A VoIP phone system uses the internet to transmit live audio data between call participants. Compared to a traditional phone system, VoIP requires much less onsite equipment. However, a business VoIP infrastructure still depends on a few key pieces of hardware and software.
In this article, we will outline everything you need to know about VoIP infrastructure, including what it is, key layers and components, important integrations, and how to optimize your VoIP infrastructure.
Jump to ↓
- What is VoIP Infrastructure?
- Layers of a VoIP Infrastructure
- Important VoIP Integrations
- How to Optimize Your VoIP Infrastructure
- Reap the Benefits of a Strong VoIP Infrastructure
What is VoIP Infrastructure?
VoIP infrastructure refers to the hardware and software components that enable a VoIP phone system to work–including routers, computers, network bandwidth, mobile devices, handsets, VoIP software applications, servers, and data centers.
Instead of using a landline voice signal, Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) makes calls by transmitting audio data packets over the web. VoIP offers tons of business benefits including easy setup and maintenance, improved audio quality, scalability and support for remote teams, and advanced digital features. While VoIP reduces hardware needs compared to a landline phone system, cloud-based calling still relies on several pieces of infrastructure in order to transmit real-time voice data between call participants.
VoIP infrastructure components vary depending on the type of cloud phone system your business uses:
- Cloud-hosted PBX systems require minimal hardware–just an internet-connected device–but still depend on advanced software applications from your VoIP provider.
- On-premises PBX systems involve additional hardware components like a physical PBX box, cables and phone lines, VoIP phones, and potentially a SIP Trunk.
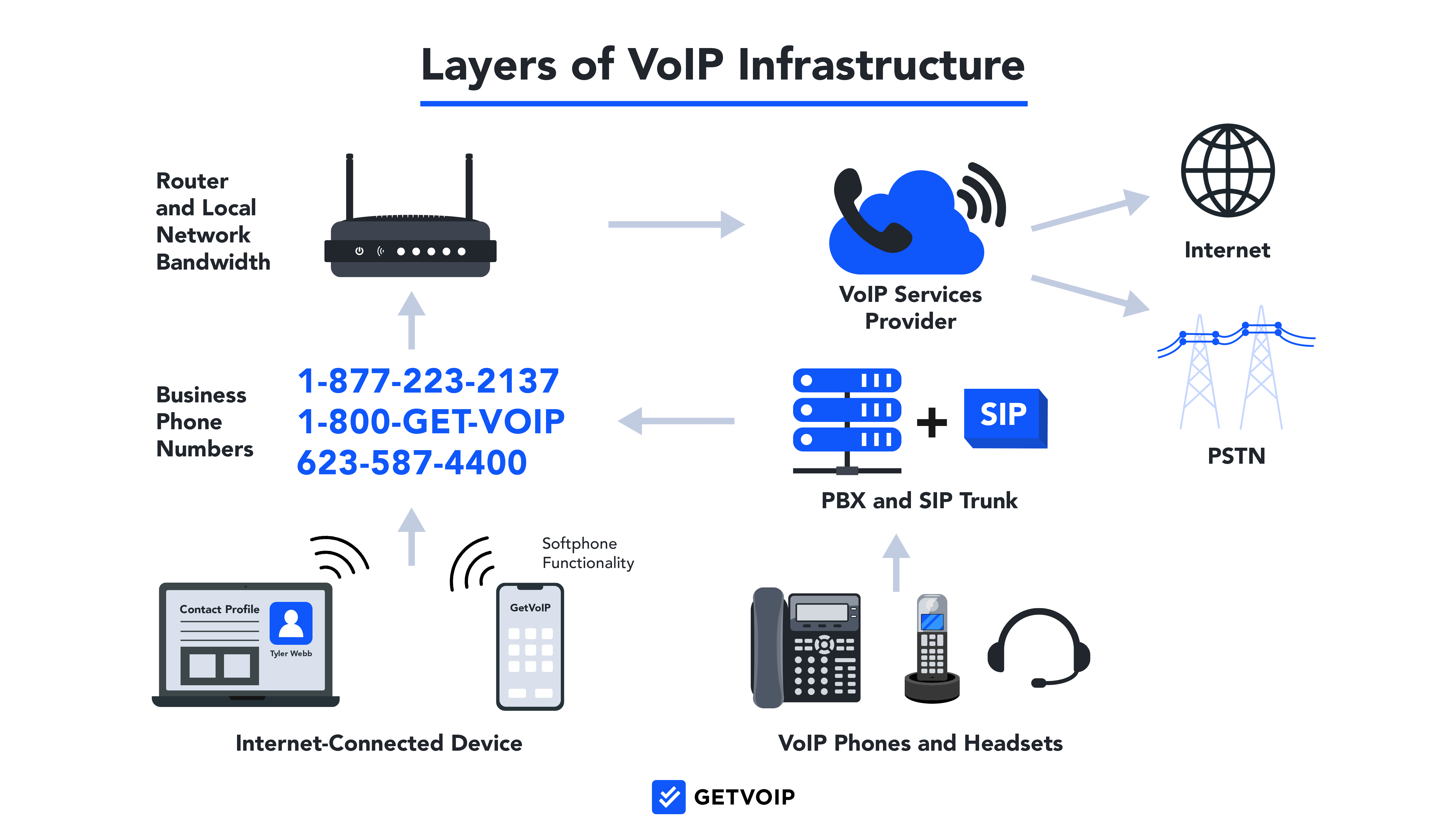
Layers of a VoIP Infrastructure
Voice over IP infrastructure includes multiple layers of hardware and software, which work together to transmit audio data between call participants.
Here are the main layers and components of VoIP infrastructure:
- VoIP software application and phone service
- Internet-connected device: computer, mobile, or tablet
- Business phone numbers
- Internet connection and bandwidth
- Router and local network
- Softphone
- VoIP phone, handset, or headset
- SIP trunk or onsite PBX system
VoIP Software Application and Phone Service
The most important part of VoIP infrastructure is the VoIP application itself–the cloud-based phone service hosted by your VoIP provider. VoIP applications are software that you can download on a computer or mobile device to make calls over the Internet.
Today’s business VoIP market features dozens of popular providers: RingCentral, Nextiva, Dialpad, Zoom Phone, Grasshopper, and many more. Users pay a monthly subscription, which enables business teams to make calls and other features through the VoIP app on internet-connected devices. The provider manages and hosts the phone service, long-distance calling network, connection to the PSTN landline, and the software itself.
Each provider’s VoIP application supports a suite of digital phone system features:
- Domestic and international VoIP calling
- Voicemail
- Call routing and queuing
- Additional communication channels like video conferencing, SMS texting, and team chat
- Call center analytics, reports, and insights
Internet-Connected Device: Computer, Mobile, or Tablet
In order to make calls on your VoIP application, you need an internet-connected device: Mac or PC desktop, web browser, and mobile devices like iOS and Android.
Once you log into your provider’s VoIP app on one of these devices, use the app dashboard to make calls, send texts, manage queues and routing, and more.
Business Phone Numbers
Each VoIP user needs a business phone number to make or receive calls, which makes DID phone numbers a crucial piece of VoIP infrastructure.
Your monthly VoIP service subscription typically includes one digital phone number, but you can purchase extra numbers via subscription. You can also port in your company’s pre-existing numbers, making them digital. Administrators can assign virtual numbers to users, IVR menus, and remote workers around the globe.
VoIP providers typically offer several types of digital business phone numbers:
- Local numbers from area codes around the US and Canada
- Toll-free numbers that spell out a word, like 1-800 numbers
- Vanity numbers such as 1-800-FLOWERS
- International numbers from area codes around the world
Internet Connection and Bandwidth
VoIP telephony uses the internet to transmit audio data packets between parties on a call. This process requires a strong internet connection and ample bandwidth for your local area network (LAN). Therefore, an internet connection and bandwidth are essential pieces of your VoIP infrastructure.
Router and Local Network
In order to have a stable internet connection with sufficient bandwidth, you must have a router that’s up to the task. A network router provides Internet connectivity for all local devices. Once the router receives audio data from your network’s devices, it transmits this data across the internet. On the reverse end, the recipient's router receives inbound voice traffic from across the web, directing it in real-time to its local device with the appropriate IP address.
A strong router, and the local area network (LAN) it provides, are critical components of VoIP infrastructure.
Softphone
A built-in software feature on VoIP apps, softphone functionality enables users to have real-time VoIP conversations directly through their computer or phone. Softphone means that you don’t need to purchase additional VoIP hardware like phones or headsets. For most users, the VoIP app’s softphone feature is a critical piece of VoIP network infrastructure.
VoIP Phone, Handset, or Headset
While not essential to a VoIP phone system, calling hardware like VoIP phones, handsets, and headsets are important pieces of VoIP infrastructure for some users. Most modern VoIP systems don’t require physical hardware phones for calling, but many call centers and agents prefer these devices because of their privacy, convenience, and traditional feel.
This VoIP hardware plays a role in VoIP infrastructure.
SIP Trunk or Onsite PBX System
If your company hosts your private branch exchange (PBX) system onsite, you will use a hardware PBX box and SIP Trunk in order to connect your IP phone system to broadband internet and PSTN landline. A physical PBX box connects to the internet and provides telephony for dozens of phone lines, while a SIP Trunk connects your landline phone system to the internet for VoIP calls.
These hardware materials are a necessary component of VoIP infrastructure for those using an onsite PBX system.
Important VoIP Integrations
Since VoIP technology itself is software-based, most VoIP providers offer cloud-based telecom systems that integrate with up to hundreds of third-party apps. These integrations expand your company’s VoIP infrastructure and synchronize with your communication system, providing new use cases and benefits.
Here are some of the most popular and important third-party integrations to expand your software VoIP infrastructure:
- CRM systems
- Calendar apps
- Collaboration and project management tools
- Analytics and AI platforms
- SMS and email applications
- Marketing automations
CRM Systems
Integrating CRM systems into your VoIP infrastructure leads to stronger contact profiles, more detailed analytics about customer journeys, and automated workflows between applications. With apps like HubSpot and Salesforce, your call-center agents have a much fuller view of each customer’s context during an interaction.
Popular CRM integrations:
- Salesforce
- Hubspot
- Monday.com
- Zendesk
Calendar Apps
Calendar applications like Google Calendar and Microsoft Outlook integrate with your VoIP infrastructure, automatically syncing events like conference calls, video meetings, and meetings with customers. Once you plan a video meeting or phone call with a customer, the integrated calendar app automatically logs the event and the join link.
Popular Calendar Integrations:
- Google Calendar
- Microsoft Outlook Calendar
Collaboration and Project Management Tools
A VoIP phone system integrates with collaboration and project management tools, syncing tasks, assignments, and communications across apps. Sync your VoIP telecommunication system with an app like Asana or Slack, so that an agent’s assigned calls and VoIP notifications populate both apps at once.
Popular Project-Management Integrations
- Asana
- JIRA
- Slack
- Basecamp
Analytics and AI Platforms
While many VoIP phone systems include built-in analytics tools, analytics integrations can be an important piece of VoIP infrastructure that tracks phone-system data to generate trends and KPIs. Apps like Gong and Chorus.ai analyze call records, transcripts, and user activity to deliver unique insights that help with marketing and customer support.
Popular Analytics Integrations:
- Gong
- Chorus.ai
- Chatlayer.ai
- Fireflies.ai
SMS and Email Applications
Integrate your VoIP phone system with SMS and email applications to add multichannel communications and bulk-messaging use cases to your VoIP infrastructure. Tools like Beetexting enable you to share SMS inboxes among multiple VoIP users, while KLaunch supports AI-powered text conversations with customers.
Popular SMS and Email Integrations:
- Beetexting
- KLaunch
- Mailchimp
Marketing Automations
Marketing VoIP integrations track customer activity to generate leads, create campaign lists for outbound SMS and email marketing, and utilize AI to facilitate automated conversations with customers across communication channels. Outbound marketing tools can play a critical role in your VoIP infrastructure.
Popular Marketing Integrations:
- Marketo
- LeadSquared
- Botfuel
- Pipedream
How to Optimize Your VoIP Infrastructure
Optimize your VoIP infrastructure by choosing the right VoIP provider, keeping your software up to date, using modern devices, and ensuring that you have enough network bandwidth.
1. Choose the Right VoIP Provider
Optimize your customer service and collaboration capabilities by choosing a VoIP provider with the pricing, calling area, and unified communications features that meet your business needs. The right VoIP phone service will offer your agents an intuitive interface, high-quality audio, and communication tools that allow them to do their job well. Therefore your VoIP service provider is the most important part of your VoIP infrastructure.
Consider the following when choosing a provider:
- Pricing: Choose a VoIP provider that offers subscription pricing plans that meet your budget. Many providers offer cost-effective pricing plans that provide excellent value with routing, queueing, analytics, and other tools.
- Calling area: While most VoIP providers support international calling around the globe and unlimited domestic calling, some providers and plans support unlimited calling areas covering multiple countries. Pick a provider that supports calling to your most frequently dialed destinations.
- Features: Each VoIP provider and pricing plan offers a unique suite of features–routing tools, queueing, call controls, call monitoring, analytics, collaboration tools, and more. Pick a plan that offers the tools you want, to get the most out of your VoIP infrastructure.
2. Keep Your Software Up to Date
Once you select a provider, your VoIP software application is the backbone of your company’s VoIP infrastructure. To ensure that your app and voice calls run smoothly, make sure you keep all related software up to date–both on your VoIP app itself and the devices that use it.
3. Use Modern Devices
To get the most out of your VoIP infrastructure, it’s important to use up-to-date hardware: routers, computers, mobile devices, and VoIP phones.
- Router: Choose a router no more than 3-4 years old, and ideally one that supports WiFi 6.
- Computers and mobile: Computers and smartphones running VoIP should be ideally no more than 5 years old, or they risk decreased performance
- VoIP phones and headsets: Select VoIP hardware from a reputable provider like Ooma, Polycom, Yealink, Cisco, or Avaya. This will ensure high audio quality on live calls.
4. Ensure Your Network Has Sufficient Bandwidth
Bandwidth is a critical part of your VoIP infrastructure because your router requires bandwidth to send and receive VoIP data during a live call. Low bandwidth jeopardizes call quality and can lead to VoIP latency and jitter.
To avoid VoIP problems and optimize your internet connection’s available bandwidth, try these tips:
- Avoid excessive network traffic: Your local network can become overwhelmed if too many devices are consuming data at once. Whether using WiFi or ethernet for VoIP, reduce the number of devices using the network for non-VoIP activities.
- Choose a good router: Most modern routers are capable of supporting multiple concurrent VoIP users. Make sure your router is relatively modern–made within the last three or four years–and if your local network supports multiple VoIP users, consider investing in a powerful router.
- Use QoS: Your router’s quality of service (QoS) settings enable you to prioritize particular devices and types of data–like VoIP–so that when your network is congested, VoIP gets priority
Reap the Benefits of a Strong VoIP Infrastructure
When your VoIP infrastructure functions well, everybody benefits. Agents have the app interface and features they need to provide great customer service, customers receive quicker and more personalized attention, and administrators can create routing and monitoring systems that allow efficient small-business functioning.
Depending on if you use a hosted PBX or on-premises PBX VoIP system, the precise components that make up your infrastructure will vary. However, all types of VoIP infrastructure rely on a strong business VoIP provider, modern computers and mobile phones, and a router that supports a local network with enough bandwidth.



