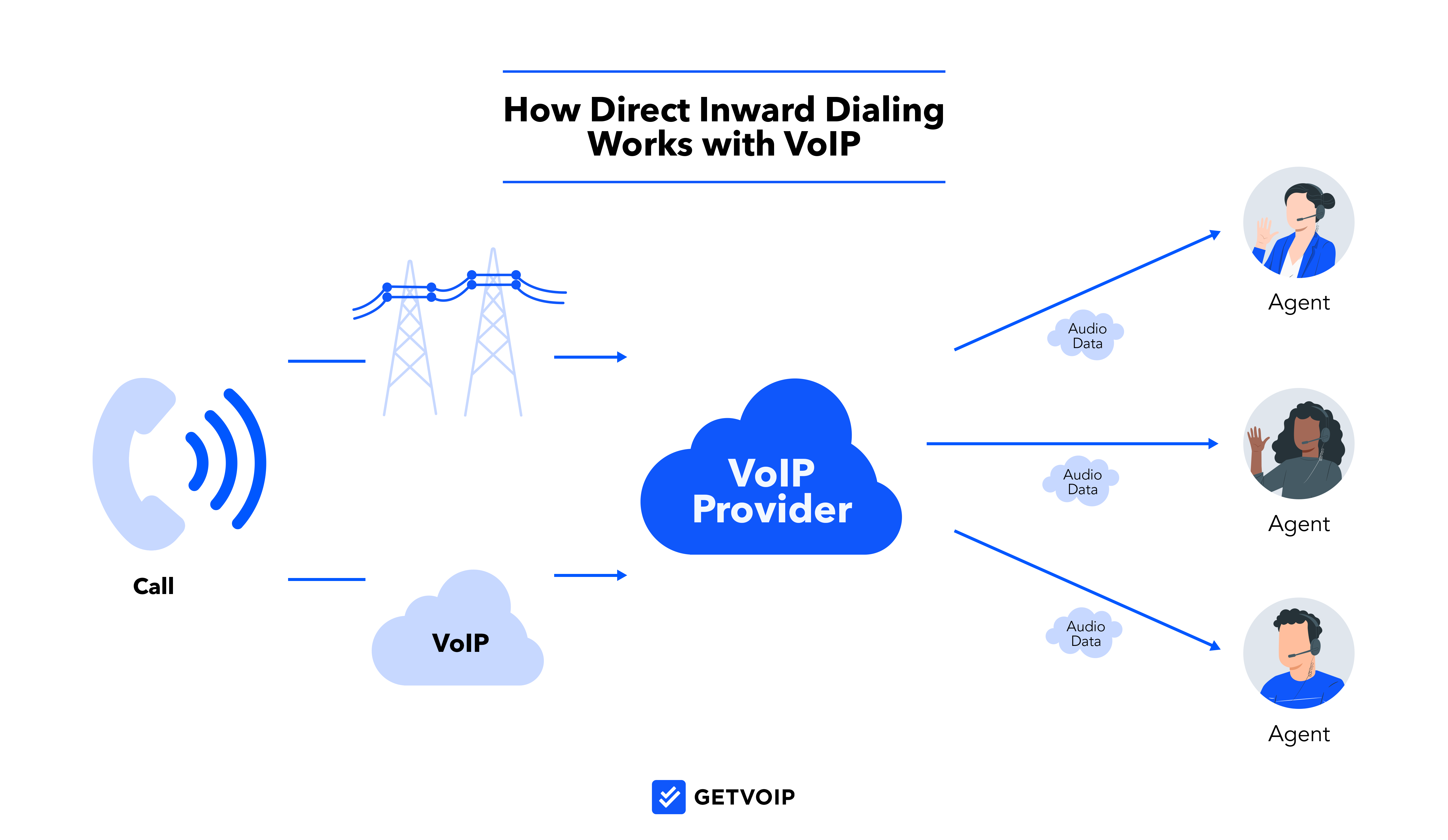
Compared to PSTN, using VoIP for DID provides distinct benefits:
- Global and remote number assignment: Your company can purchase direct dial-in numbers around the world and assign them digitally to remote users in dozens of countries.
- Better sound quality: Most VoIP providers utilize modern codecs that support HD-voice audio quality.
- Flexibility and scalability: VoIP providers offer the freedom to purchase one number at a time or multiple numbers, starting and stopping service within minutes–all from an online interface.
Direct Inward Dialing with IP PBX and SIP Trunking
An onsite IP PBX system undergoes a similar process to facilitate direct inward dialing.
Your VoIP provider receives the PSTN or VoIP transmission, then transmits the digital data to your company’s private branch exchange.
Once your IP PBX system receives this inbound data, it uses the internet to wirelessly transmit the call to the right user’s device. You can purchase phone numbers through your VoIP provider and assign these numbers to local users.
Compared to a cloud-hosted PBX, the drawback of an onsite IP PBX is that, as the end user, you still need to maintain the physical IP PBX box and data switch–which takes time, money, and effort.
Direct Inward Dialing with Traditional PSTN
With a traditional landline phone system, setting up a direct inward dialing service requires leasing and installing copper wires called Primary Rate Interface (PRI) Trunks. As opposed to virtual SIP Trunks, PRI Trunk lines are physical circuits that route analog call data from your provider, through your onsite PBX system, to the dialed user within your telephone company’s network.
Landlines limit your company to using only local DID telephone numbers from your provider and only allow for onsite phone system routing–eliminating the possibility of remote DID calls. Not only are onsite PRI circuits and physical phone lines a hassle to maintain, they also prevent more than 23 agents from making calls concurrently. This leads to more missed calls, longer hold times, and lower first-call resolution rates.
Direct Inward Dialing with Fax
In addition to phone calls, you can also use direct inward dialing to route inbound faxes directly to particular users, computers, and phone numbers.
A VoIP phone system makes this setup quick and simple.
In the number-management or user-management settings within your application interface, select the VoIP numbers you want to have virtual faxing capabilities, then set up fax-to-email for those numbers. Your provider will ensure that all inbound faxes to that virtual phone number reach the user’s email inbox in PDF form.
Direct Inward Dialing (DID) vs Direct Outward Dialing (DOD)
While direct inward dialing connects callers directly with a user inside the company’s phone system, direct outward dialing connects users directly to numbers outside their PBX system–without having to use an operator or dial a preceding number (“Press 1 to place an outbound call,” etc.)
One DOD number can be attached to multiple extensions or phones within a company network.
The Benefits of DID
Below, we discuss the primary benefits of direct inward dialing.
Faster and More Accurate Routing
When someone calls a direct dial number, they immediately connect with the intended user. This process sidesteps tedious and time-consuming self-service IVR menus and live operators.
Plus, vague or misunderstood self-service menu options confuse callers, leading many to reach the wrong destination or queue and forcing additional redirects.
Direct dial numbers guarantee the caller reaches their intended destination, especially since agents can use email and text to share direct dial numbers with click-to-call functionality. This eliminates the chances of a misdial.
Flexible Use Cases
By facilitating multichannel communication between customers and agents worldwide, DID numbers support a wide range of Enterprise-level and small-business needs.
Flexible Direct Inward Dialing Use Cases:
- Global numbers: Purchase DID virtual numbers around the world. Adjust your marketing, outreach campaigns, and CRM systems to provide particular direct-dial numbers to specific subsets of customers based on location or language.
- Toll-free numbers: Using toll-free numbers for direct inward dialing lets customers call agents from anywhere in the world–even long-distance calls–at no expense.
- Vanity numbers: A helpful marketing strategy offered by most VoIP providers, vanity numbers let businesses customize their toll-free business phone numbers with specific letters or number patterns (1-800-DOGSIT, etc.). DID vanity numbers are much easier for customers to remember and help build brand recognition.
- Conference call direct dial: Receive audio-conference direct dial numbers, which the host can share among all conference-call participants for easy access. Purchase personal audio conference numbers, for agents to host ad hoc conference meetings anytime, with hundreds of participants.
- Video conference direct dial: With most providers, video conferences and webinars generate shareable direct dial numbers for participants to dial into video conferences via phone, to listen and speak without video.
- SMS texting: Agents can send and receive SMS messages from virtual DID numbers
Personalized Customer Service
Direct inward dial numbers provide a variety of customer service benefits:
- Personal experience: When a customer gets to bypass a general routing system to connect with an agent directly, it makes them feel like the company accommodates their individual needs.
- Individualized follow-up: If a customer’s inquiry requires follow-up, they can use an agent’s DID number to reconnect with the same agent they interacted with previously. This strengthens customer loyalty and saves customers from repeating themselves, improving the customer experience while providing agents with fuller call context.
- VIP service: Use direct inward dial numbers to provide faster and more personalized service for VIP customers.
- Language- or location-based services: Depending on a customer’s language or calling location, provide them with direct dial numbers to reach agents whose business hours and language background match their own, to optimize communication.
Improved Internal Communication
Direct inward dial numbers enable team members to call each other with one click inside the phone application’s interface–instead of flipping through a spreadsheet pinned to the wall containing each company user’s name and extension.
Nearly all modern VoIP and UCaaS providers offer instant internal DID calling within their telephony app, allowing agents to transfer and forward calls between numbers.
How to Get a DID Number
Users receive DID numbers automatically upon subscription to a cloud-based phone system. Many business VoIP providers, like RingCentral and Nextiva, include free business phone numbers with each new user’s account.
Within a virtual phone system, each user’s assigned phone number is a direct inward dial number, which they can share with customers for direct inward dialing.
Administrators can purchase new virtual DID numbers for registered subscribers in the Manage Phone Numbers section of the Settings menu tab. Administrators can also activate and deactivate DID numbers in moments, change employee phone numbers, or create ring groups and call queues linked to particular DID numbers.