VoIP telephony provides countless benefits over legacy PBX phone systems, including high-quality audio, advanced features, multiple communication channels, affordability, and easy setup.
While cloud-based phone systems are generally low-maintenance and require minimal hardware, you may still run into occasional issues like audio delay, echoing, or dropped calls.
Thankfully, these issues usually have a simple fix that you can handle on your own.
In this article, we’ll outline the most common VoIP problems and strategies to troubleshoot them.
Common VoIP Problems
Potential Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) problems vary by location, chosen VoIP software and hardware, number of active network users, and daily call volume.
However, enterprise-level and small businesses face many similar VoIP call quality issues regardless of their virtual telephony provider.
Let’s explore troubleshooting solutions to the most common business VoIP problems, which are:
- Jitter and Latency
- Echo
- Devices that won’t make and/or receive calls
- Choppy audio and low-quality calls
- No sound once a call connects
- Dropped calls
- Phone doesn’t ring when receiving inbound calls
VoIP Problem 1: Jitter and Latency
Causes: Slow internet connections, insufficient network bandwidth
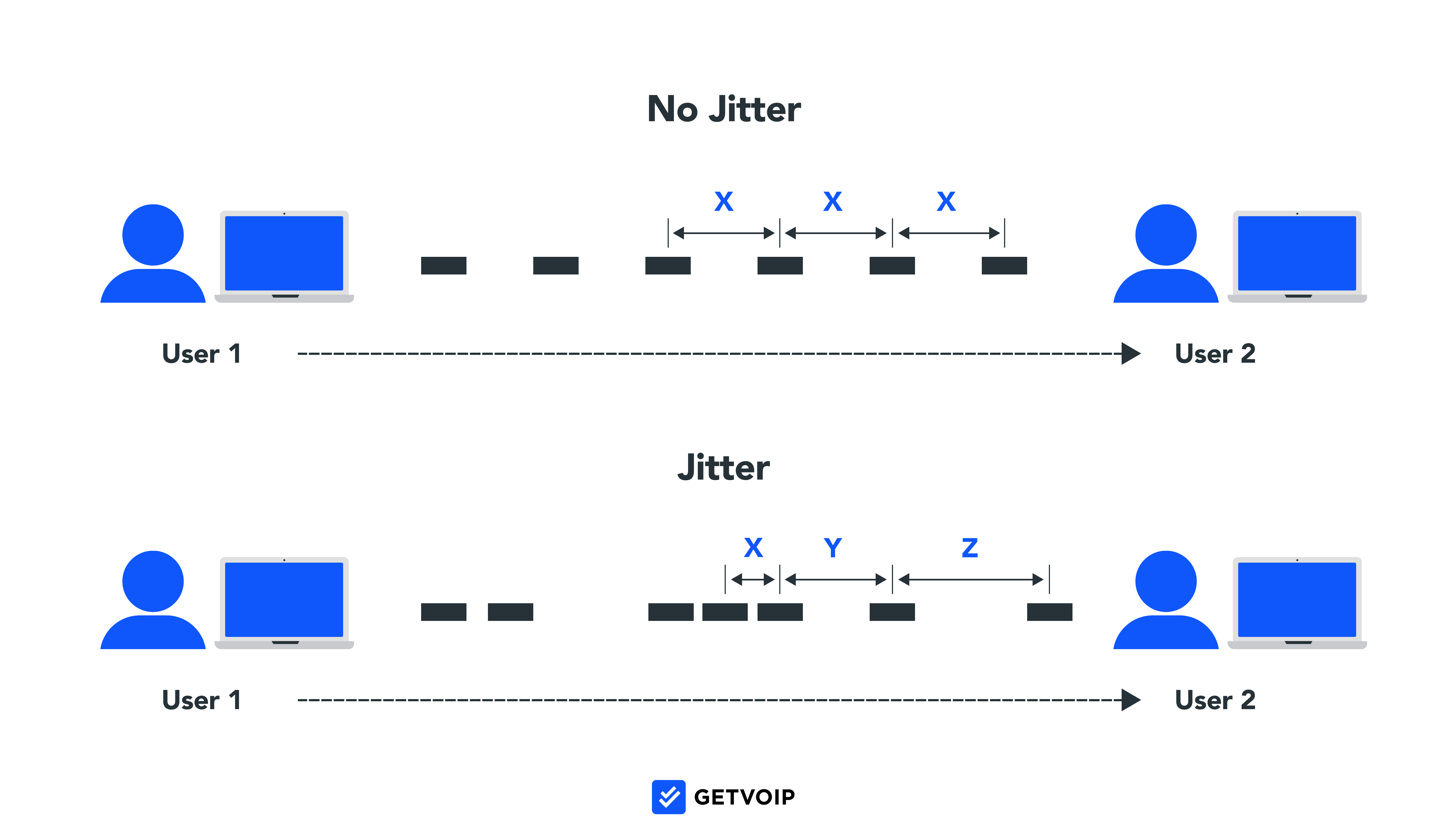
VoIP jitter occurs when parts of an active VoIP phone call are sent to the recipient out of order, making your conversation nonsensical, garbled, or choppy.
Latency results from an audio delay, meaning the speaker’s voice takes a long time to reach the recipient.
During an active conversation, VoIP phone systems rely on bandwidth and fast internet to transmit audio data between call parties. When VoIP audio data gets dropped or bottlenecked during transit, it reaches the recipient out of order (jitter) or with a delay (latency).
If you're experiencing latency or jitter on VoIP calls, run a VoIP speed test to confirm. To avoid call disruption, keep latency below 150 milliseconds (ms) and jitter below 30 ms.
How to Troubleshoot Jitter and Latency
Effective solutions to jitter and latency are:
- Clear bandwidth space on your local network: This may require purchasing a new router that supports faster data speeds, or reducing local network traffic by limiting the number of concurrent users
- Evaluate your Internet Service Provider: Your internet may not have enough bandwidth to power all your connected devices. Contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to upgrade your internet connectivity.
- Install a jitter buffer: Once installed on virtual phones, jitter buffers cause slight delivery delays in order to reorder packets in real-time, fixing jitter
VoIP Problem 2: Echo
Causes: Call participant feedback, problems with a call participant’s VoIP phone system, internet connection, or speakers
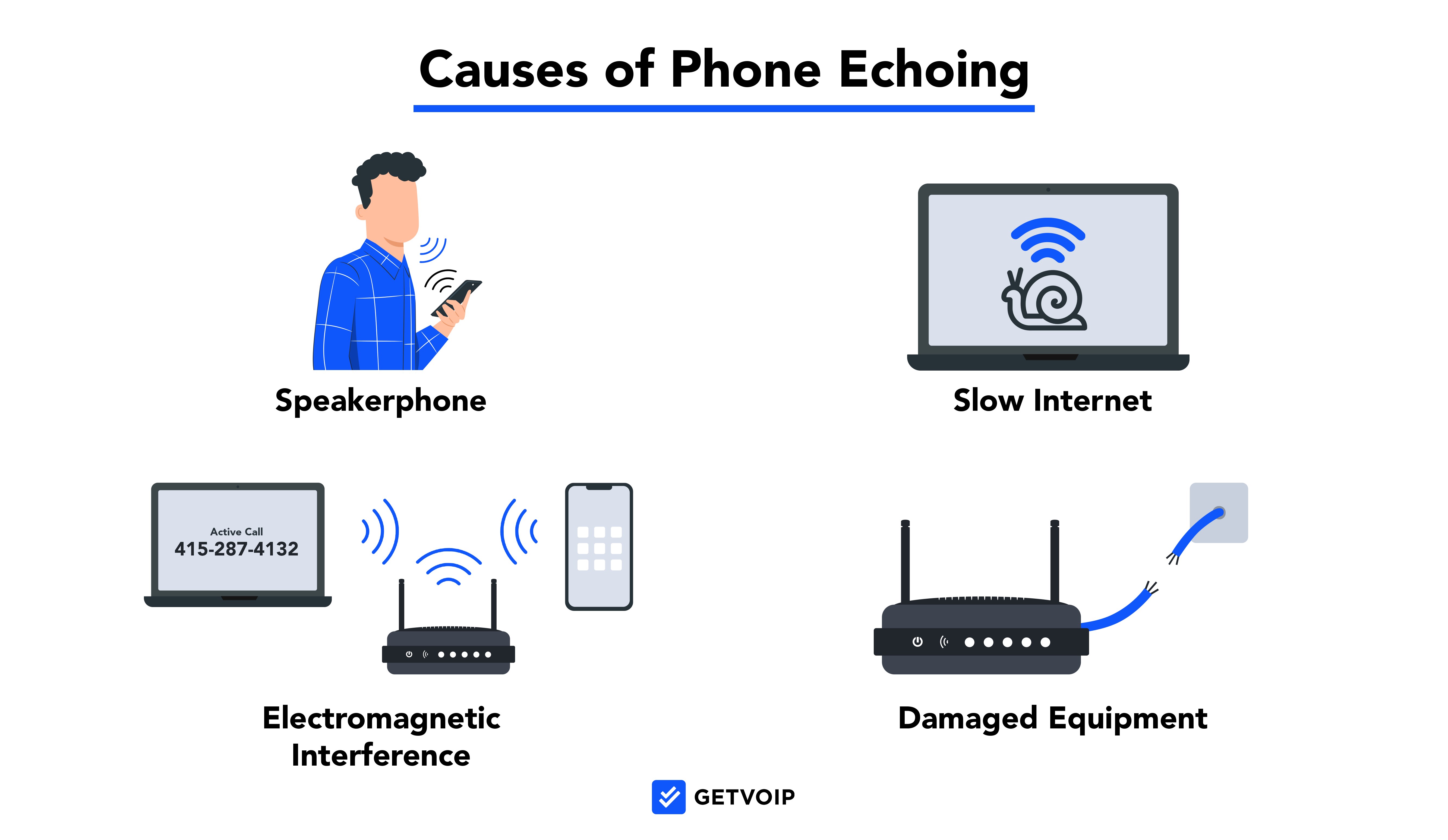
Phone echoing is when voices loudly repeat at varying intervals during a call, making it difficult to follow the conversation. If the speaker, the recipient, or all parties experience echoing, there’s a VoIP connection issue.
How to Troubleshoot Phone Echo
Effective VoIP troubleshooting tips for echo are:
- Speakerphone: The easiest way to both prevent and fix echoing is to take your phone off speakerphone. Speakerphone transmits your voice through multiple microphones and speakers, which can cause several extra cycles of audio feedback.
- Headset: There may be an issue with your current phone headset. To test this, make one call with your headset and one call without it, and see if the echo occurs exclusively when using the headset. If so, it’s time for a replacement.
- Internet connection or bandwidth: As with jitter, echoing can be caused by a faulty Internet connection. We recommend running an Internet speed test to evaluate whether or not your current level of bandwidth is sufficient for VoIP traffic.
- Electromagnetic interference: Electromagnetic interference happens when you place your devices too close to other electronic devices. For example, if you set your smartphone on top of your laptop when making calls, you’ll likely experience poor voice quality, as both devices have large electric fields.
VoIP Problem 3: VoIP Device Won’t Make and/or Receive Calls
Cause: Router’s SIP ALG tool sends outbound data packets to the wrong IP address or adjusts firewall settings to block inbound Voice over IP data
Sometimes, your VoIP platform may not allow you to make outbound calls or receive inbound calls. Typically, the phone app either fails to connect outbound calls, doesn’t register inbound calls, or displays an “X” when you try to place an outbound call.
How to Troubleshoot the Inability to Make or Receive Calls
To resolve issues making or receiving calls, try these potential fixes:
- Turn off SIP ALG: Try turning off the SIP ALG (Session Initiation Protocol Application Layer Gateway) setting in your router’s menu. The SIP ALG tool modifies a network’s outbound VoIP packets to better transmit them through firewalls. However, this modification can sometimes route the packets to the wrong IP address, so the recipient never receives your VoIP data.
- Software update: If you’re unable to receive inbound calls, try updating your VoIP application’s software and restarting the device
VoIP Problem 4: Choppy or Broken Audio
Causes: Data packet loss
Choppy voice and audio mean that, although the call isn’t completely disconnected, certain words are dropped and voices keep cutting in and out.
It can sound like you’re driving through a tunnel, only hearing every third word the other person is saying.
How to Troubleshoot Choppy or Broken Audio
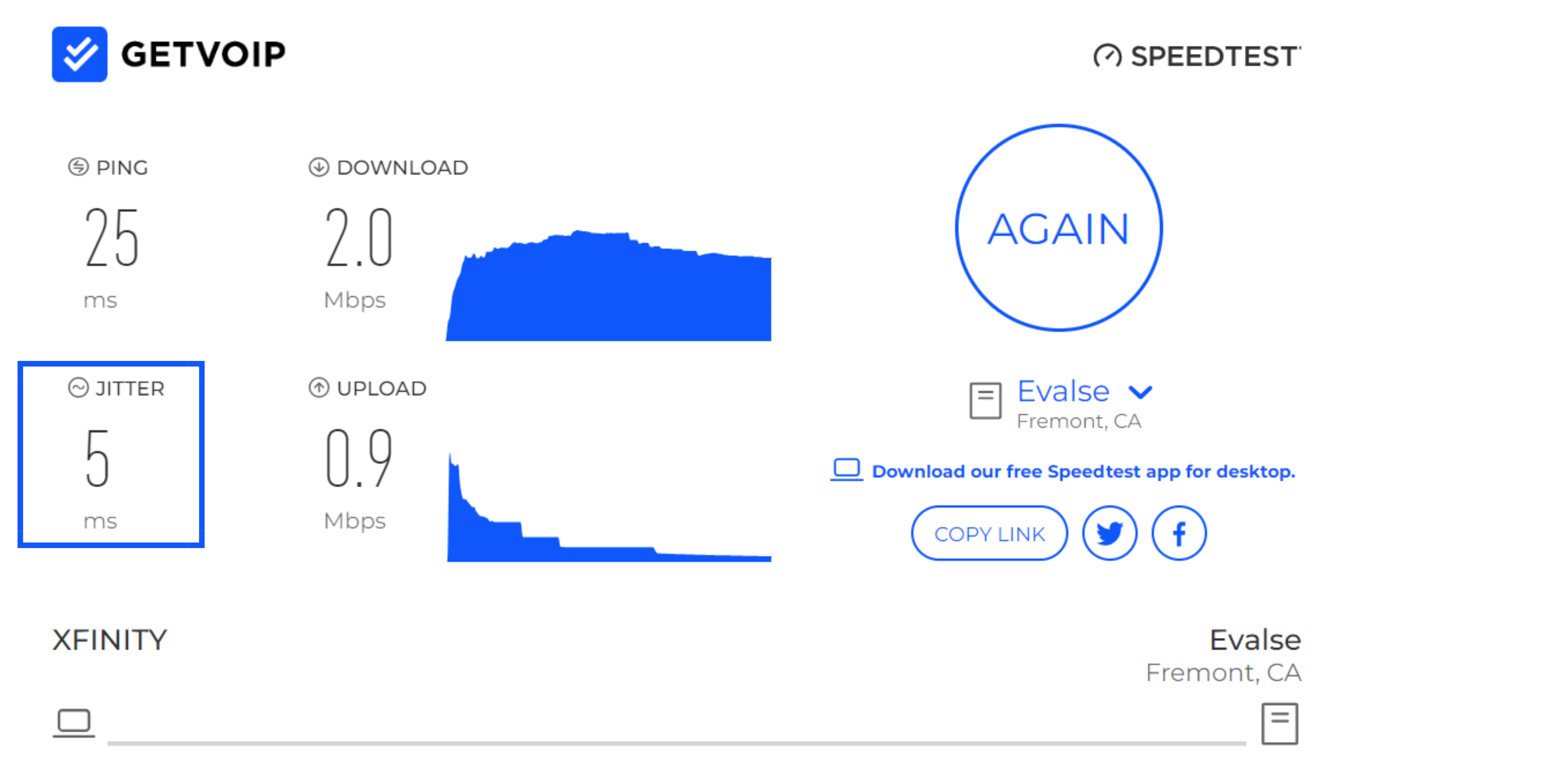
The best solution is to ensure that your internet connection has enough bandwidth and speed. Use a VoIP or internet speed test to measure your download speed and jitter. If your jitter is above 30 ms, you probably have insufficient bandwidth.
Try these strategies to troubleshoot choppy VoIP audio:
- Reduce bandwidth load on your local network: Reduce the bandwidth load on your router’s local network by minimizing the number of users engaging in data-demanding activities like video conferencing, streaming, gaming, and concurrent VoIP calls
- Adjust QoS settings: Your router’s Quality of Service (QoS) settings enable you to prioritize certain devices or types of data–like VoIP. That way, when your local network is crowded, your router ensures that VoIP data receives bandwidth priority.
- Consider your WiFi connection: Wireless networks are convenient and are generally strong enough to power basic Internet access, but Wi-Fi isn’t ideal for VoIP phones. Consider making the switch to an Ethernet internet connection.
VoIP Problem 5: No Sound Once a Call Connects
Causes: Call participant’s router sends VoIP data packets to the wrong IP address or blocks inbound data packets via firewall
You may have an issue where once your call connects, you can’t hear anything. This audio issue can be one-way, or neither side may be able to hear the other.
How to Troubleshoot a Lack of Audio
To resolve one-way audio or a lack of VoIP audio, both parties should check their router’s firewall settings to ensure that SIP ALG is turned off.
Troubleshooting strategies for a lack of audio are:
- Turn off SIP ALG: A lack of sound on connected calls is often due to SIP ALG firewall settings blocking or misrouting RTP or UDP packets, which are essential for VoIP service. In most cases, disabling SIP ALG will adjust the firewall settings so that VoIP data reaches its destination.
- Codec settings: All parties on a call must be using the same VoIP codec (G.711, G.722, Opus) to compress and transmit all audio data during a call. To ensure all parties are using the same codec, check the VoIP extension’s Codec Settings.
VoIP Problem 6: Dropped Calls
Cause: Insufficient bandwidth
Dropped calls–calls that suddenly end in the middle of a conversation without warning–are an enormous source of frustration for both employees and clients.
Dropped calls are especially common in call centers with a consistently high outbound call volume.
You may notice that your calls drop either randomly or at a consistent point in the conversation, such as a few seconds or minutes into the conversation.
How to Troubleshoot Dropped Calls
The first thing to do with consistently dropped calls is to ensure your software and any compatible VoIP hardware and equipment have been updated. After that, aim to reduce the load on your local network’s bandwidth.
Strategies to troubleshoot dropped VoIP calls include:
- Update VoIP software and hardware: Ensure that your VoIP application, devices, and routers are all up to date, and turn on auto-updates when possible. Contact your VoIP service provider to confirm you’re using its most current version.
- Disconnect and reconnect devices: Disconnect all devices currently connected to the VoIP network, then reconnect them one at a time to determine which one is causing the problem. Separate devices like a caller ID tool, dial-up modem, or network alarm systems may be causing the issue.
- UDP timeout: If calls seem to drop after a specific amount of time, your provider may have set up a UDP timeout to automatically disconnect after a set number of minutes. Contact your provider and ask them to remove the safety disconnect. In the meantime, you may have to hang up and call clients back.
- Router timeout settings: Your router may be timing out during calls, causing them to drop. Change your router settings to increase the timeout to at least 60 seconds. You can also change devices to Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) from UPD, as this enables the retransmission of lost voice packets.
VoIP Problem 7: Phone Doesn’t Ring for Inbound Calls
Cause: Your VoIP device, account, or handset isn't appropriately connected to your phone system.
When your phone sends your calls straight to voicemail instead of ringing, your business faces serious delays in productivity and potentially loses revenue.
You may find your VoIP system skips your office phone altogether and sends calls directly to another device.
How to Troubleshoot Missed Calls
If your VoIP phone doesn’t ring during inbound calls, make sure your device is logged into your VoIP application and that your account is linked to the right business phone number.
To further troubleshoot missed VoIP calls, try these solutions:
- If using a VoIP handset or desk phone: Check to ensure your hardware VoIP phone is still registered with your current VoIP provider. If not, contact the company and learn how to re-register your devices.
- Do Not Disturb: Make sure you did not accidentally leave your phone on its Do Not Disturb setting
- Call forwarding settings: Check your VoIP app’s call forwarding settings, as you may have accidentally adjusted the configuration that forwards your calls to another device or user
VoIP Troubleshooting Strategies
Faulty VoIP hardware can cause all sorts of VoIP problems, including the issues described above. If the above strategies don’t solve your VoIP issues, use the following tips to troubleshoot your VoIP hardware:
- Ensure all cable connections are secure
- Check for damaged cables
- Change your router’s placement
- Upgrade or consider a second router
- Reset your router
- Adjust your router’s QoS settings
Secure All Cable Connections
Inspect all cables involved in your VoIP phone system, including those that connect to computers, routers, VoIP phones, Ethernet wall ports, or PBX systems.
Make sure that each connection is securely connected on both ends and consider unplugging and replugging each cable in your phone system.
Avoid using a cable or Ethernet splitter, as this technology can cause jitter and lag.
While simple, ensuring proper cable connection is a valuable strategy for preventing the most common VoIP issues.
Check For Damaged Cables
In addition to inspecting connections, ensure there is no visible damage on your cables or cable connectors.
Ethernet cables plug in using a plastic jack with a clip, but these often chip or break off, causing cables to come loose.
Change Your Router’s Placement
Certain obstacles like walls, doors, and furniture can block WiFi connectivity.
Place your VoIP router in a central location near connected devices, with minimal obstacles between the router and the wireless device.
Upgrade or Consider a Second Router
While most modern routers provide plenty of bandwidth to support several simultaneous VoIP callers, an outdated router or overloaded local network can cause data-transmission issues like jitter, latency, or dropped calls.
If you support a call center with multiple agents simultaneously using VoIP–or other data-consuming activities like streaming, gaming, and video conferencing–consider adding a second router to reduce the bandwidth load on your current one.
Further, routers over three or four years old are generally considered outdated. If using one, ask your internet provider for a new router, or purchase one designed to support VoIP.
The best VoIP routers feature dual-band or tri-band technology, because these generally support high bandwidth demands and avoid network congestion.
Reset Your Router
One of the most common fixes for wireless connectivity issues is simply to restart your router. Similar to turning your computer on and off again, resetting your router will clear everything out and give it a fresh start.
You can reset most routers by pressing the round button near where you plug in the coaxial cable. Upon booting back up and reestablishing a connection, you may find your internet now works without any of the previous hiccups.
Adjust Your Router’s QoS Settings
Nearly all modern routers have a Quality of Service feature, which enables you to prioritize certain devices and types of data to receive bandwidth. For example, you can give preference to VoIP data and the computers or mobile devices that use VoIP.
When your network becomes congested, your router will ensure that VoIP data receives sufficient bandwidth.
Adjust QoS settings by logging into your router’s online account, clicking the Wireless tab, then clicking QoS Settings and Set Up QoS Settings.
Minimize Network Congestion to Reduce Packet Loss
VoIP calls rely on the constant back-and-forth stream of audio data packets between users.
This technology requires an internet connection, sufficient bandwidth, updated VoIP software, capable devices, and proper hardware. With a modern computer, cell phone, and router, your business should have all it needs to handle a VoIP call center and phone system.
However, if you begin to experience VoIP problems like jitter, latency, dropped calls, or one-way audio, the most likely issue is packet loss from insufficient bandwidth. Double-check by running a VoIP speed test, then try the troubleshooting steps outlined above.
FAQs
Below, we've answered the top FAQs about VoIP phone system problems.



