Intelligent virtual assistants automate text-based conversations that help users accomplish all sorts of tasks. IVAs assist companies too, as they gather data, integrate with third-party apps, and support call center agents with customer context.
Let’s get into detail about intelligent virtual assistant technology, discussing what it is, how it works, and how it can help your business.
What is an Intelligent Virtual Assistant (IVA)?
Intelligent virtual assistant (IVA) is an AI-powered conversational software that uses analytics and machine learning to converse with users and help them find information, take action, or complete a task. IVAs personalize conversations by gathering information from databases, customer histories, integrated apps, and previous interactions.
The technology employs natural language understanding (NLU) to interact naturally with customers across digital and voice channels, responding to a wider range of inputs, questions, and demands than a chatbot. IVAs can translate dialogue and communicate with users in multiple languages.
Companies integrate IVA into websites, apps, and dozens of communication channels:
- Webchat
- SMS
- Social media messaging
- Voice
The best-known examples of IVA include Apple's Siri, Amazon's Alexa, Google Assistant, and IBM's Watson, but many businesses use text-based intelligent virtual agent applications to enhance customer service.
Intelligent Virtual Assistant vs. Chatbot
Intelligent virtual assistants converse more naturally, understand a wider range of inputs, and offer more service capabilities than chatbots.
Chatbots rely on scripts and buttons for predetermined conversation paths, which restrict input options and responses. IVA systems are unscripted and construct each response based on a variety of factors: the customer’s input and history, previous conversations, and a variety of data. Virtual assistants continually learn and change depending on what they observe, adjusting their conversational style to improve communication with customers.
| Chatbot | Intelligent Virtual Assistant (IVA) |
| Rule-based structure that can handle straight-forward FAQ | AI can better interpret queries, leading to more specific answers |
| Robotic, formulaic answers | Language resembles human speech |
| Only able to understand specific inputs with no margin for error | Able to process queries with spelling errors, slang, grammatical mistakes, or confusing language |
| Uses auto-assigning routing logic to connect with agents | Routes users based on agent availability and context |
| Provides a small or limited number of services | Handles personalized services including data retrieval, bill payment, profile updates, and more |
How Do Intelligent Virtual Assistants Work?
Intelligent virtual assistants process a user’s text or speech input, identify keywords and intent, and then use integrated software to provide an answer or take action.
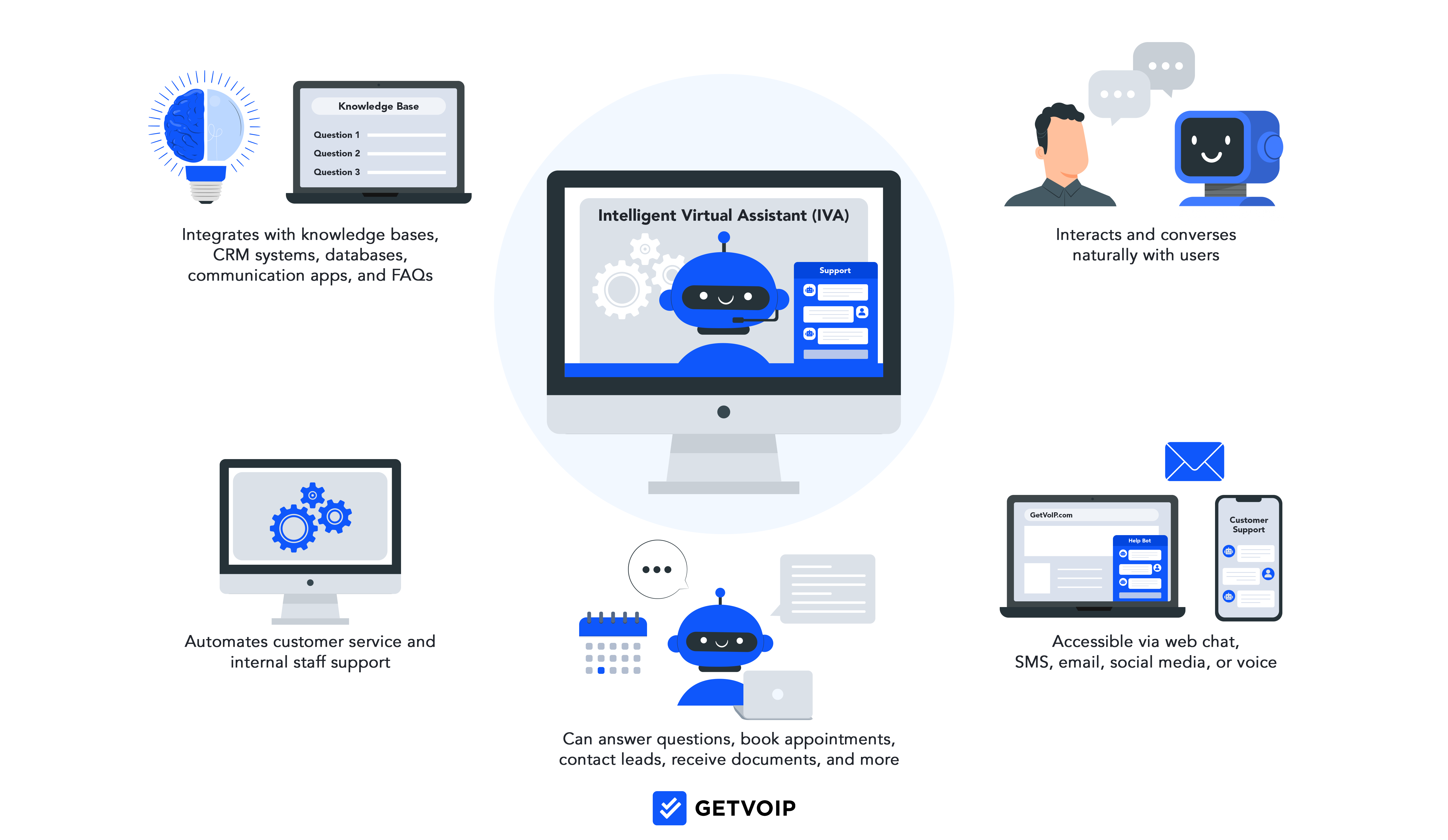
1. Process a User’s Text or Speech Input
When the user engages with an IVA via text or speech, the virtual assistant uses natural language understanding (NLU) to interpret and transcribe the input, in order to understand it. This interaction may occur on a company’s website or app, an employee portal, SMS text, phone, or app-embedded voice conversation.
NLU, a critical technology in IVA, aims to understand a wide variety of human inputs. NLU organizes unstructured, raw requests into data, queries, or topics the software can address. Advanced IVA software can translate inputs from multiple languages, dialects, and speech styles.
2. Identify Keywords and Intent
Once the virtual assistant’s NLU transcribes the user's input, it determines their intent using a few indicators: keyword, topic, sentiment, user, date, and other factors.
Depending on the types of intent you’ve trained your IVA to recognize, it identifies keywords from the user’s input in order to interface with backend databases, knowledge bases, and other integrated software. The IVA can also draw from other support tickets and the customer’s history to identify their intent.
Example: Your customer enters the query “I want to book an appointment tomorrow.” The NLU detects the keywords “book,” “appointment”, and “tomorrow.” The machine can enter these requests into an integrated appointment-booking software and take action, based on what the customer entered. If the customer’s input is incomplete and the system needs more data, it can follow up with a question such as “What is the reason for your appointment?”
3. Use Integrated Software to Provide an Answer or Take Action
The IVA inputs detected keywords, topics, or requests into your connected systems–databases and inventories, appointment-booking software, knowledge bases, CRM systems and customer profile information, ticketing systems, and more.
The IVA system then takes action. Depending on the query, it might book an appointment, share information from a knowledge base article, provide a customer’s account balance, or route the user to a relevant agent.
Benefits of an IVA for Customer Service
The main benefits of an intelligent virtual agent (IVA) are:
- Personalized customer experience
- Reduced wait times
- Around-the-clock service
- Improved agent efficiency
- Lower business costs
- Business insights
Personalized Customer Experience
Intelligent virtual assistants use context and customer information to individualize service. NLU enables virtual assistants to understand customers across channels, speech styles, and languages.
Once the IVA detects a customer’s intent, it can draw from CRM data like purchase history and location to offer personalized solutions and routing options. Since the software can translate language and scan hundreds of integrated data points in moments, it provides more personalized feedback than chatbots or live agents.
Reduced Wait Times
Intelligent virtual assistants can serve hundreds of customers simultaneously, resolving tickets without human support. Since users and customers no longer have to wait for live assistance to handle simple queries, they get in and out much faster and lower average handle time.
IVA instantly completes time-consuming tasks like language translation, data searching, typing, inputting data and requests, and updating customer records across linked accounts.
IVA can handle the following simple tasks with minimal wait time:
- Answering questions using a knowledge base
- Updating or checking personal information
- Taking simple actions like booking an appointment, processing an order, or emailing a password reset link
- Paying a bill
- Submitting materials and files
- Troubleshooting potential product or software issues
Around the Clock Service
Although self-service is helpful, users become frustrated when they can’t reach a live agent to resolve their query. Many customer-support centers only staff agents during local workday hours. This alienates customers in different time zones or who need help outside of this window.
An intelligent virtual assistant resolves customer issues around the clock, keeping users happier and preventing agents from feeling overwhelmed when they begin their shifts.
Improved Agent Efficiency
Businesses have continually sought call center solutions that decrease the burden on live agents while still providing strong customer service. Intelligent virtual agents help these businesses deflect customers from using VoIP phone, email, and live chat channels in lieu of artificial assistants. They can take over and handle customer requests, only involving live support when necessary.
This ensures that live agents focus their efforts and time on unique or urgent cases that require a personal touch.
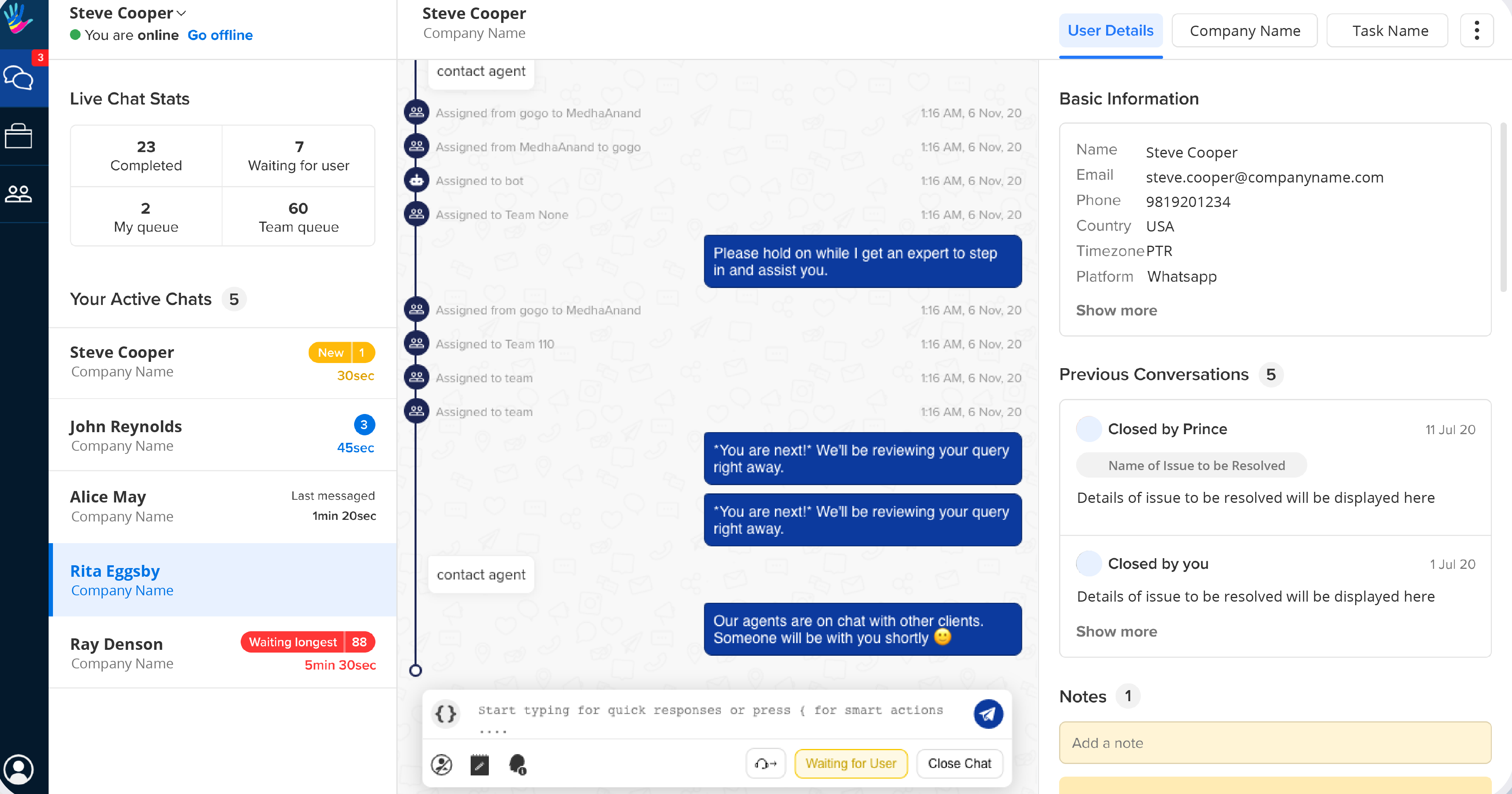
Lower Business Costs
While IVA software requires an upfront investment to pay for the software, it can ultimately reduce business expenses by trimming staffing needs and improving customer satisfaction. Virtual assistants provide round-the-clock support and handle various queries–including IT support, onboarding, routing, and answering questions–lowering the number of required live agents.
Business Insights
Advanced IVA systems track customer data like popular intents, keywords, sentiments, routing behaviors, and paths. Some software identifies trends in the data, displaying the information visually or organizing it in reports. These analytics can help administrators better understand customers and users and refine customer service strategies.
Intelligent Virtual Assistant Use Cases
Companies utilize intelligent virtual assistants for many use cases, including:
- Customer support
- Human resources and internal communications
- Talent acquisition and recruiting
- Sales and marketing
- Information technology (IT)
- Data gathering
Customer Support
Intelligent virtual agents engage directly with customers to handle many types of queries and tickets. The machine’s AI can provide account information, facilitate purchases and order returns, make product recommendations, answer questions, and route customers to agents.
The following IVA features provide strong customer support:
- Multichannel: AI can engage with customers via chat, email, SMS, social media, and voice
- Multilingual: Advanced IVA software can converse with customers in dozens of languages, providing broader and more personalized real-time interactions than human agents
- CRM integrations: Linking with CRM platforms like Salesforce and HubSpot, IVA technology can draw upon a customer’s individual context and history to provide customized support
Human Resources and Internal Communications
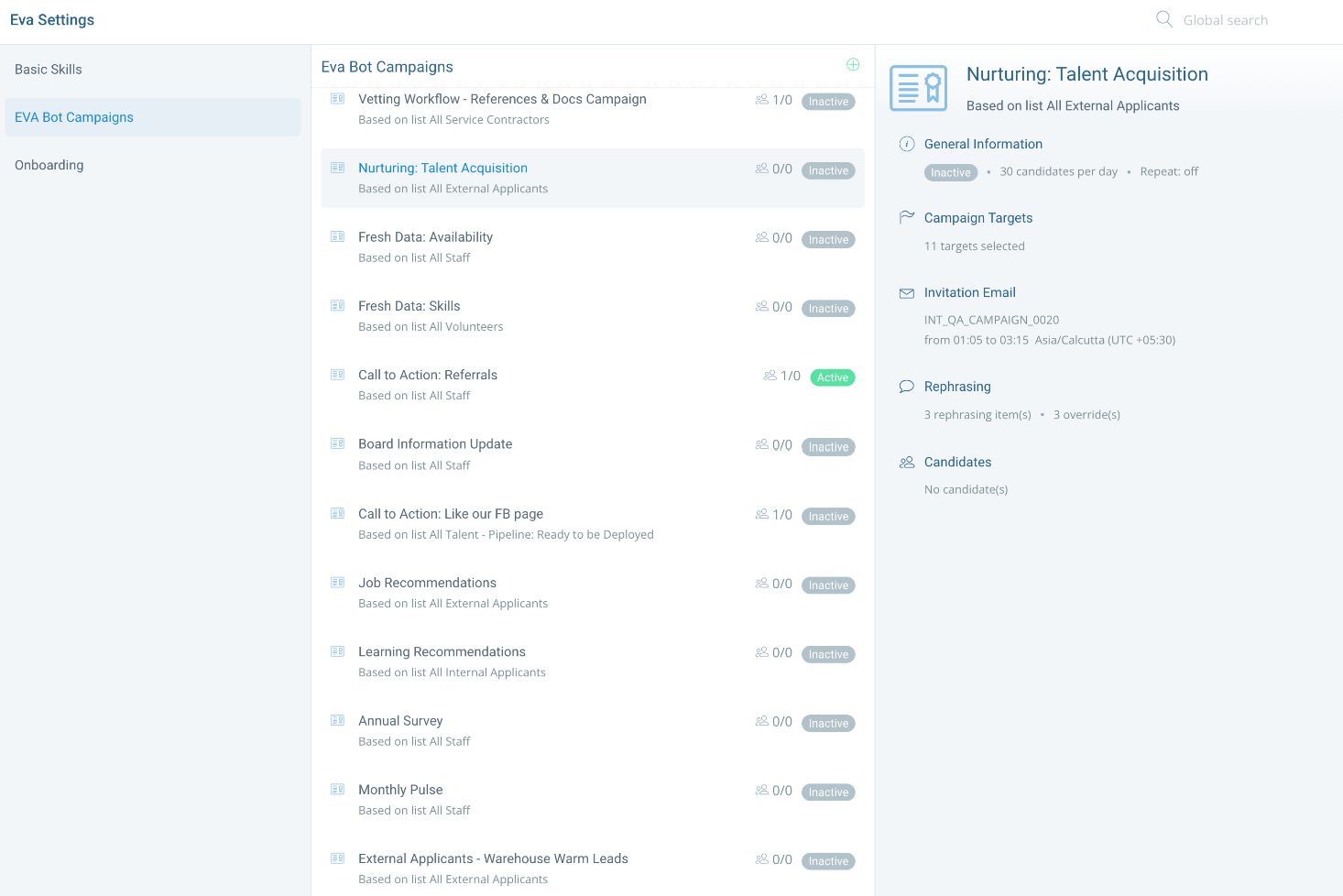
Companies use IVA to support internal employees and new staff in multiple ways:
- Onboarding: Integrate virtual agent campaigns with onboarding and training modules for new staff, with the machine able to answer questions.
- Employee benefits: IVA can update employee benefit information and provide employees with their benefit information
- Scheduling: Integrate NLU with scheduling software, enabling virtual agents to help employees request time off, retrieve schedules, and more
- Policy inquiries: Link IVR with a policy knowledge base to handle internal inquiries
Talent Acquisition and Recruiting
An IVA system can support talent acquisition and recruiting efforts in several ways:
- Accepting applications: Accept and organize application materials like resumes, ID information, and more
- Applicant information: Gain information and update application profiles
- Recommendations: Provide custom job recommendations based on a user’s information
Sales and Marketing
Virtual assistants augment outbound sales, marketing, and lead-qualification efforts through digital channels like SMS, web chat, and email. Integrating with your CRM system and marketing platform, IVAs personalize conversation based on the prospect’s lead status and stage in the marketing pipeline.
IVAs support sales in the following ways:
- Lead follow-up: Immediately engage with new or neglected leads
- Lead qualification: Use keywords and sentiment analysis to qualify leads and their intents
- Contact cold leads: Follow up with leads that have become dormant
- Routing to sales reps: Identify when a lead is close to buying, to connect them with a live sales agent
Information Technology (IT)
Companies use IVA for internal IT use cases, helping staff troubleshoot and fix tech issues.
Here are some ways IVA supports a company’s IT efforts:
- Identify account issues: Integrate with company-wide software tools to identify device and software issues and provide fixes
- Prompt for more information: Ask users for more details, to gain a fuller picture of the IT issue
- Provision software: Administer software programs to staff members
- Manage tickets: Receive, tag, solve, or route a company’s inbound IT tickets
Data Gathering
IVA systems support the company’s administrators with data tracking tools that identify trends and patterns for usage, sentiment, topic and more. This data provides valuable insights into users’ behaviors, friction points, and interests.
IVA Data Use Cases:
- Identify common issues, trends, and topics: Sort this information over historical time frames to better understand users
- Customer sentiment: Analyze transcripts and keywords to score customer sentiment and satisfaction scores
- Track progress toward goals: Monitor progress toward sales and customer service goals and benchmarks
- Categorize users: Tag and sort users based on particular data or qualities
How to Implement an Intelligent Virtual Assistant
Here are the steps to implement a virtual assistant:
- Determine who you want to serve (and how)
- Decide the channels for your IVA
- Select an IVA software
- Integrate software: actions, knowledge base, FAQs
- Design a conversation flow
- Test and edit your IVA
- Monitor data
Step 1: Determine Who You Want to Serve (and How)
Before designing your IVA, determine its purpose and who it will serve. Determine if you want to serve internal staff or customers, pre-existing customers or leads, and so on.
- If serving an internal team, consider how you want to support staff. Do agents need real-time coaching, or does the team need a resource for HR needs like billing or scheduling?
- If customer-facing, identify who you plan to help and the support they may need. Do you want to reach your leads for marketing purposes, or provide customer service or technical support?
Step 2: Decide the Channels for your IVA
Decide the channel(s) you’ll use for your IVA. Website-embedded chat is the most popular IVA channel for customer support because it’s easy for users to access whenever they visit your website. However, email works well for marketing and customer-support use cases, and SMS is effective in automating delivery and appointment booking services.
Popular IVA channels include:
- Web chat
- SMS
- Voice
- Social media messaging
Step 3: Select an IVA Software
Choose which software provider you’ll use for your IVA. Many call center solutions and UCaaS platforms support IVA as a built-in feature, including the tools you need to build and implement a virtual agent on multiple channels.
If you don’t have a solution with built-in IVA, there are dozens of software providers who offer monthly subscriptions for advanced IVA technology. Each provider specializes in particular use cases, so compare them to see which one meets your needs.
Step 4: Integrate Software: Actions, Knowledge Base, FAQs
To begin training your IVA on how to interact with and support customers, integrate it with relevant third-party applications. Each IVA software supports dozens of integrations, which you can sync in just a few clicks in your bot’s setup menu.
Popular IVA Integrations:
- Knowledge base: Knowledge integrations support your IVA with a bank of common search terms, answers to questions, and material to pull from when serving customers
- FAQs: Entering FAQs prepares your IVR for the most common terms and queries it might face
- CRM: CRM integrations like HubSpot and Salesforce give your IVA access to information about each contact, lead, and customer. IVAs can customize responses based on the user’s recent purchases, journey history, sentiment scores, and other information
- Ticketing software: Service desk integrations like Zendesk and ServiceNow automatically populate and tag tickets based on IVA interactions
- Task management: Task management integrations like Asana, Jira, and Microsoft Teams enable your IVA to create and sync tasks and notify users of activity
- Inventory databases: Connect your IVA to databases and payment platforms like Shopify and Stripe, enabling your IVA to facilitate orders and payments
Step 5: Design a Conversation Flow
Use your IVA software’s conversation designer tool to build a step-by-step flow for various processes. Many IVA design tools include drag-and-drop flow editors, and some enable you to create a “storyboard” that outlines a sequence of steps your user might take. In most cases, you can create multiple different flows, each with a unique sequence of actions and results, depending on the customer’s inputs.
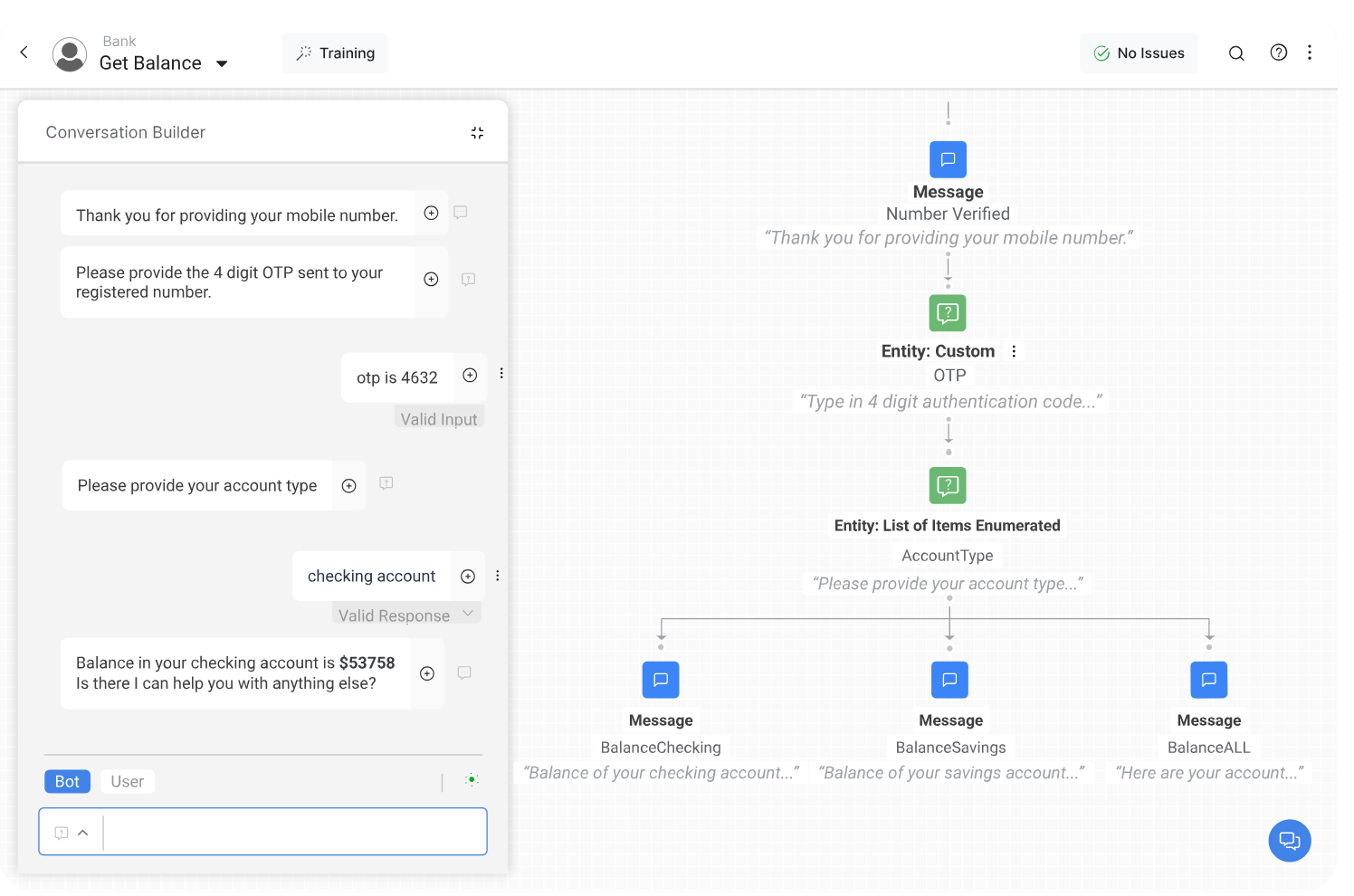
Step 6: Test and Edit Your IVA
Once you’ve created an IVA conversation flow, have a few users test it for different purposes. Notice any frustration points or errors, and return to the editor to fix the issues to add new functionality.
Step 7: Monitor Data
As customers interact with your IVR over time, track your data to see what needs adjusting. Monitor frequently mentioned topics and phrases, to make sure you have conversation paths and actions to meet your customers’ most prominent needs. If users frequently opt out of the IVA and route to live agents for particular reasons, try to add IVA functionality to meet that need.
FAQs
Below, we've answered some questions about intelligent virtual assistants.



