Consistently monitoring call center analytics reveals trends in customer and agent behavior, insights into service and support quality, and the efficiency of current operations.
Average Handle Time (AHT) is one of the most important metrics, highlighting the specific aspects of your business processes responsible for common call center problems.
In this post, you’ll learn what Average Handle Time is and how to calculate it, best practices for reducing it, and the benefits of optimal AHT.
What Is Average Handle Time (AHT)?
Average handle time (AHT) is a call and contact center metric measuring the average duration of a complete customer interaction–from the moment the customer reaches out to when both agent and customer agree the issue is resolved.
AHT encompasses every phase of the customer service and support process, not just the average amount of time an agent and customer speak on the phone (that’s Average Talk Time.)
Average Handle Time includes all time spent:
- Interacting with call menus: Listening to/interacting with IVR systems, auto attendants, IVAs, voicemail messages, pre-recorded automated greetings, etc.
- On hold: In a call queue, during the call transfer, call forwarding, or call routing processes, while an agent reviews customer data, listening to phone rings before a pickup, etc.)
- Talking to an agent
- On Follow-Up Tasks: Scheduling callbacks or appointments, after-call work (call notes, call disposition, CRM data entry, etc.), making follow-up calls, etc.
Average Handle Time includes calls that are resolved during the first call/ first contact and calls requiring one or more follow-ups.
Some businesses may choose to define Average Handle Time on a “per-call” basis, meaning that while follow-up tasks like after-call work and CRM system updates are included in the AHT calculation, follow-up calls are not.
While Average Handle Time is most often used for phone calls, it also applies to other voice and digital communication channels used to manage customer service queries like live chat, SMS, and video conferencing.
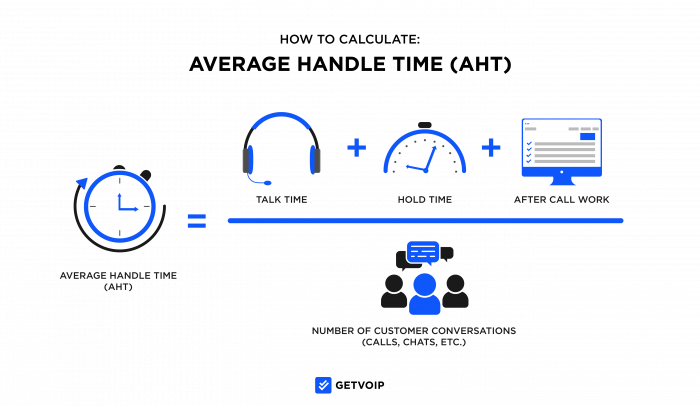
How To Calculate Average Handle Time
To calculate Average Handle Time, choose the length of time you want to measure and add up total talk time, total hold time, and total after-call work time for that period. Then, divide that sum by the total number of calls (or other customer conversations) that took place during the same time period to get your Average Handle Time.
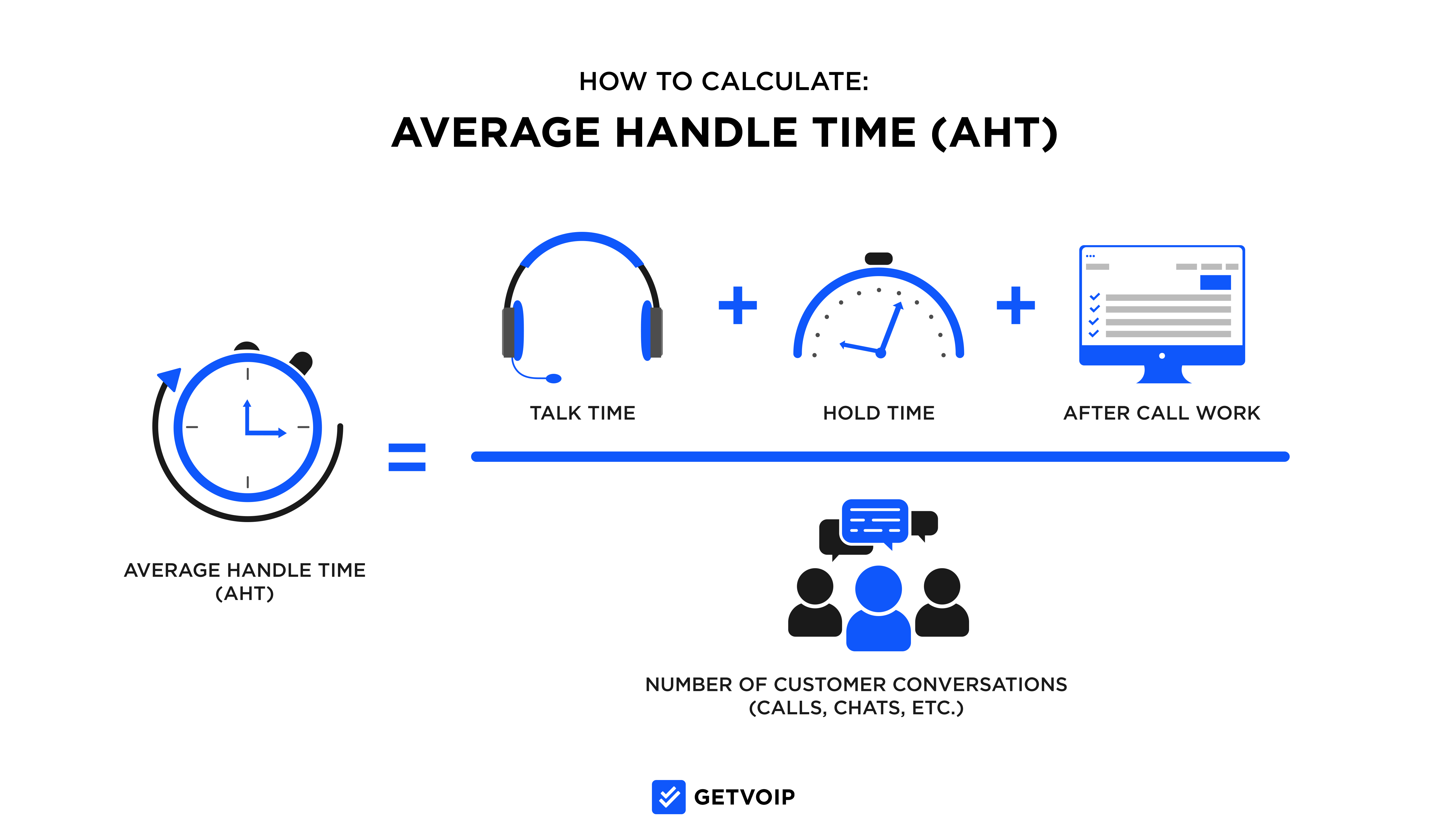
For example, to find a daily Average Handle Time for a call center with:
- A total daily talk time of 1,500 minutes
- A total daily hold time of 2,200 minutes
- A total after call work time of 3,000 minutes
- 250 total daily customer conversations
Step One: Add: 1,500+ 2,200+3000 = 6,700
Step Two: Divide 6,700/250 = 26.8
Solution: The call center has an AHT of 26.8 minutes per call
What Is A Good Average Handle Time?
A good Average Handle Time is about 6 minutes per call or contact–but AHT isn’t as uniform as other popular call center metrics and varies greatly from one business to another. A higher AHT isn’t always a bad thing–in some cases, it indicates a better approach to customer care.
Instead of aiming for the 6-minute “industry standard,” business owners should determine an ideal AHT for their specific call center according to factors like:
Business Size and Industry
Small businesses and startups will have fewer call center agents than established, enterprise-level companies–meaning small businesses will have a higher AHT almost by default.
Local or new businesses also have a smaller customer base than nationwide corporations, which means they’ll have more time to dedicate to one-on-one, detailed, and personalized customer service–something many consumers value, but that also increases AHT.
Because enterprise-level companies have more available customer service and sales reps to meet the needs of a large customer base, they may have a lower call handling time. These large companies can also afford to hire additional agents and purchase contact center software with advanced automation and AI capabilities.
The specific industry your business operates in, and the corresponding products and services offered, also impact AHT.
For example, providing highly technical, multi-step customer support for software applications will take longer–and require more follow-up time–than scheduling a service appointment or placing a food order.
The below data from Cornell University and Kustomer proves Average Handle Time isn’t a “one-size-fits-all” service metric:
| Sector & Company Size | Average Handling Time (Minutes) |
| Large Business | 8.7 |
| Telecommunications | 8.8 |
| Retail | 5.4 |
| Business & IT Services | 4.7 |
| Financial Services | 4.7 |
| Service Type | Average Handling Time (Minutes) |
| Delivery | 4.45 |
| Marketplace | 7.5 |
| Retail | 6.25 |
| Services | 8.7 |
The most effective way to evaluate your business’s AHT is to compare it against performance metrics and benchmarks from your top competitors–those in the same industry and with a similar target market.
Customer Service and Support Strategy
Your business’s ideal AHT is also influenced by your approach to customer service and support.
Call centers that are heavily reliant on omnichannel, automated customer self-service via chatbots and IVR systems have a lower AHT than businesses that provide customer support via live phone call only.
Your AHT also fluctuates depending on whether a fast resolution process (a shorter AHT) or more personalized, relationship-based customer service (a longer AHT) is your main priority.
Additional Call Center Analytics
Another way to determine if your target AHT aligns with your business goals is by examining other key metrics and call center analytics.
Doing so provides more context into the overall customer experience, as well as agent performance, support quality, and call center activity. This makes it much easier to determine if a higher AHT truly has a negative impact on your call center.
In addition to AHT, monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) like:
- First Call Resolution (FCR) Rate
- Average hold and wait time
- Average talk time
- Average call queue length
- Cost per call
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Customer survey responses
- Number of missed calls
- Total call volume
Why Is Average Handle Time Important?
Average Handle Time is important because it provides insight into:
- Agent performance and current agent training materials
- The customer journey and experience
- The effectiveness of existing call management strategies like call routing, IVR menus, call paths, etc.
- Ways to improve your workforce management strategy (adjust agent schedules, hire additional agents, identify and prepare for peak call times)
- Likely causes of customer frustration (extended call hold times, a lack of adequate self-service options, not feeling like a priority, being connected to unhelpful agents that don’t have the skills needed to resolve the issue, etc.)
- Service and support team and individual agent productivity levels, the state of agent engagement, and common support topics
How to Reduce Average Handle Time: Best Practices
Optimizing and reducing AHT offers major benefits like increased customer retention rates, decreased employee turnover, increased team productivity, and lower operating costs.
Below, we outline actionable tips to improve your AHT without overburdening call center agents or sacrificing customer service quality.
Identify the Root Cause of High AHT
As multiple factors influence AHT, it’s essential to consistently examine additional call center analytics over an extended period of time to identify the true root cause of high AHT.
To streamline the process, invest in Workforce Optimization and Workforce Management tools with features like trend forecasting, predictive analytics, and automated agent scheduling and staffing suggestions.
WFO and WFM solutions use Conversational AI, Speech Analytics, and Natural Language Processing to provide high-level insight into customer-agent conversations, common support requests, and agent performance.
Optimize Call Routing Strategies
When implemented effectively, call routing shortens AHT by:
- Connecting customers only to an available (ready to talk) agent, avoiding placing callers on hold/in call queues
- Connecting each caller to an agent with the necessary skill set and training to provide the best support possible
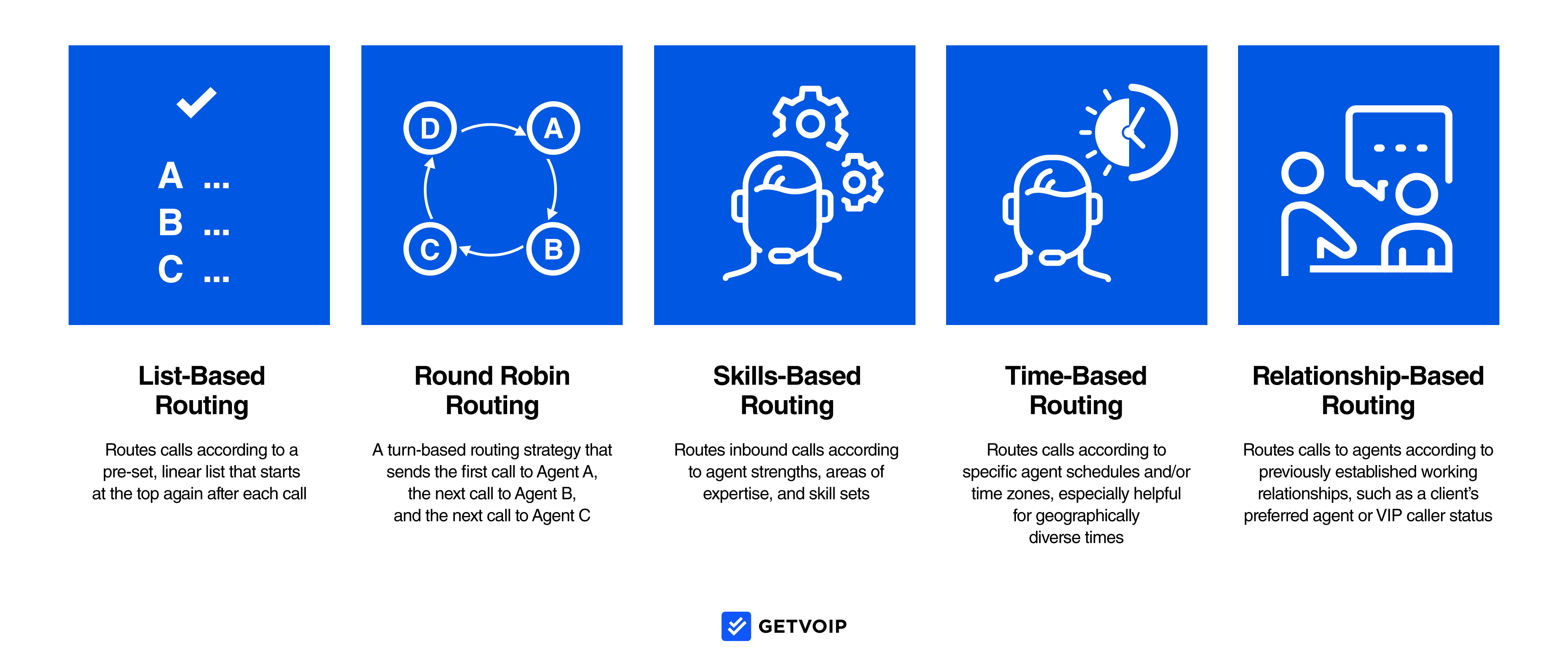
For best results, test out multiple call routing strategies and monitor them over time to determine which strategies are the most effective.
Skills-based, time-based, relationship-based, round robin, most idle, and list-based routing are some of the most popular strategies.
Expand Customer Self-Service Options and Communication Channels
Quality customer self-service cuts down customer callbacks, increased talk time, voicemail messages, follow-up conversations, and other factors known to increase AHT.
Interactive Voice Response (IVR) solutions provide automated, pre-recorded call menu options that answer common questions and allow inbound callers to complete basic tasks like checking order status, scheduling appointments, paying bills, or updating account information on their own schedules and without involving a live agent.
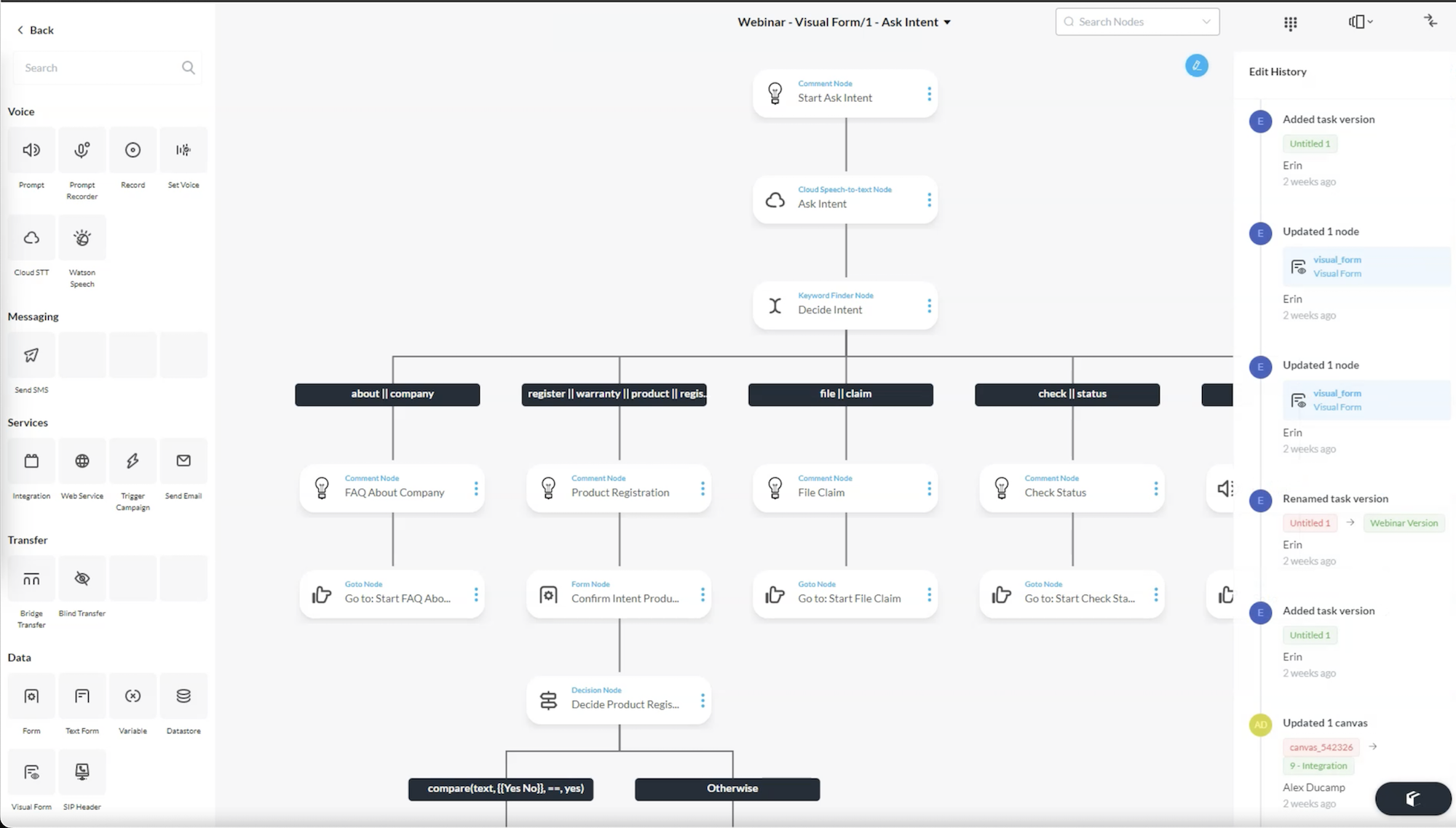
Especially if you’ve noticed a recent uptick in inbound customer calls, consider adding customer self-service channels like website chat, social media messaging, email, SMS texting, or an online support ticketing portal. Digital channels are ideal for entirely automated chatbot conversations, leaving agents free to assist with more complex customer service issues and dramatically lowering AHT.
Use Automation and AI to Boost Productivity and Performance
Call center automation shortens pre and post-call work time by automatically syncing customer data, conversation notes, and support ticket updates in CRM and call center software after every interaction.
Workflow automation eliminates the need for agents to spend time on basic, lower-priority, and repetitive tasks.
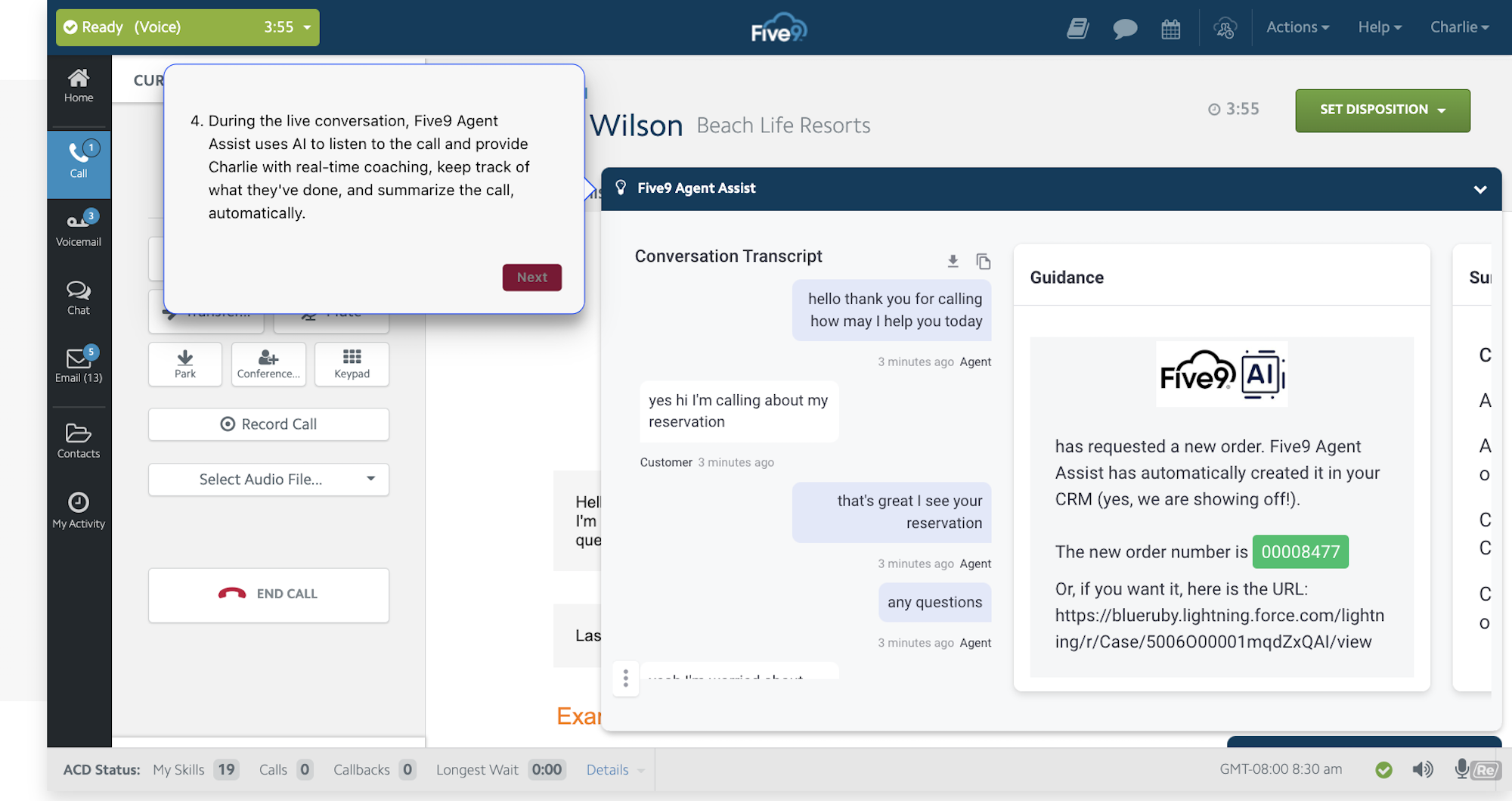
AI-powered automation, like in-conversation Agent Assist, uses Natural Language Processing, customer sentiment analysis, and Speech Analytics to recognize the customer’s issue and instantly provide relevant call scripts, canned responses, and next-step suggestions from your company's internal knowledge base.
Automation decreases AHT by ensuring agents have immediate access to CRM and wiki data, adjusting call queue assignments in real-time to keep pace with current call volumes, and streamlining after-call work (ACW) via automatic call dispositioning.
Update Agent Training and Provide Ongoing Agent Support
If call analytics indicate multiple instances of extended AHT related to specific customer queries or problems, it’s a clear sign you need to update employee training manuals.
Ask for employee feedback about gaps in training materials, schedule consistent team meetings to address recurring issues, and create SLA (service level) standards to ensure performance expectations are clear.
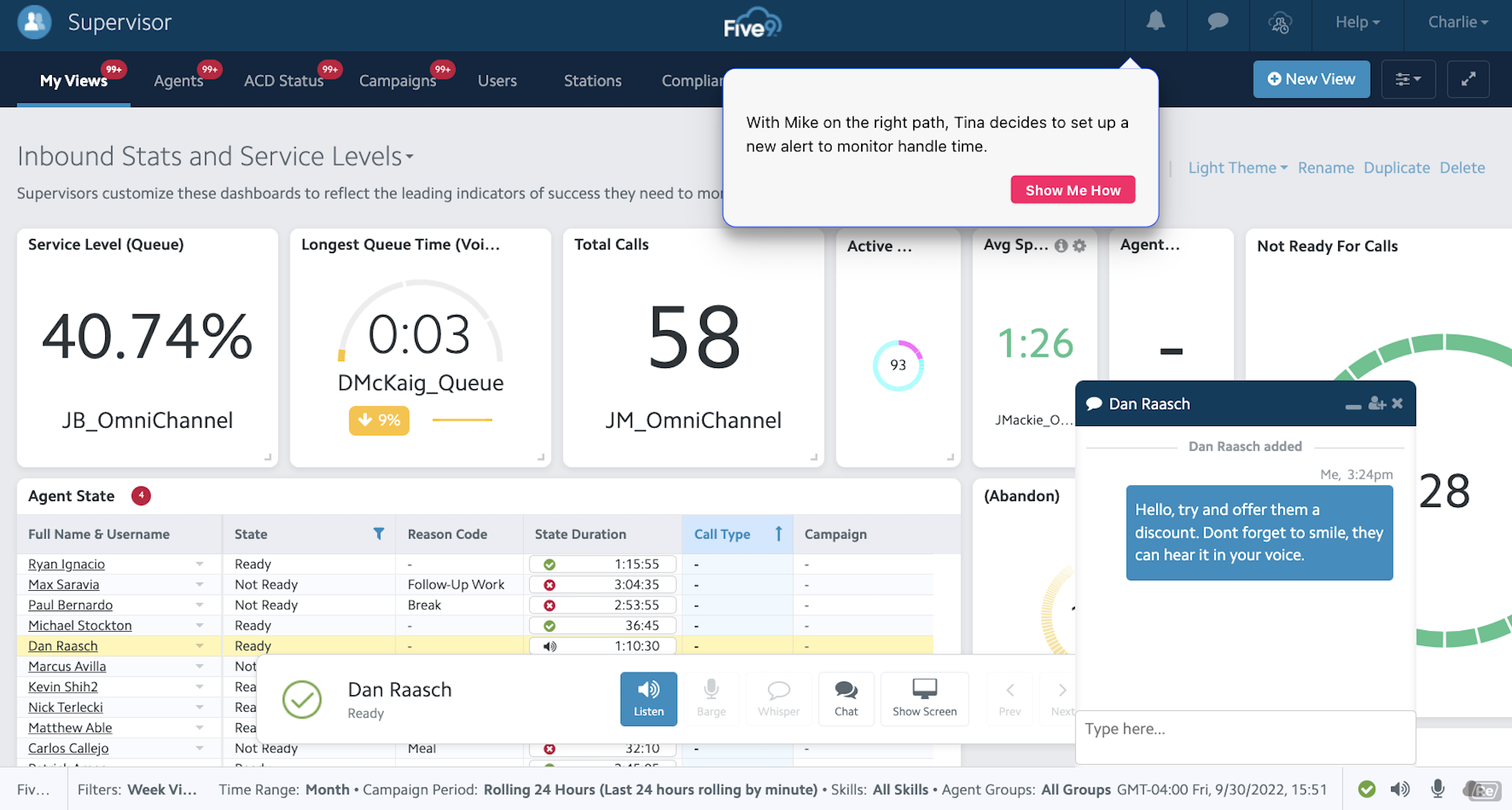
To maintain high-quality support and a lower AHT, call center managers must provide high-level ongoing employee support. In-call coaching, call whisper, agent interaction scoring, performance gamification, call recording, and individual agent activity monitoring keep employees engaged and improve the support process.
Streamline Internal Communications
Gaps in internal communications create information silos, lead to customer frustration, and extend AHT by forcing agents to put callers on hold (or schedule callbacks) while they search for relevant account data points and support information.
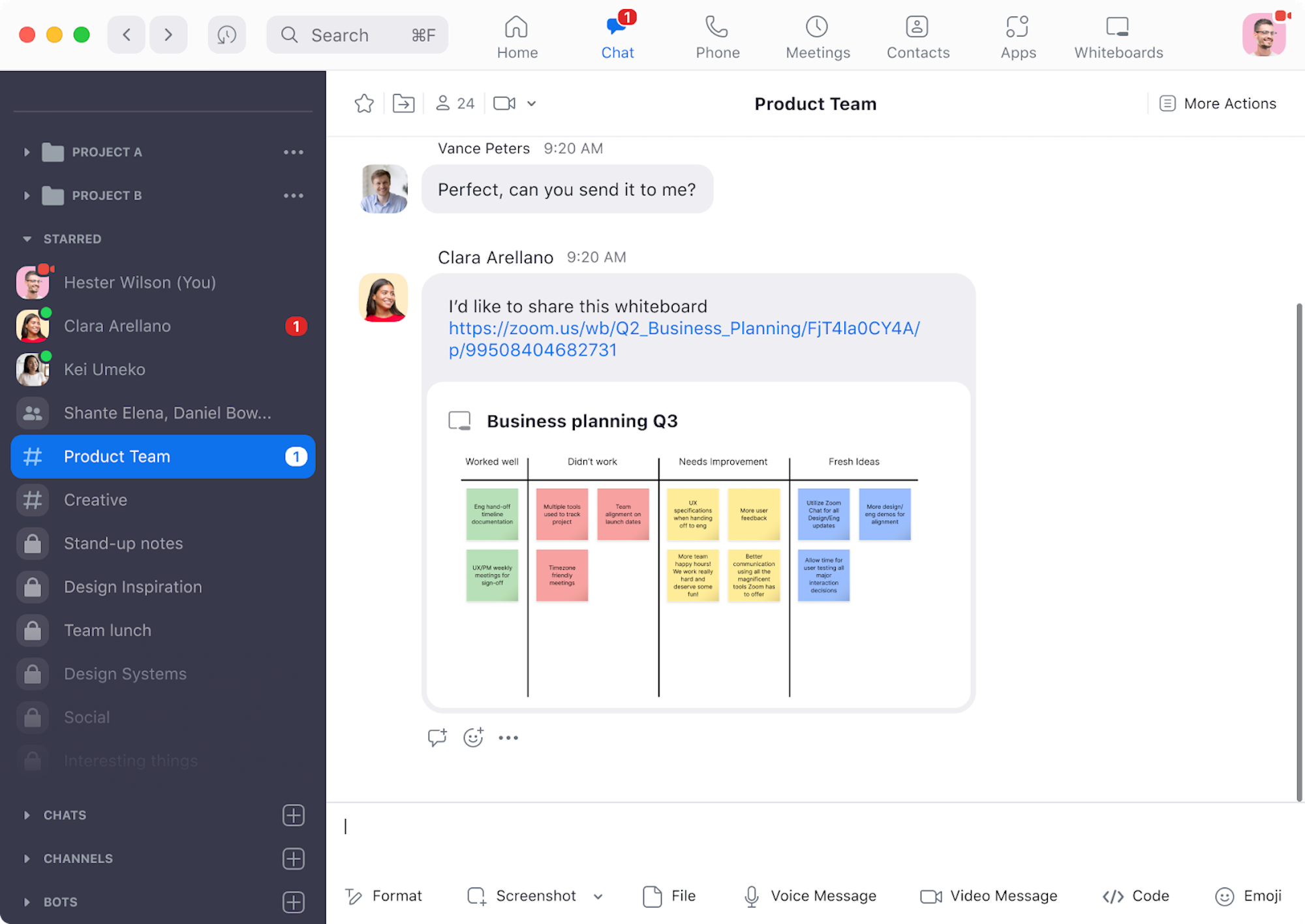
Team collaboration software features like instant chat messaging, task management, and agent presence let team members get support from each other during conversations with customers.
Unified Communications and collaboration tools include real-time file, support ticket, and task progress syncing to ensure all agents work from the same–and most current–customer data and ticketing updates.
Call Center Software Improves Average Handle Time
Quality call center software vastly improves Average Handle Time by offering features that shorten customer service call times, identify the root causes of high AHT, and provide insight into the customer and agent experience.
The top call center and CCaaS features that reduce AHT include:
-
- Live, historical, and AI-powered analytics
- Call flow design tools with real-time editing
- Call routing, call forwarding, and ring groups
- Call recording, call monitoring, call barge, and agent coaching tools
- Omnichannel customer self-service (IVR, IVA, chatbots, customer knowledge base)
- Automated CRM call pops, Agent Assist, Call Disposition, etc.
- Workforce Management and Workforce Optimization tools
- UCaaS and collaboration tools like team chat, video meetings, task management
Average Handle Time FAQs
Below, we’ve answered some of the most common questions about Average Handle Time.