IVR menus provide callers with a self-service system that helps them reach the right business department, action, or information. While IVR systems usually assist inbound calls, IVR can also act proactively through outbound calls. This is called outbound IVR, a self-service technology that integrates with AI, automations, and call center routing
This article will cover outbound IVR in detail, discussing how it works, its benefits, and how it's different from inbound IVR.
- What is Outbound IVR?
- How Does it Work?
- Inbound vs Outbound IVR
- Benefits of Outbound IVR
- Outbound IVR Use Cases
What is Outbound IVR?
Outbound IVR is a phone system technology that makes outbound calls and presents the recipient with a self-service IVR menu. It includes audio messages and menu options that customers can navigate via speech or dial-tone selections to reach their destination: a live agent or queue, self-service action, or information.
Since outbound IVR proactively engages customers and leads, its use cases include interactive surveys, customer-support notifications, reminders, bulk announcements, sales and lead contact, and more.
While outbound IVR usually refers to phone calls via VoIP, outbound IVR may also refer to intelligent virtual agent (IVA) systems that contact customers via other communication channels.
Common Outbound IVR Communication Channels:
- Voice
- SMS texting
- Webchat
- Social media
- Website-based chatbot
- Mobile app
How Does Outbound IVR Work?
Outbound IVR works by connecting with a customer–via voice or a digital messaging channel–then providing interactive menu options for the customer to take action, route to an agent, input data, or access information.
Usually, outbound IVR contacts customers using an automated outbound system like an auto dialer or proactive messaging campaign. Once connected, the system distributes the IVR menu through the established communication channel. With each choice the customer makes, the IVR system gathers data and responds by moving through a predetermined IVR call flow or path, until the customer accomplishes a task–reaching an agent, inputting information, or receiving a message.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the outbound IVR process:
- Connects with the customer
- Customer engages IVR flow
- Gathers customer information
- Provides self-service
- Routes the call
Step 1: Connects with the Customer
To initiate outbound IVR, the phone system contacts the customer proactively–usually via voice, but sometimes via SMS, web chat, social media, email, or mobile app.
Most outbound IVR systems are integrated with outbound auto dialers, which automatically dial recipients based on a list pulled from a CRM system or database. The list can contain identified leads, customers who need help, or those with certain qualities. Some phone systems also allow you to set automated outbound calls based on certain triggers–such as sending a reminder two days before a customer’s appointment, or an announcement to customers who live in a certain area.
Choose your auto dialer type–predictive dialers, power dialers, progressive dialers, and preview dialers–depending on the number of agents your call center has, and how you’d like agents to be matched with call recipients.
If the auto dialer detects a busy signal or non-answer, it can hang up or “drop” a pre-recorded voicemail message. If a live recipient answers or responds via message, the system initiates the outbound IVR call flow.
Step 2: Customer Engages IVR Flow
Once connected with a customer, the outbound IVR initiates the predetermined call flow.
Call center and VoIP software enable administrators to create custom IVR call flows, usually using a drag-and-drop editor. The editor uses call trees to build layers of menu options–weaving together announcements, dial-tone menu options, routing, call queues, automated self-service actions, and conversational responses via natural language understanding (NLU).
When building an IVR call flow, administrators can input anticipated speech responses, dial-tone options, or buttons–each triggering automated responses that mimic interactive dialogue and move toward the IVR’s goal.
Step 3: Gather Customer Information
The IVR and phone-system software gathers information about the customer with every menu option they select.
Customers use the IVR to provide a wide variety of information:
- Language preferences
- Name and identification
- Account number
- PIN numbers and passwords
- Who they’d like to speak with
- Yes/No answers to custom questions
This information has a wide variety of purposes: It can build customer profiles, inform intelligent routing, give agents context, and help the IVR system progress the conversation.
Step 4: Provide Self-Service
In some cases, the IVR can handle the customer’s customer’s needs via built-in automations and self-service functions.
IVR systems can support a range of built-in capabilities:
- Pull information from a knowledge base
- Provide a canned response
- Password reset
- Book an appointment
- Provide customer account information
Depending on your call center software, you can embed this functionality into your IVR call flow through the drag-and-drop designer. When an IVR handles a customer’s needs without involving a live agent, this boosts call center containment.
Step 5: Route the Call
Sometimes the outbound IVR menu contains the call and handles all the customer’s needs using self-service automation. However, IVR can also route the call to a live agent, call queue, or operator.
Your automatic call distribution (ACD) system chooses where to route the call based on several variables: the caller’s menu choices, language preferences, agent skills, and agent availability. Using this information, the IVR system and auto attendant route the call to the optimal available agent, who takes over. The agent receives the IVR transcript and has full context, and the outbound IVR’s job is done.
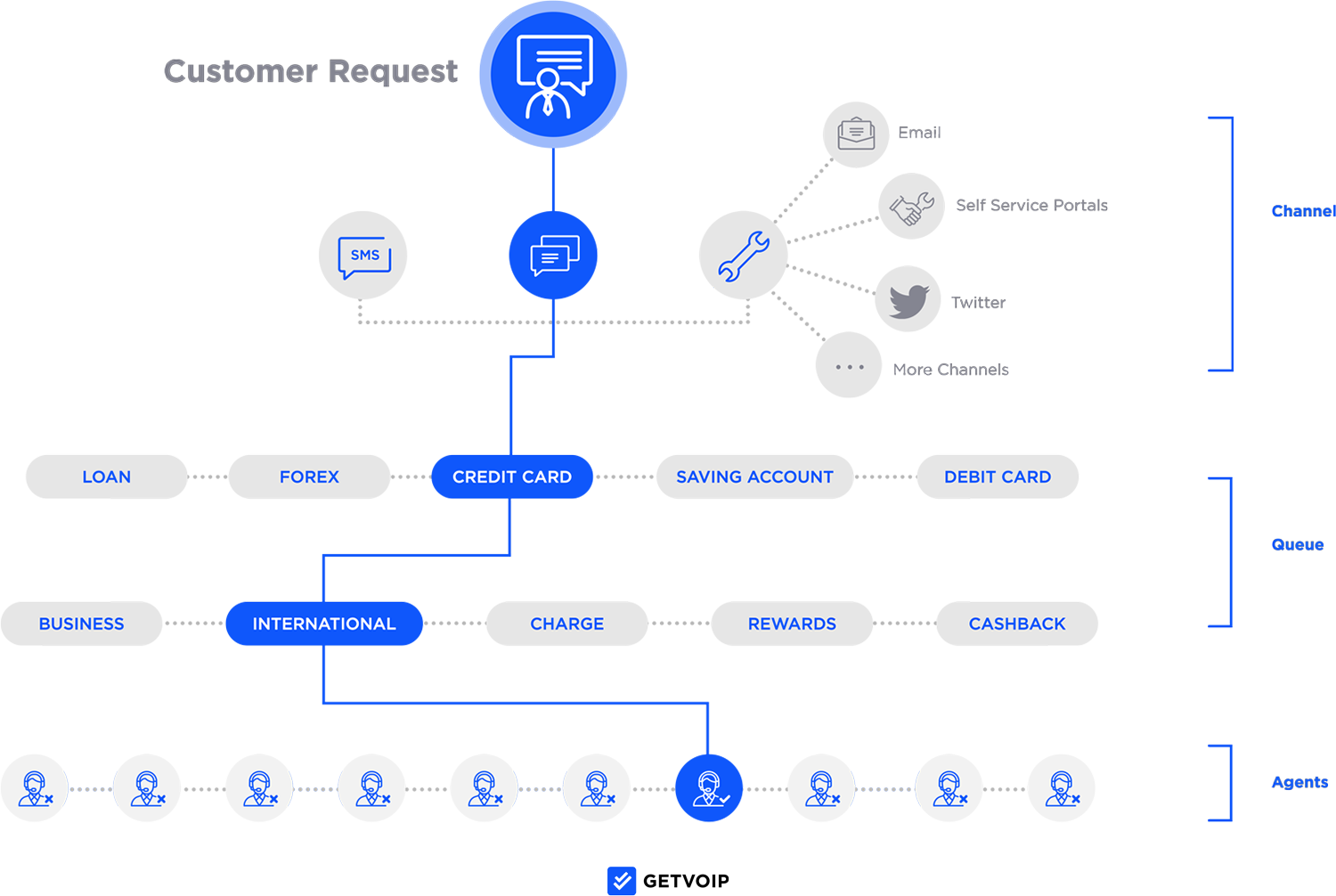
Inbound vs Outbound IVR
Inbound IVR serves incoming business calls, while outbound IVR connects through outgoing calls that your company initiated. While the IVR menu works the same in both cases, the IVR’s purpose and structure might change depending on your goal.
In general, inbound IVR focuses more on customer service and routing via auto attendant. Inbound callers typically seek information or support, so the primary goal of inbound IVR is to identify the caller’s needs and either give them information or route them to the best-fitting queue.
On the other hand, outbound IVR approaches customers with information they may not already know–such as product updates, appointment reminders, sales outreach, and lead follow-up. Therefore, outbound IVR menus emphasize interactive options like self-service, conversational responses, and yes/no questions. Although, outbound IVR typically still provides customers the option to speak with a live agent.
Benefits of Outbound IVR
Outbound IVR provides your company with a variety of benefits:
- Saves agent time
- Reduces costs
- Strengthens customer relationships
- Improves IVR Containment
Saves Agent Time
Outbound IVR automates several tasks that agents would otherwise handle manually: dialing customers, sharing announcements, gathering customer information, and providing services like answering questions or booking appointments.
With an automated outbound IVR menu, self-service, intelligent routing, and a well-designed IVR call flow–outbound IVR can handle all the activities that outbound sales and customer service agents would otherwise provide. Free from repetitive basic tasks, agents gain hours of extra time per week that they can devote to more complex customer-service tasks.
Reduces Costs
Since outbound IVR enables serving more customers with fewer agents, it enables your call center to cut down on staffing demands. Schedule outbound IVR calls or trigger them based on certain actions–like an upcoming customer appointment, emergency, or a product inventory change–providing around-the-clock service that doesn’t require your call center to be staffed 24/7.
While high-tier call center software can become pricy–averaging $100 monthly per user–it often ends up saving companies money by reducing staffing needs and converting a higher percentage of leads.
Strengthens Customer Relationships
Outbound IVR improves customer relationships because it allows you to proactively engage customers with automated, quick service.
When a company uses outbound IVR to contact customers with useful information–like appointment reminders, database updates, and emergency notifications–customers appreciate that your company considered reaching out to them, rather than waiting for customers to call in.
However, customers don’t appreciate the long wait times and draining interpersonal interactions that often characterize outbound calls. Since outbound IVR allows customers to resolve their issues quickly and often via self-service, customers appreciate the convenience.
Improves IVR Containment
IVR seeks to provide a quick and easy self-service option for your customers, but unfortunately, this isn’t how it always works out. IVR needs to be engaging so that your customers won’t simply press “0” or ask for a representative.
Unfortunately, this is where IVR tends to falter. Customers opt out of the system if it is confusing or difficult to get through.
Outbound IVR helps resolve this issue, increasing IVR containment thanks to automatic messaging. Your business can use this IVR to alert customers about promotions, bill payments, and as a means to qualify leads before an agent reaches out to them. Since outbound IVR is a much more focused style of IVR, the rates of call containment will be much higher.
Outbound IVR Use Cases
Compared with traditional IVR, outbound IVR offers several distinct use cases–especially when paired with other contact center technologies like auto-dialers, skills-based routing, and analytics.
Outbound IVR Use Cases:
- Sales and lead conversion
- Surveys and follow up
- Gathering customer data
- Bulk and automated notifications
- Emergency alerts
- Identity verification
Sales and Lead Conversion
When synced with an auto dialer, outbound IVR can dial phone numbers automatically from a list of leads or potential clients. When the recipient answers, the IVR call flow can introduce products, announce promotions, and give leads a chance to speak with a live agent.
This automation allows companies to filter hundreds of leads and potential sales, identifying those with the highest potential and routing them to live sales reps.
Surveys and Follow-Up
IVR call flows can prompt customers with yes-or-no questions and 1-5 rating scales using the phone dial pad. Similarly, app- and messaging-based IVA systems can display a scale with buttons from 1-10, allowing customers to evaluate business processes:
Example Outbound IVR Follow-up Questions:
- How satisfied are you with today’s service?
- Did you resolve your issue today?
- Did you find all the information you wanted?
Customer responses provide valuable data about service levels, customer satisfaction, and agent performance. Responses also provide feedback about your IVR call flow, including potential mistakes and customer friction points you hadn’t considered.
Gathering Customer Data
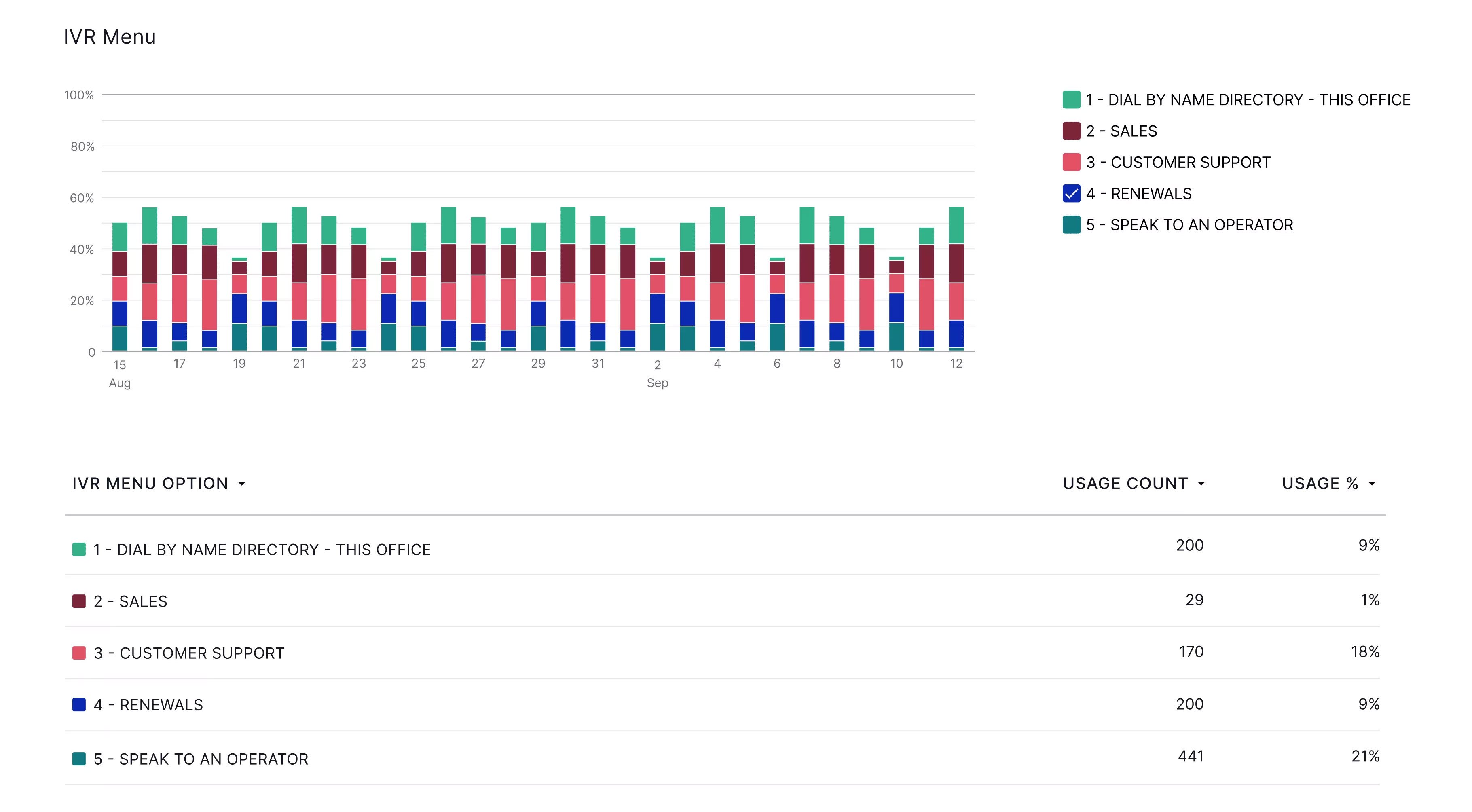
Call center analytics systems often include an IVR Report, which provides data about IVR menu functionality.
IVR insights include the following:
- IVR time: The average length of time a customer spends interacting with the IVR system
- Menu choice distribution: A breakdown of menu-choice popularity–the percentage of customers who picked each menu option
- Call center abandonment rate: The percentage of callers who resolved their issue using self-service, vs the percentage who hung up or routed to a live agent
- Queue routing statistics: Which queues customers most commonly reached when routed from the IVR menu
Further, analytics platforms track each customer’s individual journey–including their menu choices and interaction transcript, across voice and messaging channels. This information informs the customer journey history and gives agents fuller context when working with that customer.
Bulk and Automated Notifications
With virtual call center software, automate outbound IVR to contact customers based on preset triggers like upcoming appointments or inventory changes. You can create multiple IVR call flows and menus in the IVR designer, then link each one with distinct call-center triggers and actions.
Automate outbound IVR based on preset event triggers:
- Upcoming appointments
- Post-call surveys
- Inventory changes
- New product announcements
- Service deadline approaching
- Payment reminders
Integrate your call center with third-party software–like CRM systems and databases–so that an important event on another platform triggers the outbound contact. During significant events–like service outages or emergencies that affect your customers–initiate a bulk outbound IVR call to a list of affected customers.
Emergency Alerts
Outbound IVR can act as an emergency alert system, playing a message alerting customers to important news that affects their ability to use your product or service. For example, send outbound IVR contacts to notify customers about location closures, product recalls, and more.
The IVR call flow can enable customers to hear the message in multiple languages, with the option to speak with a representative if they have further questions.
Identity Verification
When a company is looking to reach out to a customer, outbound IVR can verify their identity before an agent gets involved.
The IVR system reaches out and the customer speaks or inputs their account information and social security for verification purposes. For those customers that don’t wish to speak their info aloud or use a DTMF Dialpad, the outbound IVR sends a visual IVR link that they can use from their smartphone or PC. All of these processes are completed without the need for agents to get involved, decreasing handle time and increasing agent efficiency.
Outbound IVR Automates Customer Outreach
Outbound IVR systems, with their strong self-service and customer engagement features, provide value for a modern contact center solution. They initiate customer contact and help customers get the most out of your product and service, in a way that’s more personalized than most robocalls–especially when integrated with a CRM system.
If you’re looking to bolster the performance of your call center, consider adding in outbound IVR functionality. When combined with call center software like predictive dialers, auto attendants, and standard IVR, your customer experience will improve.



