A contact center is a valuable tool for customer service. Today’s contact center technology enables agents to make outbound sales calls, send automated SMS for marketing, embed live chat and chatbots into your website, and more–all from one dashboard. But before implementing a contact center for your company, it’s helpful to know what to look for.
This article will cover everything you need to know about contact centers, including features, benefits, use cases, and best practices for implementation.
What is a Contact Center?
A contact center is a company department that communicates directly with customers via multiple communication channels: phone, SMS texting, web chat, email, social media, and video. Contact centers utilize inbound and outbound communications to provide customer support, sales, and other use cases.
While contact centers used to be premise-based, many companies now employ a remote contact infrastructure with agents based around the country or globe. Traditional call centers relied on a landline phone system, but today’s omnichannel contact centers are usually software-based and feature voice over IP (VoIP) telephony alongside dozens of other channels.
Companies utilize contact center technology for many purposes. A contact center lets customers call or message you for support, billing questions, to create an appointment, make an order, and more. Queues and IVR menus help organize inbound calls, so customers reach the right department. Multiple channels means that customers can call, text, message you through social media, or chat with you through your website. Businesses also utilize outbound contact center tools to automate sales calls from a lead campaign list or send bulk SMS texts for promotions.
An organized multichannel or omnichannel contact center improves customer satisfaction, boosts loyalty, and assists with sales and lead conversion.
Note that people use the term “contact center” to describe several related things:
- Contact center software: The software application that agents use to communicate with customers
- Contact Center as a Service (CCaaS): A type of contact center software hosted virtually, so that agents can access it via the internet
- Company department: As described above, a company’s “contact center” is the department or facility that handles customer-facing communications.
Contact Center vs Call Center: Are They the Same?
The difference between a contact center and a call center comes down to the channels they use. Call centers provide customer service via phone only, while contact centers use multiple communication channels: not just phone but email, web chat, video, SMS, and social media messaging.
Until around 2010, most companies relied on call centers, offering support via the telephone only. However, smartphones and widespread web adoption enabled customers to connect with companies from multiple touchpoints–SMS, or website-embedded live chat. Multichannel and omnichannel contact center software were developed to meet this need.
Today, companies use contact center technology to provide better customer convenience than offered by a call center. Contact center agents handle multiple channels from one interface, providing balanced and multifaceted customer service.
Let’s take a closer look at the differences between a contact center vs call center:
| Contact Center | Call Center | |
| Communication Channels |
|
|
| Infrastructure |
|
|
| Cost | $100-$250 monthly per user |
|
| Key Features |
|
|
| Use Cases |
|
|
Learn more: Contact Center vs Call Center: Differences & Similarities
Types of Contact Centers
There are several different types of contact centers. Each type varies depending on the communication methods, infrastructure, and channel unity. In the list below, numbers 1-3 refer to communication methods, 4 and 5 refer to infrastructure, and 6 and 7 refer to channel unity.
You can combine multiple types of the contact centers listed below. For example, some contact centers are blended, cloud-based, and omnichannel.
Let’s compare various types of contact centers:
Communication methods:
- Inbound
- Outbound
- Blended
Infrastructure:
- On-premises
- Cloud/Virtual
Channel unity:
- Omnichannel
- Multichannel
Inbound
Inbound contact centers only handle inbound, or incoming, customer inquiries. These are typically call centers providing customer support over the phone. As such, inbound call centers are typically voice-only, rather than multichannel or omnichannel.
Inbound call center agents generally provide a variety of customer-support use cases: technical support, billing, answering questions and booking appointments, etc. These call centers rely on interactive voice response (IVR) menus and call queues to route inbound callers to the correct department for service.
Outbound
An outbound contact center only places outbound communications and cannot receive inbound calls. These are typically call centers, although outbound contact centers may also utilize email or SMS.
Companies generally use an outbound contact center for sales or marketing purposes–such as lead calling, surveys, telemarketing, and cold calls. However, some outbound call centers also follow up on customer support inquiries and emails.
Outbound call centers frequently utilize auto dialers, which help them quickly reach customers. CRM integrations provide lead lists while giving marketing and sales teams context about each contact.
Blended
A blended contact center combines inbound and outbound service. Blended centers can receive calls from customers or place outbound phone calls. These can be phone-only call centers, or contact centers with email, web chat, SMS, phone, and social media messaging.
Blended contact centers are the most common type of contact center today. Companies use them for customer support, sales, technical support, telemarketing, and other communication needs.
On-Premises
With an on-premises contact center, the company hosts the entire communication infrastructure onsite in the office. The company manages and maintains all the equipment–phone system, landline connections, SIP trunk, servers and data storage, computers, etc.
Generally, the office building has a room devoted to housing this equipment. IT staff constantly manage the hardware, cables, and software, making sure everything stays working and updated. Since this infrastructure must remain onsite, it only works for in-person teams.
On-premises contact centers provide greater control and privacy than cloud-hosted contact centers. The business can store all data on-site and manage features, call queues, and extensions. However, the onsite infrastructure requires frequent maintenance and extra staffing. These contact centers typically support only basic features like IVR, basic call controls, and sometimes call queues.
Cloud/Virtual
Cloud-hosted contact centers, or virtual contact centers, are software-based and hosted by the provider. This type of infrastructure is also called contact center as a service (CCaaS). It’s the most common type of infrastructure for today’s contact centers.
Companies pay for a cloud contact center by subscribing to the provider’s service. Agents then download the CCaaS desktop app, which provides a dashboard with access to all channels: voice, SMS, web chat, video, and more. Users can access the CCaaS app anywhere they have a computer and an internet connection, so cloud-hosted contact centers work well for remote or hybrid teams.
Since cloud-hosted contact centers can quickly add and remove users, they are highly scalable. They also utilize virtual phone numbers from around the globe, empowering businesses to connect with international customers.
Omnichannel
An omnichannel contact center unifies all communication channels into one customer journey, which all agents can access. Customers can contact you on any touchpoint–voice, web chat, SMS–and the omnichannel software automatically tracks the interaction and syncs it with the customer’s journey history.
From an agent’s perspective, omnichannel software keeps everyone on the same page. Agents can see the customer’s entire journey history across channels. Customers can contact your company from any touchpoint, and the agent they reach will have the customer’s full context–recent orders, website interactions, and agents reached.
Omnichannel contact centers are becoming increasingly popular because they offer a consistent and convenient customer experience.
Multichannel
A multichannel contact center offers multiple communication channels but does not unify them. While an omnichannel contact center unifies all channels into a singular customer journey, multichannel contact center software initiates a new contact log every time a customer contacts the company.
Compared to omnichannel service, multichannel CCaaS leads to a more fragmented and siloed agent experience. When a customer contacts the company for a second time, or through a new channel, the agent does not receive any context about the customer’s interaction history. This forces agents to ask the same basic questions, causing customers to repeat themselves and become frustrated.
Still, multichannel contact centers offer multiple touchpoints through which customers can reach you. They are also generally more cost-effective than omnichannel platforms.
Contact Center Essential Features & Technologies
Contact centers combine dozens of features and communication channels to optimize customer service. These include agent dashboards, routing features, call queues, workforce management tools, analytics, call monitoring, and more. The individual features in each contact center vary depending on the infrastructure type, provider, and the plan you choose.
In general, here are the critical features to look for in a contact center:
- Communication channels
- User dashboard and interface
- Interactive voice response (IVR)
- Call queues
- Reporting and analytics
- Call monitoring
- Quality management
- Workforce management
Communication Channels
A contact center can include a combination of channels:
- Voice
- SMS texting
- Web chat
- Video meetings
- Social media and social media messaging
While a call center has only voice, a contact center typically adds several digital channels. Providers typically offer voice-only plans, digital-only plans with everything except voice, and blended plans with all channels.
When a company provides multiple communication channels, customers can contact them more easily. Customers can reach the company through the channel of their choice, including their website or social media account. Agents can access these communication channels in the application dashboard, which enables inbound and outbound communications.
User Dashboard and Interface
The contact center’s agent dashboard is the core of the agent’s experience. The dashboard provides access to all contact center channels and features, organized in a user-friendly interface on the provider’s desktop app.
The dashboard displays all the key features an agent uses:
- Communication channels
- Voicemail
- Call controls like transfer, hold, call park, etc.
- Customer profiles and information from CRM integration
- Task list
- Call queues
- Analytics
Especially for multichannel and omnichannel contact centers, it’s important to select a solution with a user-friendly dashboard. Agents should be able to switch between channels, access queued calls, and transfer calls in moments. An organized agent dashboard leads to quicker customer service, happier agents, and satisfied customers.
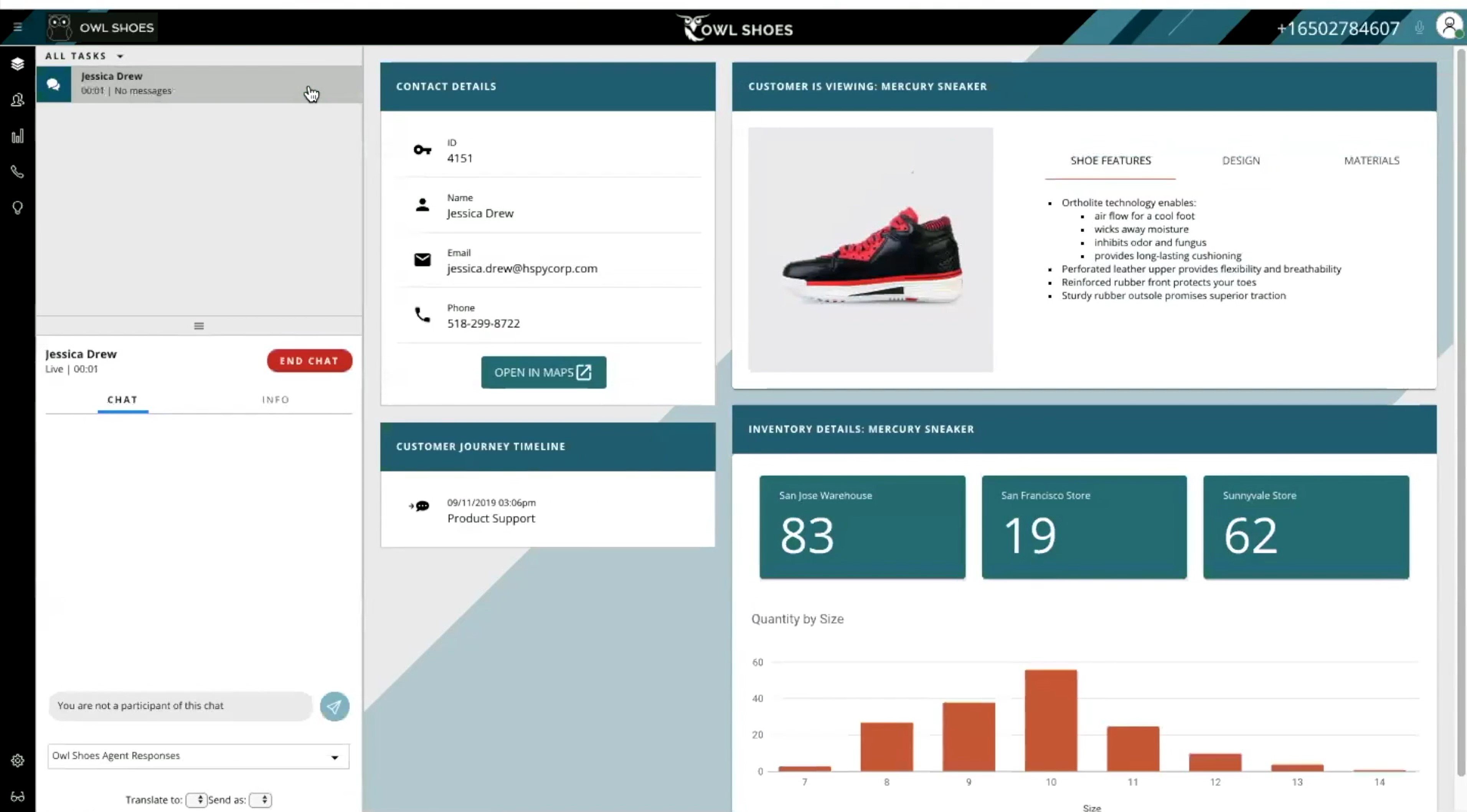
Interactive Voice Response (IVR)
An IVR menu is a recorded audio message that greets callers when they dial your company number. Also called an auto attendant, the IVR menu presents callers with menu options: For customer support, press “1”; For billing, press “2”, etc.
Typically, each number indicates a department, user, or submenu. You can also include announcements in the recording, such as new store hours. Most contact center phone systems include a drag-and-drop menu where you can build each level of your IVR call flow.
IVR menus provide self-service that routes customers to the correct location. This 24/7 service provides customer convenience, saves time and effort for agents, and improves first call resolution. Since 86% of customers prefer to contact customer support via phone, it’s useful to have a strong call routing menu.
Call Queues
Call queues organize contact center agents into departments, which share inbound call responsibility. Each department has a hold queue, which organizes overflow callers in a list if all agents are busy. Queues complement IVR menus, and many companies have queues for departments like Customer Support, Billing, and Technical Support. However, an individual agent can also have a queue, which is essentially an organized hold list.
Agent and supervisor dashboards display a live view of queue status–the number of callers waiting, how long they’ve waited, etc. Many contact centers utilize automated queue callbacks, which automatically call customers back when the agent reaches their spot in the queue. Queues help maintain shorter wait times.
Reporting and Analytics
Analytics and reports provide statistics and visual displays for hundreds of call center metrics and KPIs. In the analytics portal, supervisors can view trends and data about agent performance, call activity, channel usage, and call quality. These reports are customizable, so admins can sort the information by historical timeframe, user, and department.
Artificial intelligence (AI) based call centers include advanced tools like interaction analytics and customer sentiment scores. Supervisors can identify trends in agent service performance and view scores for each interaction’s customer experience.
These tools help supervisors identify agent strengths and weaknesses, for coaching and feedback. These tools also provide valuable information about how customers interact with your website and contact center, including a breakdown of IVR choices and customer needs.
Call and Interaction Monitoring
Call monitoring technologies enable supervisors to observe and manage agent performance in real-time. Many contact centers require one supervisor to manage a team of agents, which can be challenging when multiple agents are on the phone simultaneously.
Tools like listen, whisper, barge, and takeover enable a supervisor to actively listen or join calls as a third party. AI tools like live transcription and sentiment detection monitor interactions for problematic customer experiences, notifying supervisors when something may be concerning.
Call monitoring tools make it easier for supervisors to manage larger teams of agents, fixing problems as they occur and improving customer service.
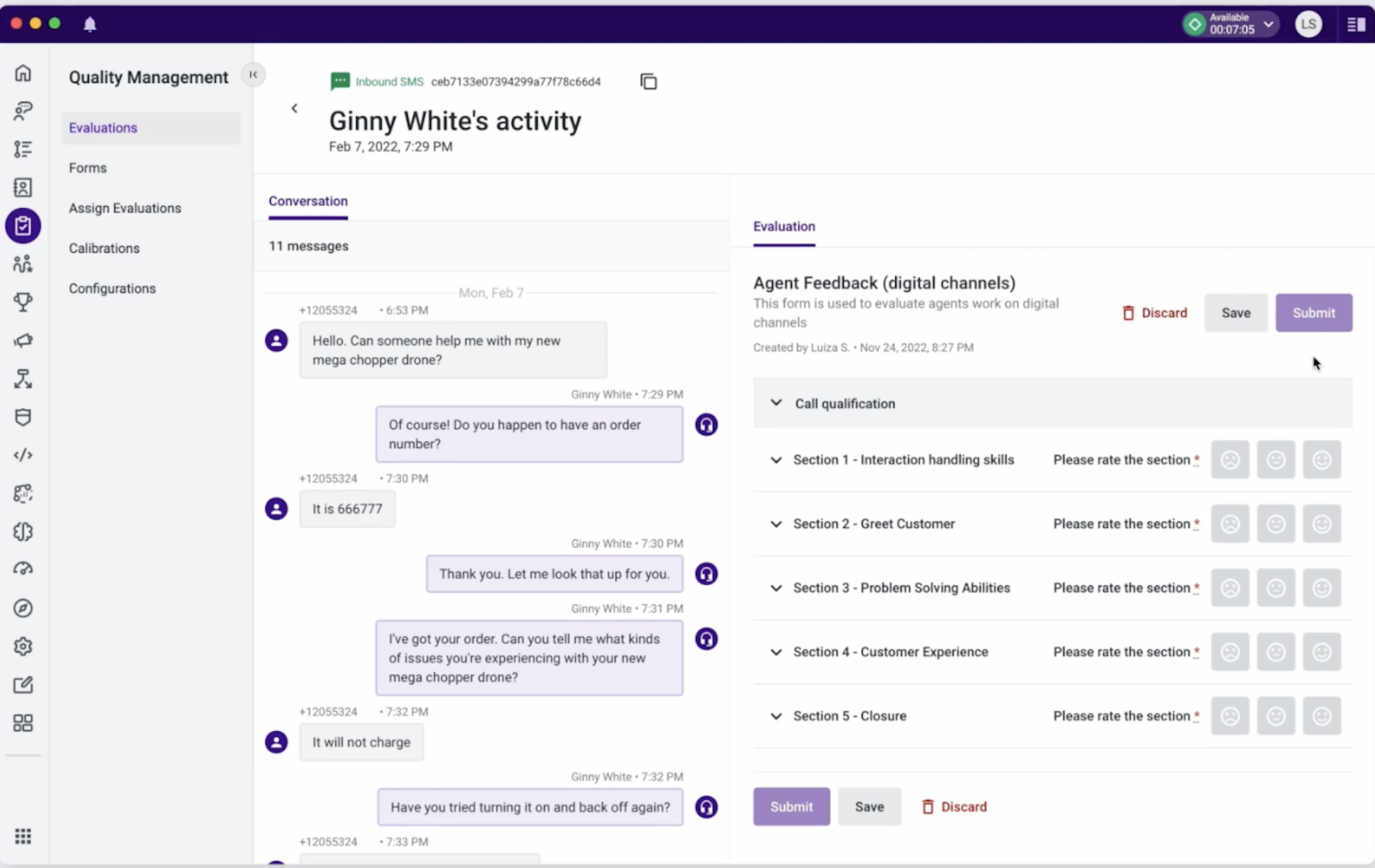
Quality Management
Quality management (QM) features help supervisors evaluate and coach agents. The most common QM tools include feedback forms, call logs and interaction reports, and AI-assisted evaluations.
Contact centers let admins create custom feedback forms, which streamline the evaluation process. Combine various question types, like yes/no questions, checklists, 1-10 scorings, and short answer sections. Agents can use these forms to self-evaluate, or AI algorithms can use call transcripts to complete the forms and evaluate agents.
When supervisors visit an agent’s interaction history, clicking into interaction reports displays each interaction’s recording, transcript, summary, key moments, and sentiment score. This in-depth record enables supervisors to provide deeper feedback for agents.
Workforce Management
Workforce management (WFM) tools simplify the manager’s experience in predicting staffing needs and scheduling agent shifts. Many of today’s contact center platforms utilize AI assistance for WFM.
Machine learning algorithms can identify daily, weekly, and seasonal trends in call center activity, using this data to forecast future staffing needs. CCaaS platforms also enable agents and staff to submit their FTE, availability, and schedule preferences. The contact center weighs these inputs data and creates schedules for all staff.
WFM tools save administrators substantial time and headache, while saving the company money due to more efficient staffing.
Business Benefits of a Contact Center
Using a multichannel or omnichannel contact center offers benefits for customers, agents, and your company. Here’s a quick look at some of the top benefits of using a contact center:
- Better customer experience
- Reduced staffing needs
- Lower costs
- Scalability
- Improved agent performance
- Supervisor support
- Customer data
- Advanced features
Better Customer Experience
A multichannel contact center makes it much easier for your customers to reach you. With multiple communication channels and touchpoints, including SMS and your website, customers can reach you through the method of their choosing.
This flexibility is especially important to the younger generation, 87% of whom highly value convenience. Self-service tools like IVR and virtual assistants provide 24/7 support, so customers can get answers even when your staff are off the clock.
When customers reach an agent, CRM integrations and in-depth customer profiles lead to more personalized support, quicker issue resolutions, and more loyal customers.
Reduced Staffing Needs
Contact centers automate and support most agent tasks, enabling your company to accomplish more while reducing staffing needs. Virtual agents and IVR menus can answer questions and route calls, eliminating the need for a live receptionist.
AI-assisted chatbots can provide rich services like booking appointments, facilitating transactions, and retrieving customer data, replacing tasks previously done by agents. In fact, AI is expected to reduce customer support staffing needs 20-30% by 2026.
Lower Costs
Hosted contact center software is often cheaper than an on-premise call center that uses landline. A landline call center requires frequent hardware updates and maintenance, plus the cost of IT staff to upkeep the equipment.
By contrast, hosted contact center software subscriptions cost between $75 and $250 monthly per user. They require no maintenance, extra staff, or additional hardware besides a computer. In the long run, companies generally save money by switching from a premise-based call center to a hosted contact center.
Experts predict that contact centers increasing AI adoption will lead to further savings. Gartner expects conversational AI to reduce labor costs by $80 billion dollars in 2026, and AI-assisted contact centers will play a major role in that.
Scalability
Cloud-based contact center software makes it easy to add and remove users. Administrators purchase new phone numbers and subscriptions online in minutes, inviting new staff via email.
Call center agents can access the dashboard, communication channels, and other features from their laptops, so teams don’t have to purchase new hardware. Easily add remote staff, who can handle call center duties wherever they have an internet connection.
Virtual phone numbers companies to expand business presence beyond their local area code. International VoIP numbers provide a local presence anywhere you choose.
The digital nature of cloud-based contact centers makes them scalable, easy to set up, and compatible with remote work.
Improved Agent Performance
Contact center dashboard, advanced features, AI support, and integrations empower agents to provide better service. The dashboard provides a hub for agents to organize all channels and tasks. Omnichannel technology means that reps can view a customer’s journey history, which provides a valuable context for better customer calls. CRM integrations also provide customer information that gives agents helpful context.
AI support tools like response suggestions, relevant articles, and live checklists ensure that agents follow correct protocols. Call monitoring tools and AI-based coaching help agents learn from their errors and grow as customer service reps.
Advanced Features
Modern contact centers, especially hosted contact center software, include dozens of advanced features that traditional call center technology does not have.
Having multiple communication channels provides several convenient touchpoints for your customers. Workforce management and quality management tools help supervisors, while call queues and IVR menus keep incoming calls organized. AI tools like live-agent assistance and interaction analytics provide unique insights.
Contact centers offer dozens of features, like auto dialers and call monitoring, that may replace some of your other software or unlock new business use cases.
Contact Center Use Cases
In general, contact centers work for any use case involving customer communication. This includes industries like healthcare, retail, education, finance, and many more. Companies use contact centers for customer support, sales, marketing, and other purposes.
Let’s take a look at the main use cases for a contact center:
- Customer support
- Sales
- Self-service
- Retail
- Financial services
Customer Support
A contact center works well for all types of customer relationship management. Multiple communication channels like voice, social media, live chat, email, and SMS enable your agents to serve customers on the platform of their choice.
Call queues and IVR enable a company to split the contact center into as many departments as necessary, to provide different customer-service branches like technical support, billing, order status, etc. CRM integrations, sentiment scores, and interaction analytics provide insights about customer experience, helping teams refine their service strategy.
Sales
A contact center’s communication channels, workflow automations, and outbound dialing tools support sales efforts. Agents can send automated emails, trigger bulk texts for marketing purposes, and automate surveys to understand customer attitudes. Outbound auto-dialers link with your CRM system to call leads rapidly.
AI-based tools analyze transcripts and customer behavior to segment leads, helping sales teams develop stronger prospects.
Self-Service
Call center software functionality enables self-service use cases. Automated tools like virtual agents and chatbots are highly conversational, able to answer questions and route inbound customers.
Companies can integrate chatbots into their websites to serve customers across touchpoints. Use CCaaS to build a knowledge base of articles, which answer customer questions and empower chatbots with smarter responses. Modern-day IVA systems can handle advanced actions like booking appointments, processing orders and transactions, updating orders, and more.
Businesses can use AI-based contact center technology for any use cases involving customer self-service.
Retail
Online and in-store retail companies often utilize contact centers to provide multichannel customer support. Businesses can integrate chatbots into their website, to help customers find products or speak with live representatives who can facilitate sales. Virtual assistants can connect with your CRM system or database to provide information about order status and product inventory.
Companies can use email to set up automated purchase confirmations or use SMS for shipping updates. Create call queues for relevant departments like order status, sales, technical support, product information, general support, and more.
Financial Services
Companies in the financial services industry often use contact centers for customer service. These include banks, insurance companies, investment companies, and other businesses that assist customers with finance. Companies in this sector use contact centers to answer customer questions, automate reminders, manage customer information, and more.
Customers visit their bank’s website and use a chatbot to ask questions about their account balance. To verify their identity, the company can integrate two-factor authentication via text message. If the customer wants, they can speak with a live representative with one click from the live chat window. This cohesive flexibility is enabled by omnichannel contact center technology.
How to Implement a Contact Center at Your Organization
When setting up call center technology for your company, there are a few guidelines to keep in mind. Use the following process to get started with implementing a contact center for your business:
- Establish goals and purposes: First, define the business goals you want to accomplish with your contact center. List all the reasons and purposes for your customer communication, what services you want to provide for customers, and which channels would enable this.
- Determine “must have” features and channels: As you begin to compare contact center providers, list the features and channels that you consider essential in handling your business needs. For example, voice, call queues, and customer sentiment scores.
- Utilize free trials: When you’ve decided on the top four or five contact center options, contact the providers to arrange a week-long free trial with each product. Ask agents about their experience with the dashboard, analytics, and channels.
- Thoroughly compare options: Examine the pricing, plans, and features for ten or more contact center providers. Determines each plan’s value by noting which ones provide all the channels and features you consider essential, at the lowest per-agent cost.
- Focus on IVR and call queues: In most cases, IVR menus and call queues will form the backbone of your customer engagement strategy. Begin by carefully creating your departments and menu recordings, trying to anticipate the volume that each department will receive.
- Train agents on the features: As you get started with your platform, train agents on how to use the features and channels. Assign one agent or administrator to understand the advanced features and create training segments for other contact center staff members.
Best Practices for Contact Center Management
As you begin to roll out your contact center platform, it’s helpful to have a few strategies to guide growth. Keep the following call center management strategies in mind:
- Start slowly with features: Depending on your experience with contact center software, choose a plan that offers a manageable number of features. It can feel overwhelming to begin using a product with hundreds of advanced features. Better to begin with a more basic product, then upgrade to a more advanced pricing tier once you’ve mastered the basics.
- Use analytics to improve: Analytics and reports provide valuable data to help you ensure high service quality. Data like customers’ IVR choices, satisfaction scores, call volume trends, and agent performance provide valuable insights to drive business decisions.
- Integrate third-party software: Contact center software is designed to integrate with third-party platforms like CRM systems, unified communications and collaboration tools, ticketing software, and databases. These integrations provide better context for customer interactions and power self-service tools. It also makes agents’ lives much easier when they can sync data and activity across apps.
- Take advantage of self-service tools: Customer self-service tools save agents tremendous time and effort. IVR systems increase the likelihood that an inbound caller reaches the right destination. Chatbots answer questions that otherwise consume agents’ time. Set up these tools to reduce staffing needs and help your agents focus on person-to-person service.
- Use AI to support agents and supervisors: Use AI tools that improve call monitoring and live agent support. Capabilities like real-time assistance and auto-generated interaction summaries save agents time, and help support new hires. Call transcriptions and AI-based scheduling help supervisors evaluate and schedule agents.
Learn more: Call Center Management Best Practices, Dos and Don’ts
A contact center lets you communicate with customers across multiple communication channels. It enables you to provide customer service via email, SMS, voice, live chat, video, and social media–all from one dashboard. This is why research suggests the omnichannel industry will maintain a 13.6% annual growth rate through 2029.
To compare contact center solutions, pricing, and features, check out our rankings and detailed comparison of the best contact center software.



