Customers communicate with brands through a variety of voice and digital communication channels. They expect to resume support conversations exactly where they left off–even when switching between channels.
Omnichannel routing makes meeting customer expectations possible, providing seamless and personalized customer support across channels without overburdening agents.
Read on to find out what omnichannel routing is, how it works, and how best to leverage it to grow your business.
What is Omnichannel Routing?
Omnichannel routing is the process of intelligently directing customer queries to the most appropriate agent or department across a range of service channels, including voice, social media, text/SMS, email, and live chat.
Call centers use call management strategies like call routing, IVR and ACD, call queuing, ring groups, and business rules to connect incoming callers to the best available agent.
Similarly, omnichannel routing ensures that whatever communication method customers use to connect with the business, the interaction is assigned to the best agent or the appropriate self-service resource.
Several CCaaS providers offer omni channel routing as a part of an all-in-one solution that unites multiple communication channels into one agent interface. This single pane of glass communication inbox organizes interactions according to customer conversation history, preventing communication silos.
For providers that don’t include it as a feature, integrations with third-party apps such as Salesforce omni channel can be used.
Popular omnichannel routing features include:
- Web messaging/Live chat
- SMS messaging/Text
- Social Media listening and engagement tools
- Chatbots and Voicebots
- Predictive engagement (AI is used to find out who is using your website and why)
- Co-browse and screen share (Enables customers to share their screen with agents)
- Knowledge base creation tools
- Unified agent workspace/service console
- Workflow automations
- Reporting and Analytics
How Does Omnichannel Routing Work?
Omnichannel routing uses intelligent routing software to direct inbound calls, messages, live chats, and more to the best agent according to pre-set rules determined by the company.
When new queries come in, the call center software uses Artificial Intelligence (AI), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) to determine customer intent. Machine learning means intelligent routing strategies, call flows, and automated responses only improve with time.
Once intent is determined, customers are automatically routed through an Automatic Contact Distributor (ACD) to a qualified agent–regardless of the channel used
Representatives can review essential client information like IVR input, CRM data, preferred channel, geographic location, conversation history, and more before connecting to the customer and during the conversation.
Communications are routed based on how long the customer has been in queue, to ensure wait times are as low as possible. Omnichannel routing systems can also prioritize phone calls and other work items according to the company’s preset routing rules. When an agent starts work for the day or finishes an interaction, omnichannel routing will automatically update the agent’s availability in order to maximize productivity.
Omnichannel routing configurations include:
- Predictive behavioral routing (AI is used to direct the query to the best agent based on personality, communication preferences, or other behavioral characteristics)
- Skills-based routing (contacts are sent to an available agent with the appropriate skills to handle the query)
- Round robin/rotary (queries are sent to the next available agent on a list)
- Least occupied (priority is given to the agent with the most idle time)
- Data directed (contacts are sent to agents based on various criteria such as customer location)
- Fixed order (contacts are sent to the next available agent on a list starting at the beginning of the list for each query)
- Time-based (routing rules are adjusted based on the time of day)
Benefits of Omnichannel Routing
- Improved agent productivity: With access to a complete customer history and AI-powered assistance, agents are able to focus on serving customers instead of combing through databases to find answers.
- Decreased wait time and abandon rates: Providing self-service options such as chatbots and IVAs will reduce agent workloads and lead to shorter wait times.
- Reduced average handle times: Because items are always assigned to the right agents who possess the skill set needed to handle the query, issues will be resolved faster.
- Increased Outreach: Providing multiple touchpoints, especially social media platforms, will increase a company’s visibility to potential customers that are active on those channels.
- Reduced costs: Omnichannel routing can help businesses to reduce costs by eliminating the need for multiple call centers. Global customers will have access to digital channels and self-service tools 24/7/365. Self-service options also lessen the workload for live agents.
- Improved customer satisfaction and loyalty: Customers appreciate being able to communicate with businesses through the channel of their choice and use self-service resources 24/7. Decreased wait times will also lead to a better overall customer experience.
- Increased Sales: Empowered with prior purchase history and customer preferences, agents can optimize customer interactions and more easily upsell or cross sell.
Difference Between Multichannel and Omnichannel Routing
Multichannel routing refers to routing communication in a contact center on multiple channels such as voice, email, and chat. A call center that has multichannel routing may route queries on some or all of the channels they use. Omnichannel routing also provides multiple avenues of communication, but the difference is that, with omnichannel routing, all interactions are unified on a single pane of glass.
With multichannel customer service, an agent is generally assigned to one channel at a time and will only have access to customer history that occurred on that particular channel. This can be frustrating for customers who utilize more than one channel during the resolution of their issue. For example, if a customer calls and speaks with an agent about a defective product, then later sends an SMS with a picture of the defect.
An omnichannel customer service solution will display all channels on one agent dashboard, allowing employees to get a complete 360 degree view of the customer journey for every interaction. Additionally, the unified workspace enables agents to interact on multiple different channels throughout the day instead of focusing on one channel at a time.
How to Implement Omnichannel Routing
To implement the ideal routing strategy for your omnichannel contact center, you will need to first take inventory on what channels your customers currently use and how they would most like to interact with your company. That could include tagging your brand on social media sites such as Twitter, sending text messages, or speaking with someone face-to-face on a video chat.
More and more customers are finding self-service customer service options helpful as well–resources such as chatbots, knowledge bases, and self-pay platforms. After you have determined which omnichannel routing features are non-negotiable, you will want to select the best cloud contact center platform for your needs and begin implementing an omnichannel strategy.
Step 1: Prepare Communication Channels
Once you have researched and determined which channels to offer, you will need to ensure that your company has a presence on those channels. For example, if your customer base is highly active on Twitter, you will need to ensure your company has a Twitter account that can be connected to your omnichannel routing system.
Step 2: Define Capacity Rules and Agent Statuses
Many contact center software providers allow you to set agent capacity rules in order to balance the workload among agents. Limits will be applied to automatically assign tasks. For example, a company could specify that only ten open email tickets at a time can be assigned to particular agents. Unified agent status will provide a way for agents to control availability on various channels from a single menu. Some providers allow for custom unified agent statuses to be edited or deleted. Admins may also be able to configure an idle timeout rule to automatically change an agent’s status to idle or offline.
Step 3: Set Up Routing Rules
The routing options and the way rules are defined will vary depending on the provider, but in general, admins will define how communications are handled by defining triggers, conditions and actions. For example, when a new email is received (trigger) with a billing question (condition), the email is forwarded to the billing department (action). This is also when you will decide on a routing model such as skills-based or rotary.
Step 4: Set Up Self-Service Options
Most CCaaS providers that offer omnichannel routing will include tools to create self service options for your customers such as a knowledge base, chatbots, intelligent virtual agents and/or voicebots. Bots will use NLP and conversational AI to determine customer intent and provide them with an appropriate resource or send them to a live agent. Admins can define which resources will be auto delivered and how escalations are handled.
Step 5: Analyze Interactions and Make Adjustments
Finally, your omnichannel routing will likely need to be adjusted once you have more data. Most CCaaS providers include reporting and analytics tools to monitor key metrics such as channel usage, first response time, and average handle time. When you have this information you can change capacity and routing rules if necessary.
Providers That Support Omnichannel Routing
Here are some of our favorite CCaaS platforms that include omnichannel routing capabilities:
| Provider | Pricing | Key Features | Best For |
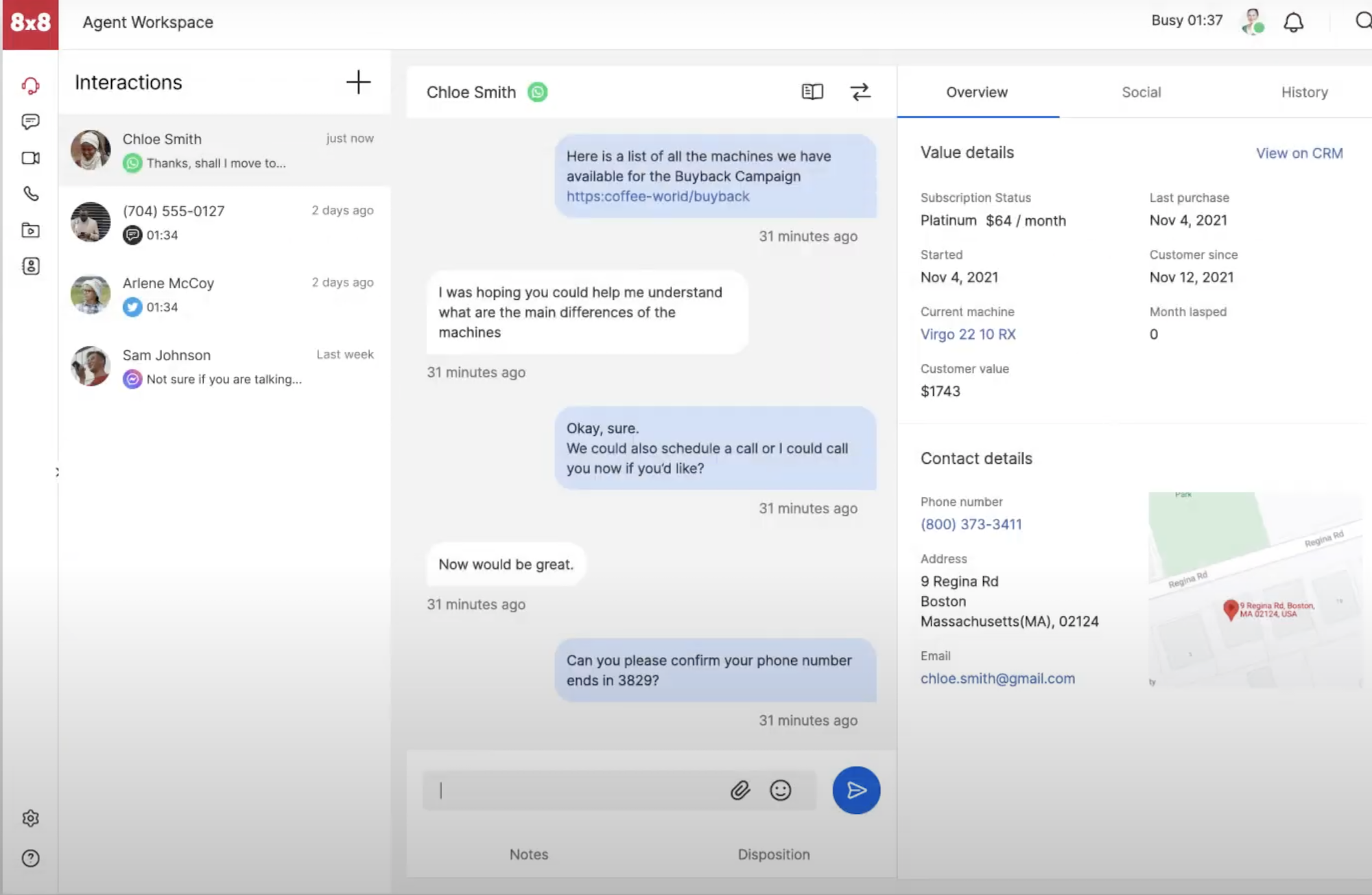
| 8x8 | $85-$140 per user/mo. |
|
SMBs and enterprises that need self service options |
| RingCentral | Contact provider for a custom quote |
|
Large contact centers and enterprises that need a high level of security and reliability |
| Twilio | $1 per active user hour or $150 per named user per month |
|
Medium and large businesses that need a customized and flexible solution |
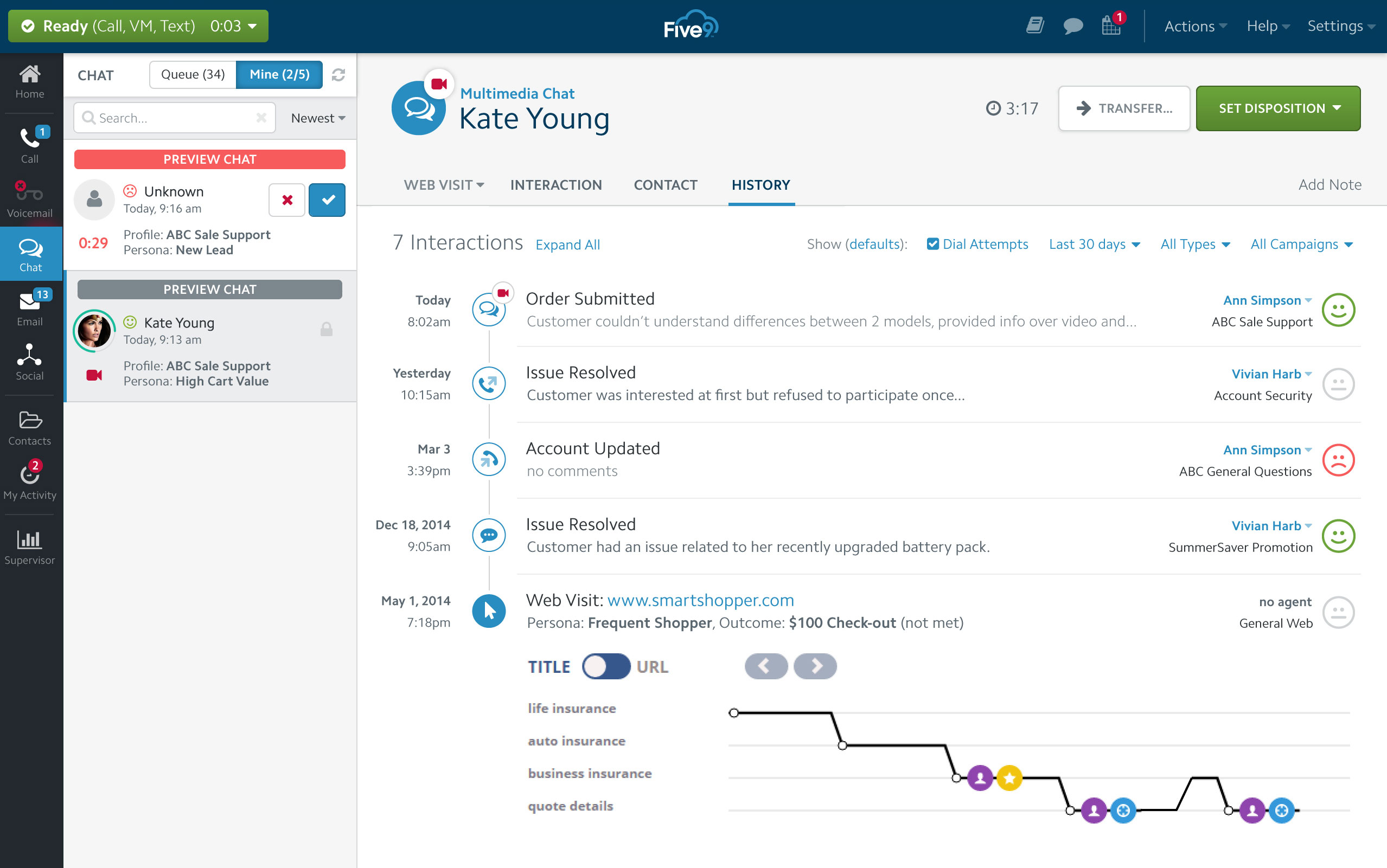
| Five9 | $149-$229 per user/mo. |
|
Blended inbound/outbound contact centers |
| Genesys | $75-$155 per user/mo. |
|
Small contact centers and SMBs |
| NICE CXone | Contact NICE CXone for a custom quote |
|
Enterprise-level companies with heavy contact across multiple channels |



