Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is a technology that lets users make and receive phone calls over the Internet instead of the traditional analog phone.
VoIP has many names: virtual telephony, online phone system, cloud-based phone system, IP telephony, virtual calling tool….the list goes on.
All these terms mean the same thing: instead of using a traditional landline phone for voice calls, VoIP manages phone communication over the Internet.
VoIP vs Landline
The below table comparing landlines to VoIP communication quickly breaks down the differences.
| VoIP | Landlines |
| Communicate over the Internet via transmitted voice data packets | Communicate via copper and fiber optic cables of the PSTN |
| Needs Internet connection to function | Needs an analog phone (physical phone) to function |
| It Lets users make free local and long-distance calls. International calls are often more affordable | All calls come with a charge, and long-distance and international calls will be expensive |
| Easy to scale and add on new features as needed | Need wired phone lines and additional equipment to access features that are still limited |
| Usually not functional during a power outage unless a backup power source is use | May still be functional during a power outage |
- What is VoIP?
- VoIP vs Landline
- How it Works
- VoIP vs SIP vs PBX
- Pros and Cons
- Key Features
- VoIP Cost
- Equipment and Hardware
- Choosing a Provider
- FAQs
How Does VoIP Work?
VoIP technology breaks up the voice audio from a phone conversation into digital data packets, then sends these data packets to the recipient over the Internet.
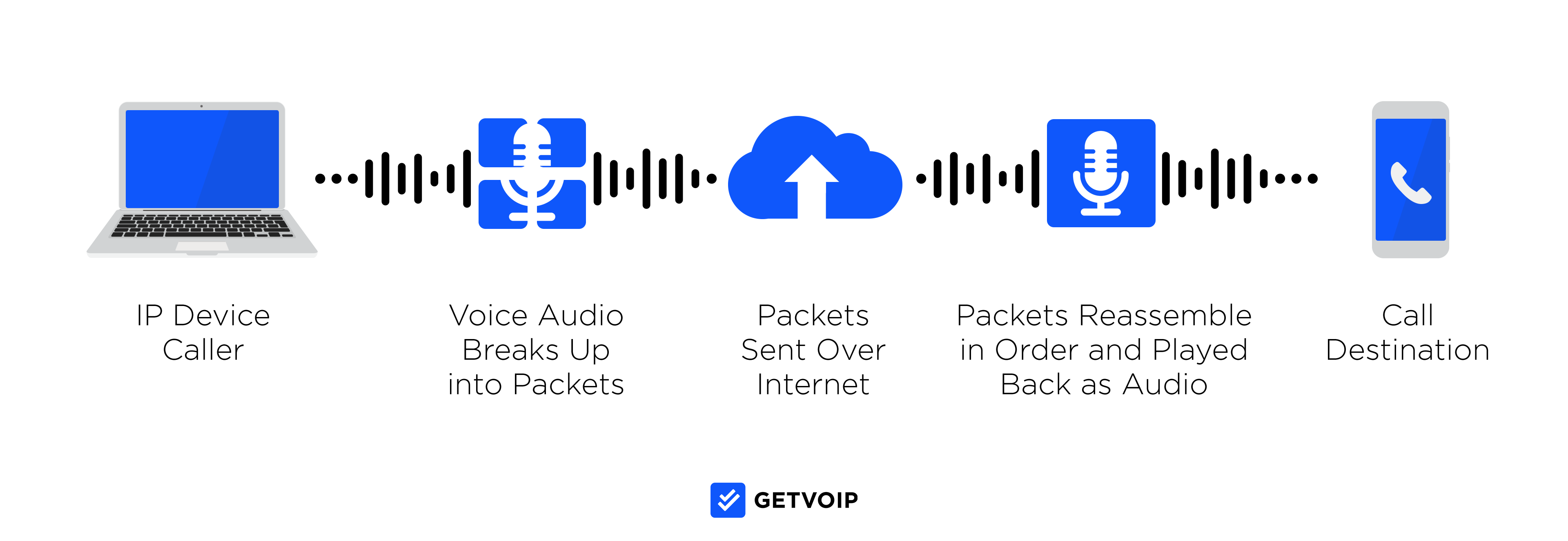
VoIP codecs compress/disassemble these voice data packets to travel over the IP network (a local area network or a wide area network.) Once these voice data packets reach their destination, they’re decompressed/reassembled and sent to the recipient, transformed back into words and phrases instead of just digital signals in transit.
VoIP users can make calls via VoIP softphones, VoIP phones, and/or by connecting traditional analog phones to a VoIP system via an analog telephone adapter.
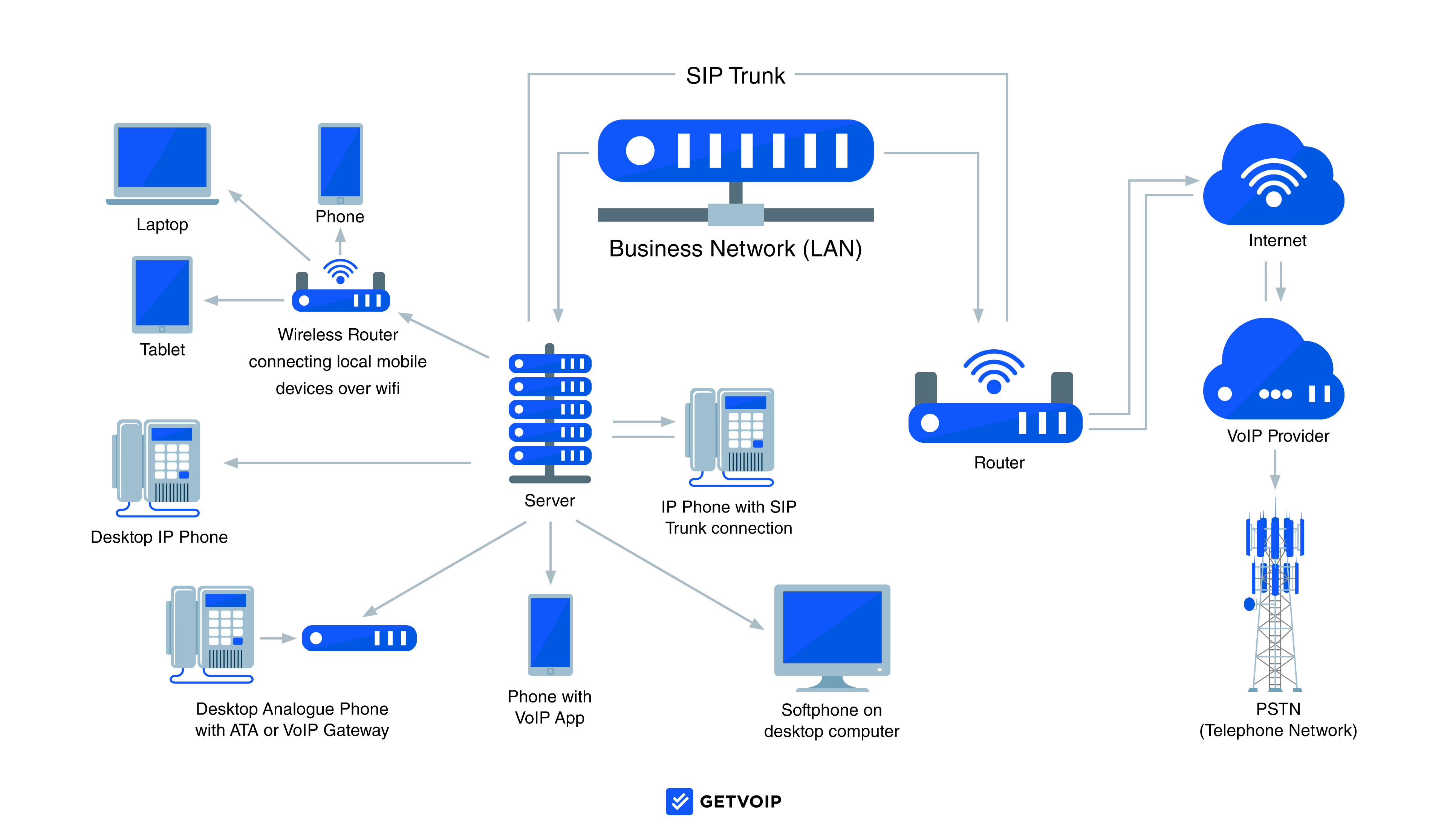
VoIP, SIP, and PBX: Understanding Key Differences
Especially as you become more familiar with the VoIP world, you'll notice other phone system acronyms like SIP and PBX popping up in feature lists, provider reviews, and pricing models.
Let's quickly outline the differences between VoIP vs. SIP vs. PBX.
- PBX stands for "Private Branch Exchange", and it's a premise-based or cloud-hosted private business phone system. Premise-based (onsite) PBX requires physical servers, wiring, wall jacks, and other hardware to be installed within the company's office space. Businesses are also responsible for the costs and process of system maintenance, often requiring an onsite IT staff. Because analog phone systems are on their way out -- and prohibitively expensive for many -- most PBX business phone solutions are now hosted entirely by the provider in the cloud (Hosted PBX/IP PBX.)
- Hosted PBX uses VoIP technology to facilitate voice calling and provide other communication/collaboration features to a private business phone network. However, instead of being physically located on-site, cloud-based PBX is hosted and maintained by the provider via a designated offsite server.
- SIP stands for "Session Initiation Protocol", and its job is to enable VoIP technology on existing on-premise phone systems. SIP Trunking is the process of bringing SIP technology -- and all the advanced features that come with it -- to your existing premise-based phone system.
The Pros and Cons of VoIP
The below table outlines the pros and cons of VoIP. Then, we’ll go into more detail on where VoIP shines and where it falls short.
| Pros | Cons |
| Cheaper and more scalable than landline phone service | May require users to upgrade current Internet speed |
| More advanced features than standard business phones | Access to advanced features may require users to scale up to a higher plan tier |
| Increased portability and flexibility | Has a higher learning curve than traditional phones |
| Better overall voice and call quality | Dependent on a strong, uninterrupted Internet connection to avoid jitter and latency |
VoIP's biggest advantage is how much money it saves on telecommunication costs.
Users can expect to save up to 50% on telecom charges if they switch to VoIP phones. Plus, because you don’t have to purchase new equipment (as VoIP works with multiple devices like smartphones and desktop computers), you’ll save even more.
Not only that but VoIP is proven to increase employee productivity. Its advanced features can save agents over 30 minutes of call time per day and add an extra 3.5 days of productivity per year per employee. As a whole, VoIP raises team productivity rates by roughly 20%.
The truth is that especially now, it’s tough to find a bad thing to say about VoIP aside from its dependence on an excellent Internet connection.
The only real downside you may encounter?
These new features and functionalities can come with a learning curve. The best way to avoid that is to ask the provider about their team training opportunities.
Key VoIP Features
Though there are over 100 VoIP features -- and counting! -- to choose from today, we’ve outlined the essential functionalities that define virtual phone communication.
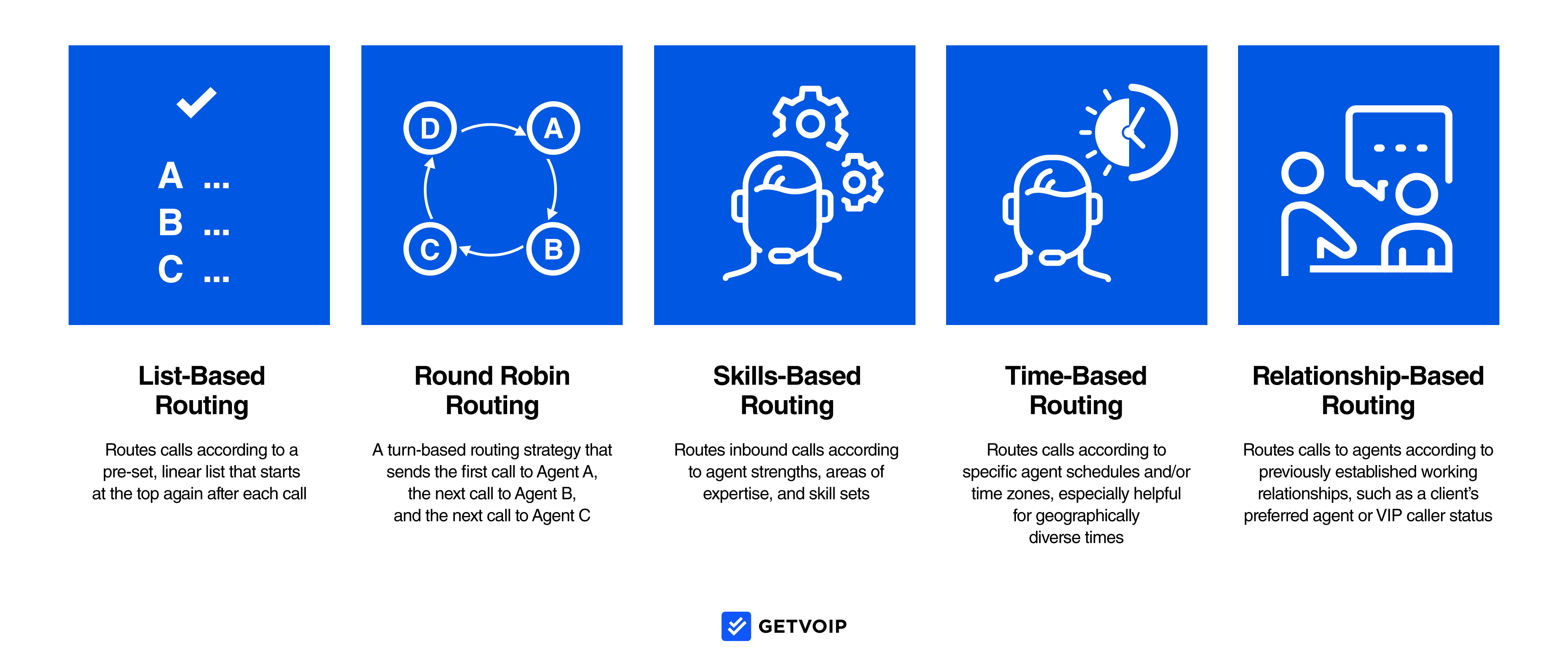
Call Routing
Call routing is a call management strategy that distributes incoming calls to agents according to pre-set criteria.
The goals of call routing are to ensure that the caller is connected with the best available agent, decrease call wait times and transfer rates, and increase first-call resolution rates.
There are numerous different routing techniques to choose from, with the most popular being:
- List-Based Routing: Routes calls according to a pre-set, linear list that starts at the top again after each call. For example, the call is first sent to Agent A, and is only sent to Agent B if Agent A is unavailable. The next call is again sent to Agent A.
- Round Robin Routing: A turn-based routing strategy that sends the first call to Agent A, the next call to Agent B, and the next call to Agent C. Ideal for commission-based sales teams and to prevent overburdening specific customer service agents.
- Skills-Based Routing: Routes inbound calls according to agent strengths, areas of expertise, and skillsets. For example, if a customer calls in with questions about which product they should buy from your business, they’ll be sent to a product specialist. But if a customer called in with questions about how a product worked, they’d be sent to technical support.
- Time-Based Routing: Routes calls according to specific agent schedules and/or time zones, especially helpful for geographically diverse times
- Relationship-Based Routing: Routes calls to agents according to previously established working relationships, such as a client’s preferred agent or VIP caller status
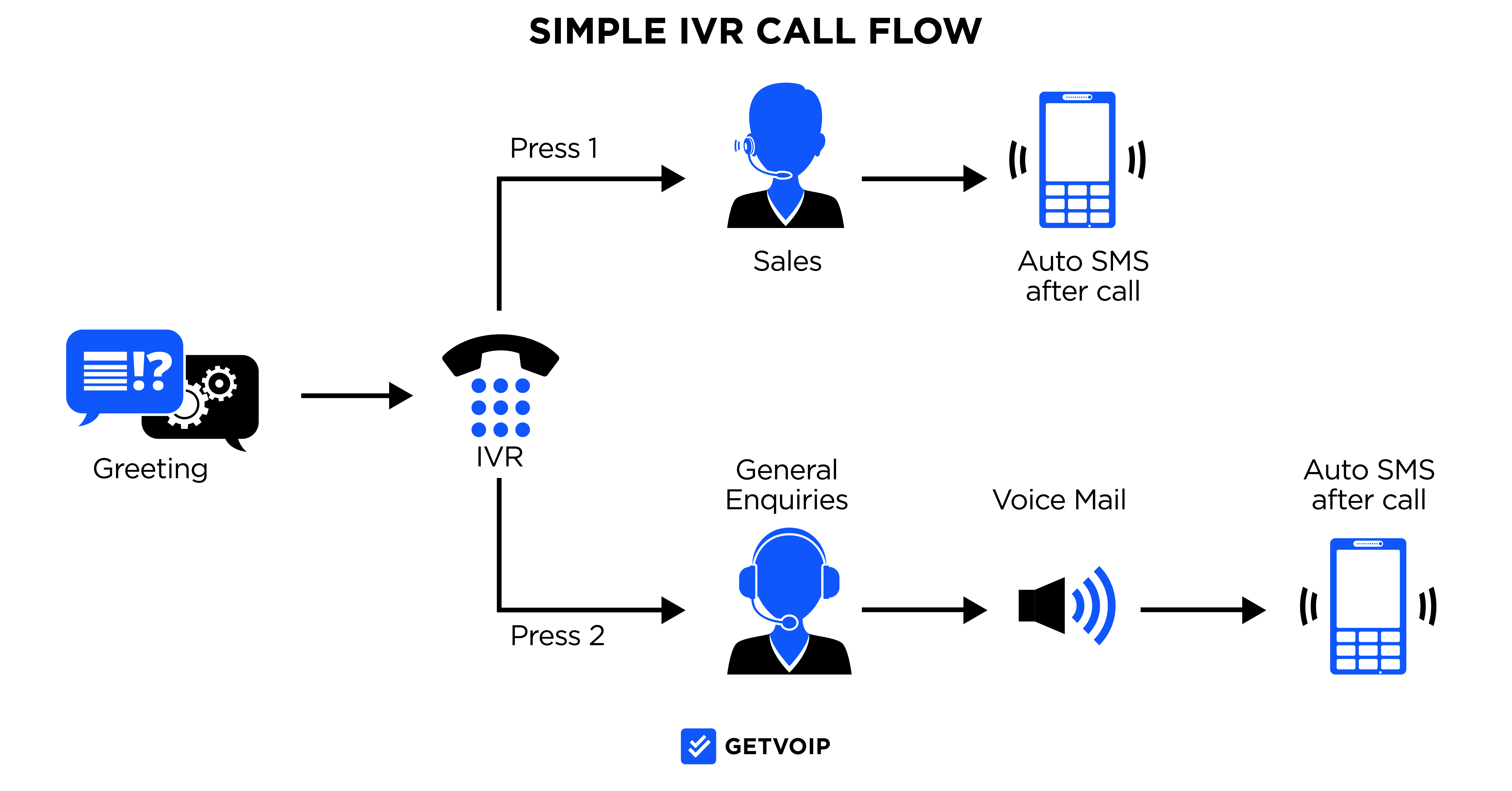
Interactive Voice Response (IVR)
Interactive Voice Response (IVR) is a VoIP feature that uses pre-recorded voice prompts, speech recognition, and/or customer interactions via dial pad to direct calls to the proper departments or individual agents.
When a customer places an outbound call to a business phone system with IVR, recorded messages collect essential information such as:
- Customer contact information
- The reason for the call
- Desired department or representative
- Payment Information
IVR is designed to automate business processes that either completely negates the need for the caller to speak to a live agent or drastically reduce call times.
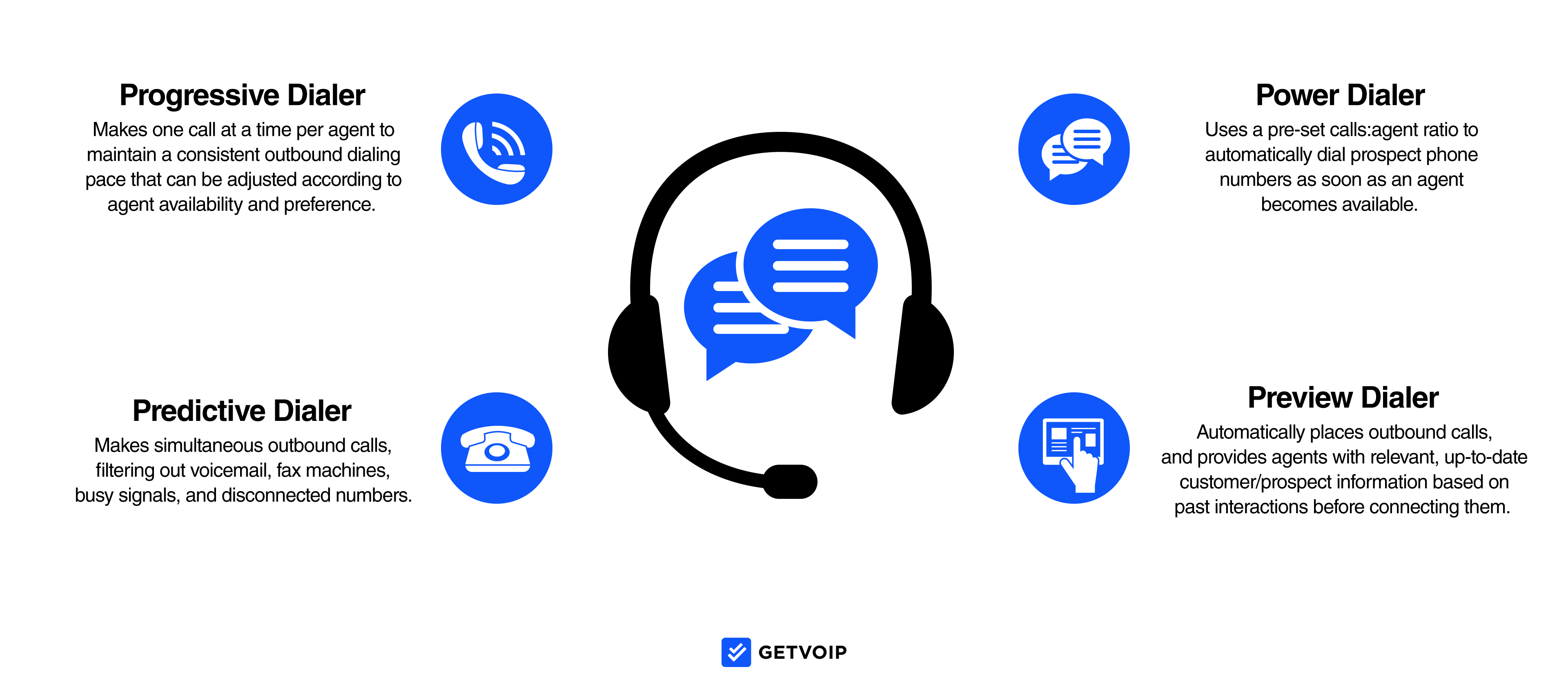
Auto Dialers
Automated outbound dialers (auto-dialers) expedite lead list penetration and increase overall talk times by eliminating the need for agents to physically enter in phone numbers and ensuring that agents connect to calls only when a prospect is on the other line and ready to talk.
This feature automatically filters out busy signals, disconnected numbers, and voicemail machines.
There are several dialing modes to choose from, outlined below:
- Predictive Dialer: Makes simultaneous outbound calls, filtering out voicemails, fax machines, busy signals, and disconnected numbers. Uses an algorithm to “predict” agent availability and accordingly transfers live leads to agents.
- Progressive Dialer: Makes one call at a time per agent to maintain a consistent outbound dialing pace that can be adjusted according to agent availability and preference. Agents must end their current calls completely before the next phone number is automatically dialed.
- Power Dialer: Uses a pre-set calls: agent ratio to automatically dial prospect phone numbers as soon as an agent becomes available. Only connects agents to a live lead. Ideal for smaller teams facing large lead lists.
- Preview Dialer: Automatically places outbound calls and provides agents relevant, up-to-date customer/prospect information based on past interactions before connecting them. Agents may or may not be able to choose whether or not to take a call based on preview mode data.

Call Recording
Call recording is a form of call monitoring that either automatically records calls between agents and callers or records them on an on-demand basis.
Call recordings are then automatically stored in the cloud for later review. Call recordings are often automatically transcribed, and transcriptions can be searched/organized by keywords or phrases.
These recordings allow for:
- Agent and department evaluation and quality assurance
- More in-depth customer insight
- Evaluation of current training materials
- Infallible records of what was or was not said on a call
Ensure you comply with local and federal call recording laws before setting up this feature.
Visual Voicemail
Visual voicemail is a VoIP feature that transcribes voicemail messages left for agents via voicemail-to-text and/or voicemail-to-email.
This means agents do not have to take the time to listen to each voicemail and that they can easily prioritize callbacks according to voice-message content.
Visual voicemail also allows agents to listen to recorded messages if needed.
Call Forwarding
Call forwarding is a call distribution strategy that automatically sends (forwards) incoming calls to different telephone numbers associated with the same agent or department in a pre-set order.
Forwarding calls allows for greater team flexibility and is especially ideal for remote or blended agents because it eliminates the need for agents to be physically tied to a single location to take calls. It also prevents callers from having to hang up and dial multiple phone numbers in the hopes of reaching the desired agent.
For example, if an agent receives a call to their desk phone and doesn’t answer, the call is forwarded to their smartphone after a set number of rings. If the agent doesn’t answer their smartphone, the call is sent to their home phone number. If there’s no answer at home, the call can be directed to the agent’s voice mailbox or sent to another agent.
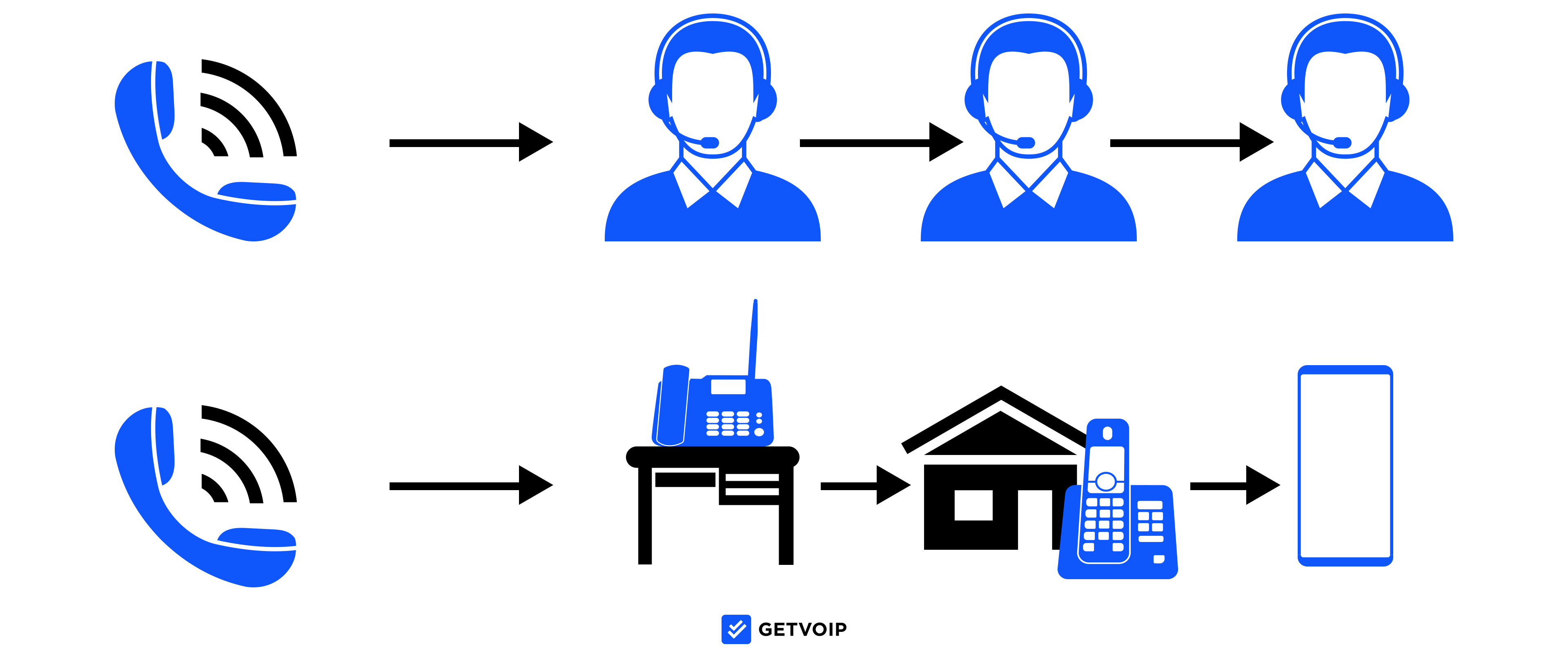
How Much Does VoIP Cost?
To understand the true cost of VoIP, you need to consider more than just the monthly software price. Factors like hardware/equipment, regulatory fees, and taxes impact VoIP pricing.
This table shows factors and average costs influencing monthly VoIP costs (one-time setup/installation and equipment fees vary greatly on an individual level and are therefore not included.)
| Pricing Factor | Average Cost |
| VoIP Software Package | $20.00/user per month |
| Regulatory Fees | $5.00/user per month |
| Surcharges (including one-time number portability fee) | $8.00user per month |
| VoIP Taxes | $7.00/user per month |
| Average Total Monthly Cost of VoIP | $40.00/user per month |
Below, we’ll break down all the expenses associated with VoIP. Please see our post on VoIP taxes and fees for a more detailed explanation of common VoIP phone system costs.
VoIP Pricing and Plans: Average $15-$25/User per Month
Let’s start with the basics: how much the provider charges for the VoIP services it offers.
Most VoIP services offer scalable plans, allowing businesses to avoid paying for features or levels of service they don’t need. This tiered pricing option also means it’s easy for businesses to scale up to the next plan if/when their needs evolve.
Factors that influence VoIP plan costs include:
- Number of users and/or administrators
- Features and functionalities
- Available third-party integrations
- Amount and type of VoIP phone numbers needed (local, toll-free, etc.)
- Number of toll-free minutes per month
- Desired level of provider support (priority support, omnichannel support, etc.)
- Setup and installation
Plans are usually payable monthly or annually (with an annual subscription offering savings between roughly 10-20%.) Customizable quote-based packages are also available, but you’ll need to contact the provider directly to discuss their cost.
Suppose you don’t want to upgrade to the next pricing level but still need features that aren’t available on your current plan. In that case, you’ll likely be able to purchase “add-on” features such as call recording and transcription, additional VoIP phone numbers, or visual voicemail.
For example, the image below shows the three available plans and tiered pricing from VoIP provider RingCentral.
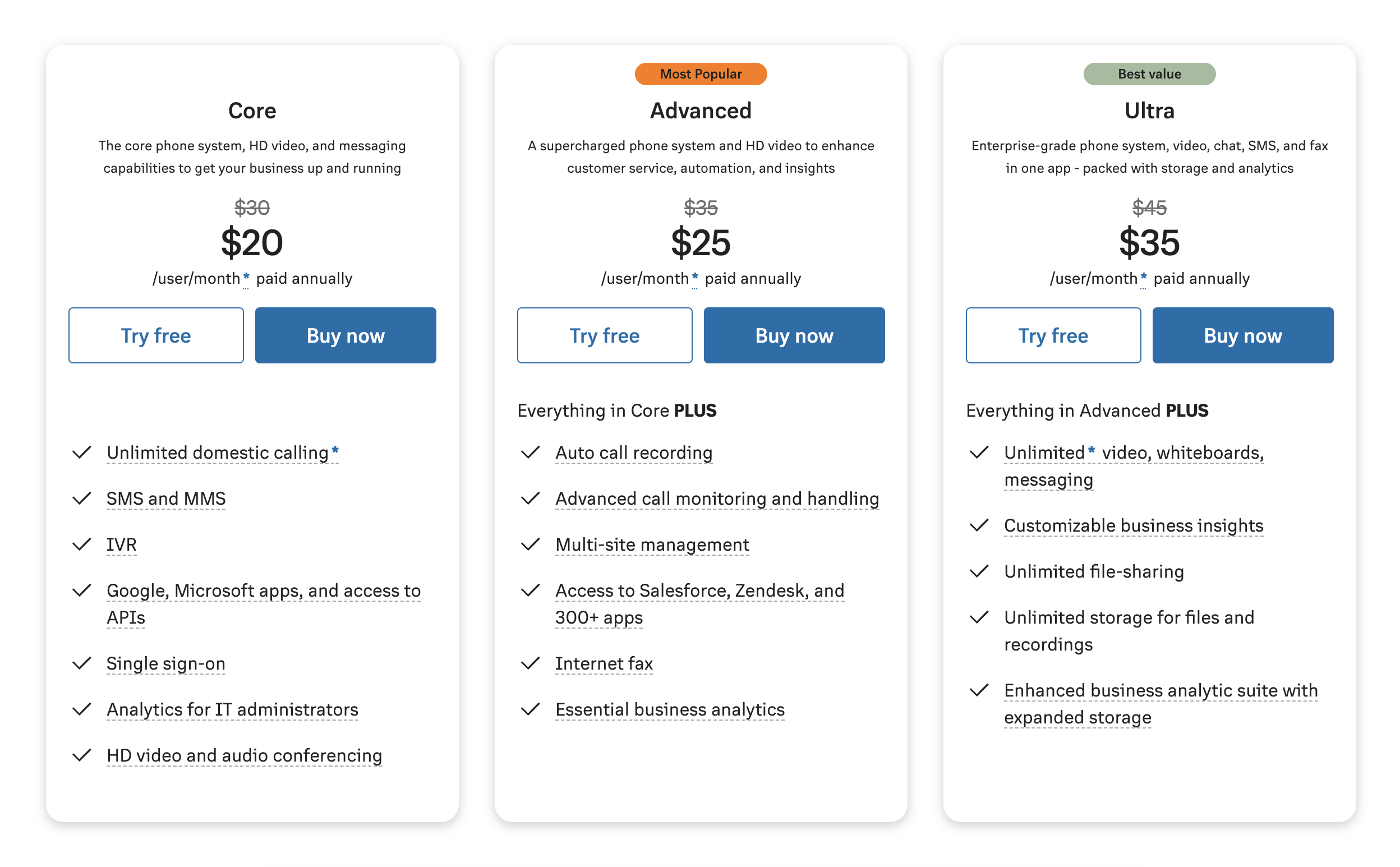
As mentioned above, virtual phone companies usually offer unlimited local VoIP calling on every plan.
However, some providers also offer “pay-as-you-go” calling, which charges per minute or in blocks. This usually only offers a significant cost benefit to micro businesses, newer companies, or teams that don’t primarily communicate by phone but still want a business number.
A final factor in VoIP pricing is whether you opt for cloud-hosted PBX (Private Branch Exchange) or premise-based services.
Premise-based communications services come with a high upfront cost of $3,000-$5,000, but allow businesses greater control over their VoIP services. Cloud-based options are more popular, as they cost between $15.00-$25.00/month and make system maintenance the provider’s -- not the user’s -- responsibility.
VoIP Regulatory Fees And Surcharges: Average $33/Month
While paying under $30.00/user once a month for VoIP service is reasonable, be aware that providers can charge additional fees. Some of these fees are legal, but others may be sign of a fraudulent company.
Because the FCC regulates VoIP, providers must contribute to the funds and services outlined below. As a result, customers will likely see the below legal charges on their monthly VoIP bills to assist the provider with covering regulatory fees.
E911 Fees
E911 (Enhanced 911) fees help to offset the cost of the FCC’s emergency service requirements.
Providers must make 911 service a mandatory feature of every plan and ensure that emergency services have access to the caller’s location.
E911 Fees can range from $0.20 to $2.00/per user per month.
Universal Service Fund Fees
Universal Service Fund (USF) fees help providers cover the costs of required contributions to the USF. This fund provides VoIP, landline, and Internet access to low-income and rural communities, schools, and healthcare professionals.
USF fees generally cost per line every month. If you’ve noticed your monthly USF fee fluctuating, it’s not an immediate cause for concern, as required contributions change 4 times a year.
Expect to pay between $2.00-$4.00/per user per month for USF fees.
Non-FCC Surcharges: Prices Vary
The below surcharges are not associated with the FCC, but you’ll often see them on your VoIP bill. Though their presence alone is not cause for concern, unscrupulous providers may use them as an excuse to charge you an exorbitant monthly rate -- so be aware of what surcharges normally cost.
Number Portability Fees
Most VoIP service providers do not charge fees for number porting (a one-time cost that allows businesses to transfer existing phone numbers to the new provider.)
However, they are legally allowed to. The average cost of number porting is $10.00-$20.00 per ported telephone number and could take 1 to 3 weeks, depending on your existing carrier.
Internet Infrastructure and Intercarrier Compensation Service Fees
Though not mandated, some providers charge Intercarrier Compensation and Internet Infrastructure Service fees to cover the costs of Internet service and fees between carriers.
These fees are generally less than $1.00/month.
Additional Surcharges
Other surcharges can include:
- Early Termination Fees
- Regulatory Recovery Fees
- Regulatory, Compliance, and Intellectual Property Fees
- Add-on feature fees
- Admin/service charges
In total, the average cost of surcharges ranges from $5.00-$50.00+/user per month. This is where sneaky providers attempt to tack on excessive charges, so review your monthly bill carefully.
Business VoIP Taxes: Average $7/user per month
VoIP service providers must legally charge and remit federal, local, and state taxes.
These taxes can also include city, license, franchise, public utility, and even transit taxes. These tax rates will vary based on location and services provided but generally cost around $5.00/user per month.
Gross Revenue Surcharge
Though not legally required, users may also encounter a Gross Revenue Service charge.
A GRS charge offsets the costs of a provider’s federal and state taxation charges and is based on a percentage of the taxable revenue each customer generates for the provider.
Though charges will vary, they generally range between $1.00-$3.00/per user per month.
The below image shows an example of a monthly VoIP bill:

VoIP Equipment and Hardware
Though VoIP BYOD compatibility eliminates much of the need for expensive equipment, a few basic hardware options are still required.
We’ll cover those, as well as popular optional VoIP hardware, below.
Read our guide to the top VoIP equipment and manufacturers for additional information.
Essential Equipment and Hardware
The equipment below is required for getting your VoIP phone system up and running.
Internet Connection and Router
The most important thing you’ll need to operate a VoIP system is a high-speed broadband Internet connection and router.
In general, VoIP systems need a minimum bandwidth of 90-156 kbps to function properly -- meaning you may need to upgrade your Internet service. Note that sufficient bandwidth is the user's responsibility, not the VoIP provider's.
A router connects VoIP devices to the Internet and keeps those VoIP calls connected.
Compatible Device
Once you have working Internet, you need to determine the specific devices you’ll use to make and receive VoIP calls.
Popular VoIP compatible devices include:
- Standard desk phones (via ATA or VoIP phones)
- Smartphones
- Desktop computers
- Laptop computers
- Tablets
Ethernet Cable
An ethernet cable provides your VoIP system with a powerful, consistent Internet connection. Though VoIP calls are possible over WiFi, an Ethernet Internet connection is much more reliable than a wireless one.
PoE Adapter
A PoE adapter is connected to the Ethernet cable, then plugged directly into a wall outlet to ensure the cable has sufficient power.
Analog Telephone Adapter (ATA)
An Analog Telephone Adapter (ATA) allows users to connect existing desk phones, (analog phones) fax machines, or other on-premise devices to their VoIP network.
In short?
It’s what enables standard phones to make and receive VoIP calls.
VoIP Gateway
A VoIP gateway converts analog phone signals to virtual SIP, (Session Initiation Protocol) creating a link between the traditional phone system setup and the network.
Optional Equipment and Hardware
Though you don’t need to have this equipment, having it elevates your VoIP experience.
VoIP Desk Phones
Even if users primarily rely on desktop computers and cell phones to communicate via VoIP voice, many also choose to invest in a traditional desk phone (also called a hard phone or an IP phone.)
Key features to look for in VoIP phones include:
- LCD color touchscreen
- Programmable keys and shortcuts
- Built-in video calling screen
- Built-in USB ports
- Busy light indicator
Headsets
VoIP headsets provide a better overall sound quality, have noise-cancellation features, and make it easier for employees to hear and stay focused on current conversations.
Both wired and wireless headsets are available, though the latter is more popular and allows for greater flexibility.
Look for VoIP headsets with:
- A Bluetooth range of at least 5 feet
- Basic call control functions on the headset itself
- Adjustable microphone
- Compatible smartphone app
Conference Speakers
Headsets make one-on-one conversations clearer, but speakers can make conference calls a much better experience for everyone involved.
Look for speakers with:
- Built-in microphones
- Background noise suppression
- An audio pickup radius of 7-10 feet at a minimum
- User controls like mute, remove from speakerphone, intercom, volume controls
- Bluetooth connectivity/USB ports
What To Look For In A VoIP Provider
What else should you consider when evaluating VoIP software besides a fair and transparent pricing structure?
Our research shows that there are four main factors to pay attention to when choosing a VoIP service:
- Scalability
- Available Features
- Compatibility
- Customer Service and Support
Scalability
Scalability refers to how easy users can “scale up” or “scale down” their VoIP plans when their needs change. For example, a provider that offers only 2-3 plans is not as scalable as one offering 4-5 different pricing structures.
Scalable solutions matter because they:
- Prevent you from paying for features you don’t need
- Let your VoIP service grow with your company (by adding additional users and/or additional features)
- Offer a better overall value, even if you can get “cheaper service” elsewhere
Also, consider whether or not the provider offers you the ability to scale up from a business phone system to a contact center software or unified communications system. This allows you to add more communication channels, like video conferencing or live chat, in the future without changing providers.
Available Features
When it comes to evaluating provider features, more isn’t always better. Too many features can confuse and overwhelm new users, often causing more work than they were meant to save.
Instead, focus on whether or not the provider offers the most important features to your specific company.
For example, if you work in the healthcare industry, you’ll need a VoIP solution that’s HIPAA compliant. If you’re operating an outbound call center, you’ll likely prioritize many available dialing modes over features like visual voicemail.
Compatibility
The best pricing and all the features in the world won’t matter if your VoIP system isn’t compatible with your current business tools and operating systems.
Ensure that any provider you’re considering is compliant with:
- Your mobile devices (Apple and Android mobile apps, etc.)
- Your current OS (Mac, Windows, etc.)
- Your preferred web browser (Google Chrome, Safari, Firefox, etc.)
- Third-party software (CRM system, project management tool, team chat app, etc.)
- Any additional hardware (analog phones, headsets, etc.)
Customer Support and Service
Finally, ensure the VoIP provider offers quality and responsive customer service and support.
You need to know:
- How many support channels are available? (Phone, live chat, email, etc.)
- What are the available hours for each channel? (24/7 on at least one channel is best)
- How long does the provider generally take to resolve a customer’s issue?
- What is the provider’s average response time?
- What is the guaranteed uptime? (99.9% is the minimum you should consider)
- What security standards/certifications does the provider offer? (End-to-end encryption, GDPR compliance, HIPAA and PCI compliance, SOC II Compliance, etc.)
- What user training materials are provided? (Online courses, tutorials, custom in-person employee training, etc.)
- Is priority support available?
- How active are the provider’s online support forum and developer community?
Our detailed guide on choosing a VoIP provider offers additional insight and a breakdown of top VoIP platforms like Nextiva, RingCentral, and Grasshopper.
Now that you know what to look for in a VoIP telephone service, it’s time to start thinking about which platform best suits your current and future business communication needs.
Whether you’re already considering a specific service provider or if you don't yet have one in mind, our Business VoIP comparison table provides detailed information on user experience, pricing, available features, VoIP softphones, and more.
VoIP FAQs
Below, we’ve answered some of the most common VoIP questions.



