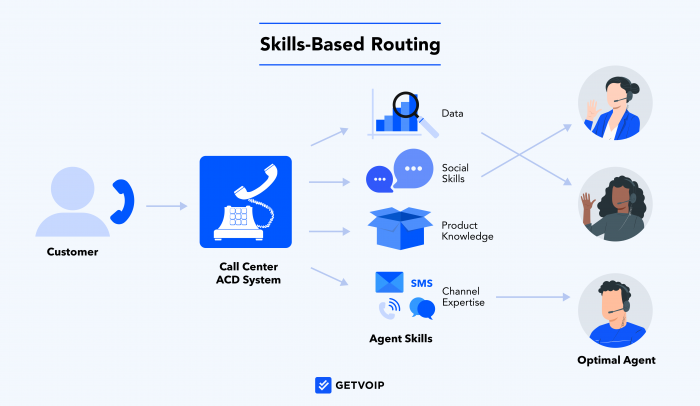
Skills-based routing optimizes call center efficiency and service by leveraging each agent’s skill set and areas of expertise–sales skills, spoken languages, channel proficiency, technical knowledge, and more.
This article will overview skills-based routing, discussing what it is, how it works, its benefits and best practices, and how it’s different from other types of routing.
Jump to↓
- What is Skills-Based Routing?
- How Does Skills-Based Routing Work?
- How to Set Up Skills-Based Routing
- Skills-Based Routing vs Other Routing Types
- Benefits of Skills-Based Routing
- Best Practices for Setting Up Skills-Based Routing
- Is Skills-Based Routing Right Right for Your Business?
What is Skills-Based Routing?
Skills-based routing is a call distribution strategy that directs inbound queries to the agent–or group of agents–with the skills best suited to meet the caller’s particular needs. It applies to VoIP calls, SMS texts, chat messages, and emails. It routes incoming calls to available agents based on skill level rather than other factors like idle time, shortest queue, or preset sequence.
How Does Skills-Based Routing Work?
Skills-based routing (SBR) works by the phone system’s automatic call distribution (ACD) technology analyzing the inbound call’s details and needs, then routing it to an agent with the best-matching skillset.
ACD gathers call details and context through multiple methods: Self-service IVR ascertains the call reason, the CRM system describes purchase history and customer journey, call tracking provides details like the phone number and location, and the customer’s profile shares insights like language preferences. In addition, the ACD system utilizes preset call routing rules–such as business hours, caller location, and agent availability–for fast and effective call assignment.
Skills-based routing is an ACD strategy that prioritizes agent skill above all other call routing rules.
How to Set Up Skills-Based Routing
To configure skills-based routing rules in the contact center settings, administrators select Skills to create agent skill types and indicate the communication channels, menus, queues, and call centers where these skills apply.
Evaluated agent skills may include…
- Languages spoken and conversational ability
- Technical skills like programming, writing, proficiency with various types of software
- Product knowledge in a sales or customer-service context
- Data aptitude
- Channel experience and proficiency
- Compliance and consistency following processes
- Problem-solving ability and critical thinking
- Communication skills, and more
Next, administrators set each skill’s priority value, so the ACD knows which skills to prioritize when a query has multiple.
Administrators then evaluate and score each agent 1-100 on their proficiency for each skill.
When the ACD receives an inbound call, message, or email, it undergoes the following process:
1. Determine caller needs and context
2. Check agent availability and skill levels
3. Route the call to the agent with the highest scores for the highest-priority skills
Skills-Based Routing vs Other Routing Types
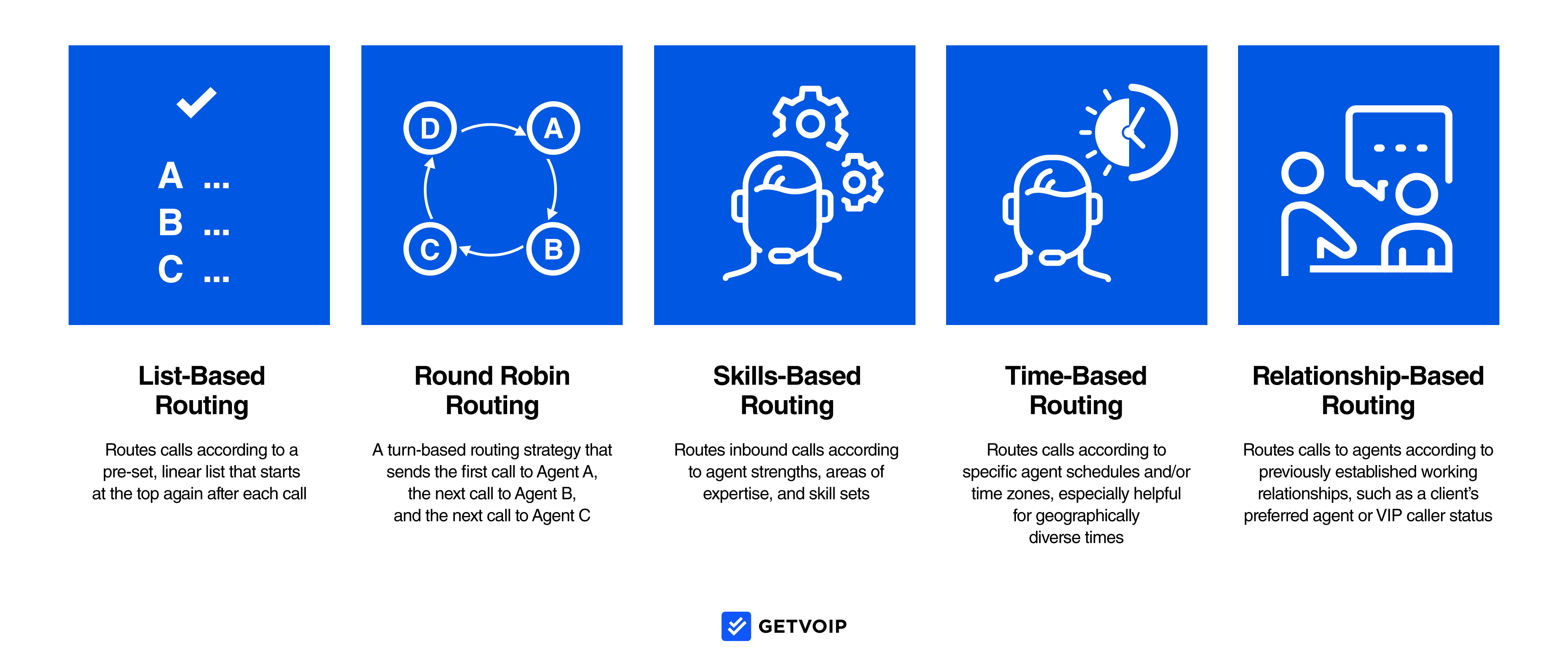
Skills-based routing distributes calls based on agent skill rather than other ACD routing rules, such as agent idle time, business schedules, preset orders, or customer relationships and interaction history.
Common ACD Routing Rule Types
- Skills-based routing: Routes calls based on evaluated agent skills, prioritizing agents with the highest skill rankings to meet each customer’s particular needs
- List-based routing: Routes calls according to a preset list of agents. When the top-listed agent is unavailable, ACD routes to the next available agent, restarting after each call.
- Round-robin routing: Routes calls to agents in a preset sequence, moving to the next-listed agent after each call. When the automatic call distributor has routed a call to each agent, it restarts at number one.
- Longest-idle routing: Routes calls to whichever agent has been idle the longest
- Time-based routing: Routes calls according to time of day, agent schedules, and company business hours
- Relationship-based routing: Routes calls to agents with whom the customer has previously interacted, or based on customer VIP status
| Routing Rule | Routes based on | Best For |
| Skills-based | Agent skills, specialties, and abilities | Companies where customers call for a wide variety of reasons, issues, and products |
| List-based | Preset list of agents, restarts after each call | Queues that want to maximize call volume for certain agents |
| Round robin | Preset list of agents, restarts after a complete sequence | Queues that receive many uniform queries or with agents equally prepared to handle queries |
| Longest idle | Agent idle time | Large call centers where each agent is equally prepared to handle queries |
| Time-based | Business hours, location, and time of day | Companies with geographically dispersed agents, callers, and call-center locations |
| Relationship-based | Customer-agent relationships | Companies who have frequent follow-up queries, or with high-profile customers |
Benefits of Skills-Based Routing
The primary benefits of skills-based routing are improved agent performance, better customer experience, reduced agent training demands, and efficient call resolution.
Improved Agent Performance and Satisfaction
Skills-based routing ensures that agents receive tickets regarding the issues and topics most in line with their expertise and experience. This not only leads to more effective agents, but happier and more confident ones.
Agents can better resolve queries when the call’s topic, language, and needs reflect their specialties, knowledge, and familiarity. For example, a sales agent will achieve a higher success rate selling a product that she knows well–that she has sold before, answered questions about, and researched–as opposed to a newly stocked product that she hasn’t had time to research.
A higher agent success rate fuels greater agent productivity, confidence, and satisfaction. Customers are more pleasant, agents feel less pressure, and the mental bandwidth saved when facing a manageable issue allows agents to focus more on the interpersonal aspects of customer support and sales.
Better Customer Experience
Customers feel reassured when they believe their agent has the knowledge and abilities to serve them. This is true both in customer support–when customers want an agent with proper tools and know-how –and in sales–when customers expect an agent to know the product offerings well enough to give them the best deal.
Skills-based call routing connects the caller to the best agent no matter the context or type of call, optimizing customer experience and retention.
Reduced Agent Training
With a skills-based routing strategy, not every call center agent needs to have expertise on all topics. Agents can utilize the channels, languages, and topics they already know well or have experience with. If an agent is brand new, he can specialize in just some products and channels. This leads to faster training and learning on the job, due to rapid exposure to similar queries.
Efficient Call Resolution and Handling
Skills-based call routing utilizes ACD and IVR automation to route calls to the right agent immediately, increasing the first call resolution rate and meeting service level agreements (SLAs) more often.
A skills-based distribution rule reduces the chances of routing to a poorly qualified agent, who would then have to route the call to someone more specialized. Instead, more calls get answered on their first try, sparing customers from repeating themselves and handling more calls over a given timeframe.
Best Practices for Setting Up Skills-Based Routing
The following practices will help ensure that your skills-based routing system functions optimally.
1. Use Customer Data to Determine Which Skills to Evaluate
Use your CRM data, IVR records, call logs, and customer profiles to decide which skills to feature for routing and agent scoring. When combing through these data sources, look for frequently recurring metric results–product pages clicked, channels utilized, call reasons, products requiring support, IVR menu questions, or languages spoken.
Use these recurring needs to determine the most important categories for agent skills.
2. Consider Skills by Category
When setting up skills-based routing, many phone systems will prompt you to first enter skill categories before entering specific skills. For example, language spoken and channels are skill categories, while Spanish and SMS are specific agent abilities. This distinction helps your intelligent routing system evaluate multiple agent skills concurrently, improving matching effectiveness and preventing random assignment when two agents score a “tie” for a given skill.
3. Match Agent Staffing with Skill Demand
As you decide which skills to use as routing criteria, notice each skill’s popularity and activity demands. Naturally, depending on your customer base, some skills–channels used, languages spoken, product knowledge–will generate more demand than others.
In order to prevent overloaded hold queues and unbalanced agent workload, aim to match agent staffing numbers with the demand you anticipate for each skill. The most demanded skills–for example, the most commonly spoken customer language–should have the highest number of proficient agents.
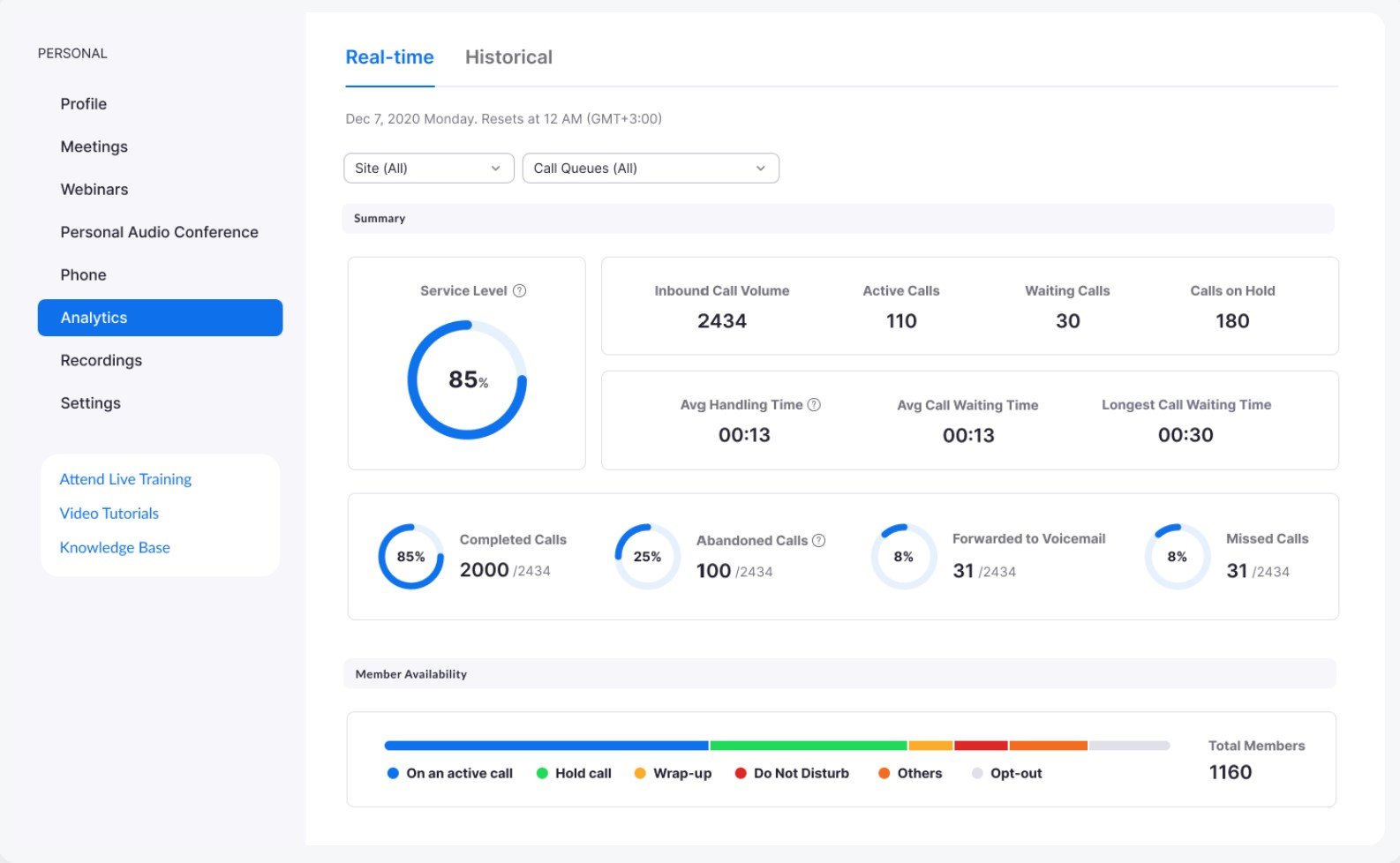
4. Monitor Key Analytics
To track the effectiveness of your omnichannel routing strategy and make necessary adjustments, monitor KPIs and analytics like average queue length, customer wait time, ticket handling time, and customer satisfaction score. Mark starting points before implementing skills-based routing, then indicate KPI goals.
Over time, if you’re not seeing improvement, look more deeply into these metrics to determine bottlenecks or instances of suboptimal routing.
Is Skills-Based Routing Right for Your Business?
If your company’s contact or call center faces a low first-call resolution rate–or if agents are frequently forced to route calls to more specialized peers–skills-based routing might better utilize your agents’ skills.
Companies with low customer satisfaction scores, low first-call resolution rates, long queue hold times, or uneven agent workload should also consider skills-based routing.
On the other hand, if your call center customizer experience is already optimized, you might be better off sticking with a different call routing strategy.