Call routing is an indispensable part of improving call center operations and customer experience. It expedites phone-based customer support by connecting callers to agents with proper product knowledge and customer service skills.
In this article we’ll take a closer look at what is call routing, how exactly it works, explore popular routing strategies, and outline best practices.
What is Call Routing?
Call routing is a call management feature that automatically directs incoming calls to the optimal queues, departments, ring groups, or agents according to a variety of predefined rules and conditions.
Call routing rules can be based on factors like:
- Current or predicted call volumes
- The customer’s specific issue and/or its priority level
- Agent schedules and business hours
- Customer and agent behavior
- Current agent availability
- Existing customer-agent relationships
- The importance and value of the caller’s account
- The caller’s preferred language
- AI-powered algorithms
Call routing often eliminates the need to transfer callers or place them on hold, instantly connecting the customer to the best available agent instead.
However, the ultimate goal of call routing is to determine which representative is most likely–based on their availability, job title, and skillset–to provide the highest quality of customer support and, ideally, completely resolve the customer’s issue on the first call.
How Does Call Routing Work?
Call routing works by determining caller intent, sending callers to the correct queues based on caller input, pre-established rules, and routing strategies, then directing those callers to the best available agent.
The call routing process consists of three main steps:
Step One: Call Qualification
The first step in routing business calls is to collect and analyze customer data to determine the caller’s intent.
In some cases, the caller’s intent is determined by the specific business phone number or extension dialed.
But most of the time, the reason for the customer’s call–as well as additional key customer data–is determined based on the customer’s input into the Interactive Voice Response (IVR) system.
The IVR system (sometimes called an auto attendant) automatically plays a series of pre-recorded prompts, greetings, and call menu options, which customers respond to via speech or dial pad input. Common examples of IVR prompts include “To report your card as lost or stolen, please press 2,” or “To speak to the billing department, say ‘billing.’”
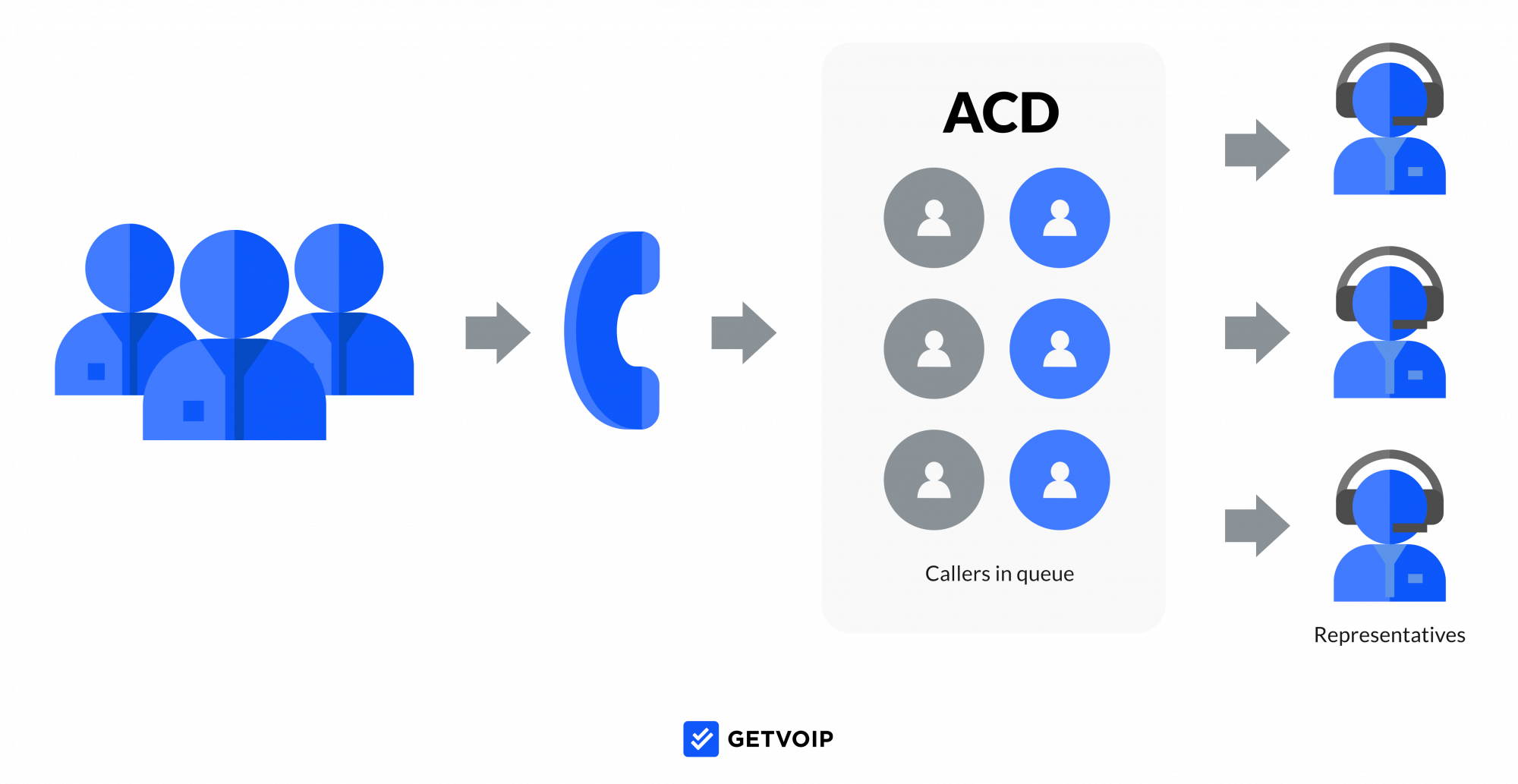
Step Two: Call Queuing
The next phase in the call routing process is the call queuing stage.
Here, Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) analyzes customer IVR input, contact information, and other key data, routing calls to the ideal queue based on pre-established rules and caller needs/intent.
IVR input can be analyzed via Speech Recognition, Natural Language Processing, or Conversational AI.
The Automatic Call Distributor routes calls to specific queues based on pre-set call rules, selected routing options, and criteria like call flow paths, agent availability, current call volumes, and more.
Step Three: Call Distribution
The Call Distribution phase, the last step of call routing service, directs calls from call queues to individual agents.
As with the Call Queuing phase, call handling and distribution is determined by pre-established calling rules, agent availability and skill sets, and customer data stored in your CRM solution.
This ensures that the caller will be connected to the ideal agent for their unique issue.
Different Types of Call Routing
Implementing a variety of call routing strategies decreases hold times, increases first call resolution rates, and evenly distributes the workload among available agents. Most importantly, effective call routing ensures customers get accurate, current, and personalized support from the representative they speak to.
While popular call management features like simultaneous ringing, ring groups, and call forwarding increase the likelihood of connecting callers with a live agent, the below call routing strategies optimize the entire call queuing and distribution processes, leading to happier agents and customers.
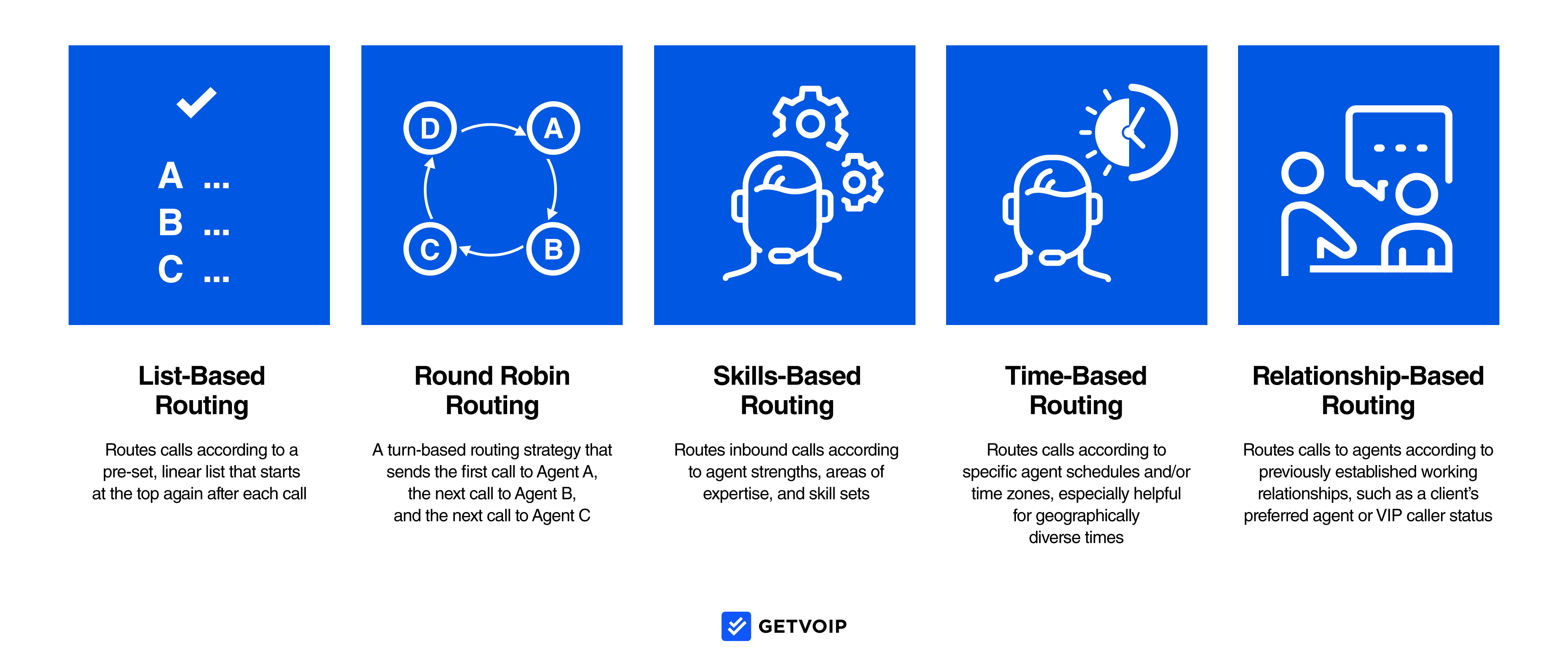
- Skills-Based Routing: Skills-based routing uses information the customer provides the IVR system to connect them to agents with the relevant skill set, training, or qualifications to provide the best assistance. For example, if a customer has a question about an unfamiliar account charge, skills-based routing ensures their call is routed to an agent in the billing department, not an HR representative without access to customer accounts.
- Least Occupied Routing: Least occupied routing, sometimes called most idle routing, connects an inbound call to the agent that has taken the fewest number of calls–or has the lowest talk time–that day. This is especially helpful for customer service and support departments, as it prevents individual team members from getting overburdened with calls.
- Round Robin Routing: Round robin routing evenly distributes inbound calls among agents. If agents A, B, and C are all on deck to answer calls, the first call goes to agent A. Once agent A has taken a call, the next call will go to agent B, and then agent C. This prevents agent A from being “first in line” to receive every call.
- Predictive Behavioral Routing: Predictive behavioral routing (also called intelligent call routing) uses live and historical call center data to connect the caller to not just the best available agent, but the best available agent that the caller is the most likely to prefer according to customer and agent behavioral analysis. This routing strategy uses Artificial Intelligence (AI) to create a routing algorithm based on factors like the caller’s account history, personality and communication preferences, prior support interactions, and more.
- Time-Based Routing: Time-based routing (also called schedule-based or time of day routing) routes calls based on the agent’s time-zone or business hours. It’s especially popular with global and geographically diverse call centers, as it prevents agents from receiving customer calls at 2:00 AM their time or outside their scheduled work hours.
- Sequential Routing: Also called fixed order routing, sequential routing directs calls according to a list-based order that begins with the same agent, regardless of other agent activity or skill sets. For example, if agents A, B, and C are all taking calls, agent A will accept the first call, but will also be the first responder for second, third, fourth, etc. calls. Agents B and C will only take calls if agent A is busy or if agent A transfers a call to them.
- VIP Routing: VIP routing (also called relationship-based routing) lets businesses prioritize important, high-value clients by automatically pushing them to the front of the call queue.
- Language-Based Routing: Language-based routing directs callers to agents that are fluent in their preferred language, an ideal option for international businesses.
The Benefits of Call Routing
Properly-executed call routing streamlines and simplifies business processes and workflows for callers, managers, and call center agents.
Some call routing benefits are obvious, like higher customer satisfaction levels, reduced customer wait times, and increased productivity thanks to agentless automation.
Additional call routing benefits for large and small businesses include:
- More balanced workload: Call routing strategies assess daily agent activity, schedules, current agent status, and more to evenly distribute calls among representatives. While this diffuses tension in sales teams, it also lowers agent turnover rates, boosts employee engagement, and improves the overall quality of customer service and support
- Stronger customer experience: Call routing improves CX by only connecting callers to qualified agents, increasing customer talk time while preventing customers from repeating themselves, providing 24/7 self-service via IVR and IVA, and integrating with CRM tools to provide a personalized support experience that makes customers feel like a priority
- Lower operating costs: Call routing lowers the average cost per call, prevents business owners from having to hire additional agents to manage high call volumes, optimizes available agents, improves customer retention rates, and gives agents more time to dedicate to sales calls
- Decreased call abandonment rates: In addition to lower call abandonment rates, routing also decreases the number of missed calls, call transfers, and voicemails
- Improved FCR: Because routing connects callers to both available and relevant, qualified agents, it’s much more likely the customer’s issue will be entirely resolved during the initial conversation–meaning higher first call resolution rates
- Shorter AHT: Even though call routing may increase customer talk time, it still lowers overall average handle time–the length of time it takes to completely resolve a customer issue from start to finish (including IVR interactions, callbacks, talk time, and after-call work)
Call Routing Best Practices
Essential call routing best practices to implement in your business phone system include:
- Keep IVR prompts brief and straightforward, direct callers to additional IVR submenus as opposed to including unnecessary details in the call menu greeting
- Provide callers with estimated wait times and queue position updates when placed on hold, enable customer callbacks
- Continually optimize your call routing strategies by reviewing customer surveys and feedback, call center metrics and KPIs, current business needs, employee performance, and call recordings/transcripts
- Always provide customers with the option to be transferred to a live agent when interacting with an IVR or IVA system
- Use Workforce Optimization and Management features like trend forecasting, predictive analytics, and automated agent scheduling tools to prepare for busy seasons and peak call volume periods
- Frequently update call menus to reflect holiday operating hours, annual sales or events, or even quality assurance/reputation management issues like product recalls
- Consider creating standalone local or toll-free business phone numbers for your busiest departments
- Invest in a CRM software that lets agents keep and access detailed customer account information, conversation history, agent notes, and more to personalize and improve customer service calls
Implementing an effective call routing system ensures customers get quality assistance quickly, prevents agents from getting overwhelmed, and frees up time to focus on more pressing projects.
In addition to call routing, take advantage of other cloud-based contact center and call center software features designed to improve your call handling process, like push notifications, shared voicemail boxes, and AI-powered Agent Assistance.
FAQs
Below, we’ve answered some of the most common call routing questions.