An effective call flow strategy improves the customer experience by clearly guiding callers through each step of the customer journey and providing 24/7 customer self-service. IVR call flows also streamline operations, reduce call center agents stress, and cut down on extended wait times.
But what is the call flow process, and how can you ensure your call flows meet business needs without sacrificing fast and efficient customer service?
This article explains the components of a proper call flow, how to build them, and how to leverage them to take your contact center to the next level.
What is a Call Flow?
A call flow is a customized, company-designed call path dictating how incoming calls are handled and distributed.
Call flows automatically manage every stage of a phone call, from initial greeting message to post-call documentation. When properly implemented, call flows provide a consistent customer experience, speed up the resolution process, and ensure customer service calls are efficiently distributed to the best available agents.
Call flows are mainly used in contact centers to improve the inbound call management system, automate the call routing process, reduce call hold times, and keep more live agents free. Some businesses also have outbound call flows that include voicemail drops, pre-recorded scripts, and automated post-call management.
Why is a Call Flow Important?
A contact center call flow is important because it establishes a consistent communication strategy, manages high call volumes, and eliminates customer frustrations like long hold times, multiple call transfers, and connecting to unprepared agents.
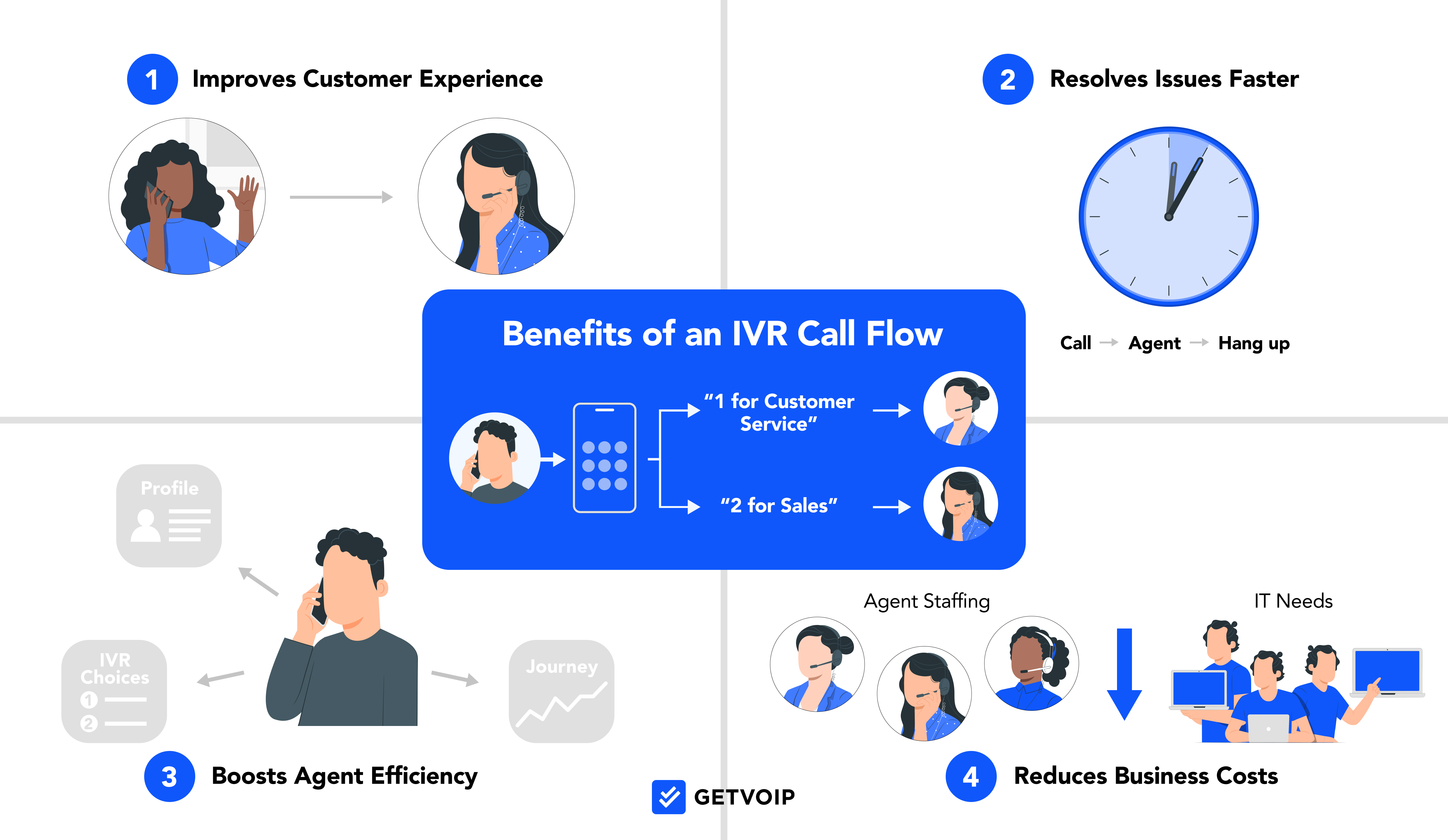
These inefficiencies will not only lead to abandoned calls and poor customer service ratings, but also to agent burnout, lost revenue, and higher communication costs.
Key benefits of effective call flows include:
-
- Personalized Customer Service: Creates a bespoke experience by connecting customers to the agent best suited to help them with their specific issue
- Faster Resolution Times: Improves First Call Resolution (FCR) rates and decreases Average Handle Time by automatically pairing callers with the ideal agent and automatically adjusting call paths according to time of day, employee schedules, and custom routing rules
- Better Employee Retention: Reduces call center agents’ manual tasks by automatically triaging calls, updating CRM data, and entirely managing minor customer service issues, leading to less agent frustration, job satisfaction, and more time to hone specialized skills
- Agent Performance Evaluation: Key metrics from call flows show supervisors which agents are hitting KPI goals, identifying opportunities for improvement, and providing real-time call monitoring for in-call troubleshooting
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Shorter wait times, faster resolutions, happier agents, and being connected to the right person all lead to better customer service
Key Components of a Call Flow
Key call flow components are:
- Welcome Greeting
- Authentication
- Call Routing and IVR
- Queue Management
- Escalation
- Post-Call Documentation
Welcome Greeting
The welcome greeting is the pre-recorded announcement that automatically plays when customers call your business phone number. It usually contains call menu prompts and basic business information like location and hours. As first impressions are important, keep welcome greetings short, friendly, uncomplicated, and in line with your company’s core values.
Authentication
In some situations, callers will need to be authenticated. For example, if the call center is only accepting calls from current customers, part of the call flow may include asking the caller for an ID and PIN, and then verifying them against a customer database.
Several call flow designers include an authentication component that automatically asks for an ID and PIN, and then performs validation via Web Service REST.
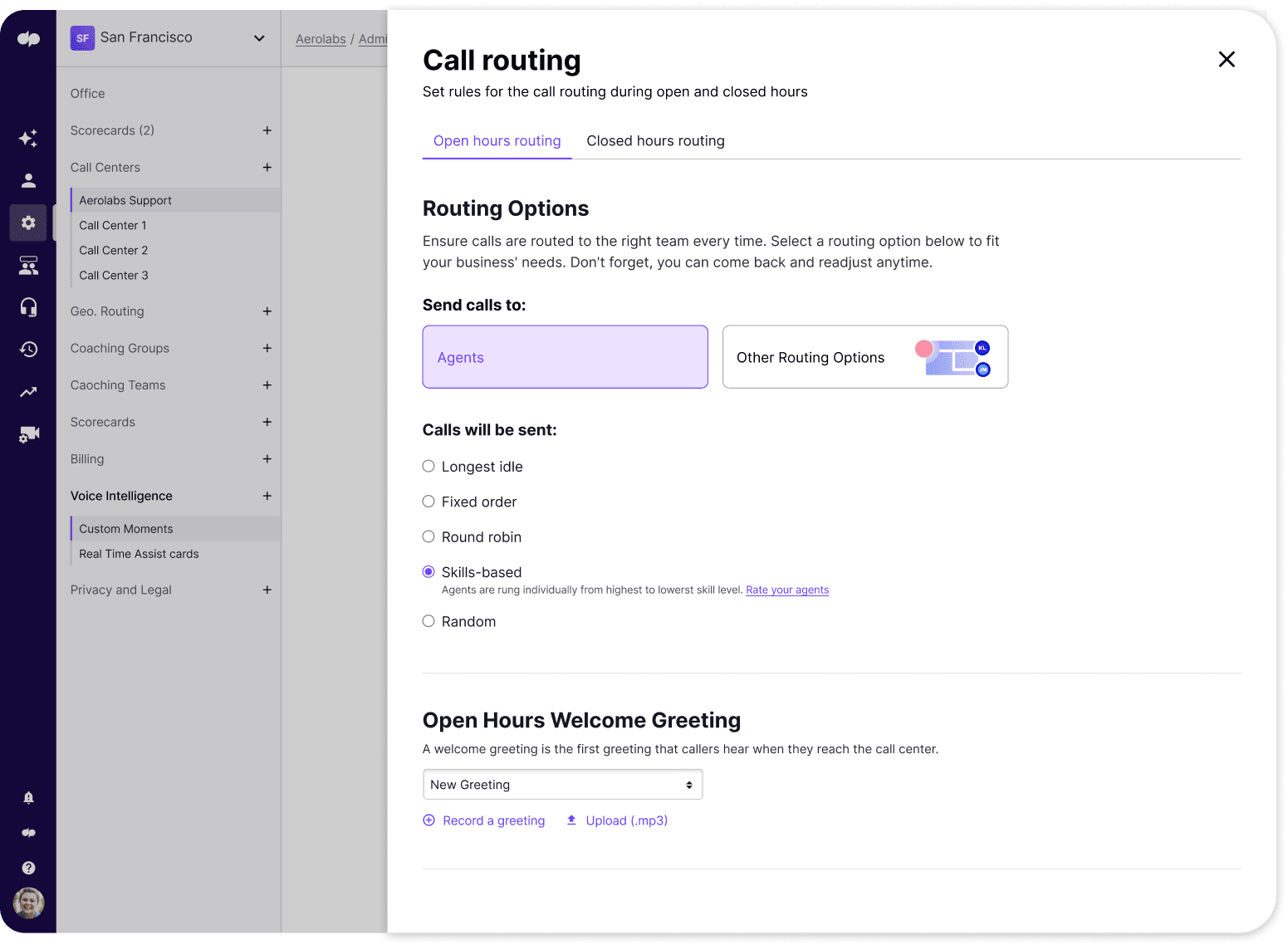
Call Routing and IVR
Once the caller has been welcomed and validated, the Interactive Voice Response (IVR) system plays pre-recorded prompts that determine the purpose of the call and collect the essential customer information needed to route the call to the ideal agent.
Once the caller responds to these automated menu prompts via dial pad touch tone or speech, the IVR system uses Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) to initiate the call flow process. The caller may be directly connected to an agent, transferred to a call queue, given self-service options, forwarded to an external phone number, routed to a ring group, disconnected, or sent to voicemail.
Common call routing rules include:
- Fixed Order: Calls are transferred to the first available agent on a list, and the list starts over again after every call
- Skills-Based: Calls are directed to agents with the appropriate skills to address the caller’s issue
- Rotary/Round Robin: Calls are assigned to agents on a rotating basis
- Percentage-Based: The company allocates a certain percentage of calls to a predetermined department
- Most Idle: Calls are transferred to the agent with the lowest talk time
- Time-Based/Business Hour Routing: Calls are forwarded to agents according to business hours, agent schedules, or a specified time of day
- Language-Based: Ideal for international teams, callers are routed to agents that speak their native language
- Relationship-Based or VIP Routing: Calls are sent to specific ring groups, queues, or agents based on pre-established business relationships or account value
- Intelligent Call Routing: Uses AI, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and sentiment analysis to direct calls or provide self-service IVR to entirely automate support interactions
Queue Management
Queue management is the call queueing process businesses follow–and continually improve–to keep call hold times within a healthy statistical range or outperform industry standards.
There are several ways to manage queue times, including:
- Offering automated callbacks
- Displaying call center queue metrics to agents in real-time via wallboards
- Utilizing call recording and playlists to train live agents
- Leveraging live call coaching features (call barge, call whisper, etc.)
- Have managers and agents test queues before taking calls
- Send customers surveys and analyze feedback
Escalation
Building an escalation matrix into the call flow can help agents achieve faster resolution times while easing customer frustration.
Escalation is a conditional component of a call flow that only comes into play if a customer has been on the line for a certain amount of time without a resolution, or if a specific predetermined issue has been brought up.
Types of call escalation include:
- Hierarchical: Calls are escalated to another agent with more seniority or experience with the specific issue
- Functional: Calls are escalated to an agent with a more relevant skill set
- Priority: Calls are escalated based on the urgency of the issue
- Automatic: Calls are automatically escalated if a resolution has not been reached in a specified amount of time
Post-Call Documentation
At the end of the call, after call work (ACW) is required.
After-Call Work includes:
- Logging calls
- Preparing call summaries and recaps
- Escalating issues
- Updating another department on follow-up actions
- Updating customer information on CRM software
Many phone systems include automation functionality, enabling users to build post-call wrap up automations and integrate them right into the call flow.
How to Create an Effective Call Flow
Most CCaaS providers include editable, drag-and-drop call flow builders and pre-made templates on their platforms.
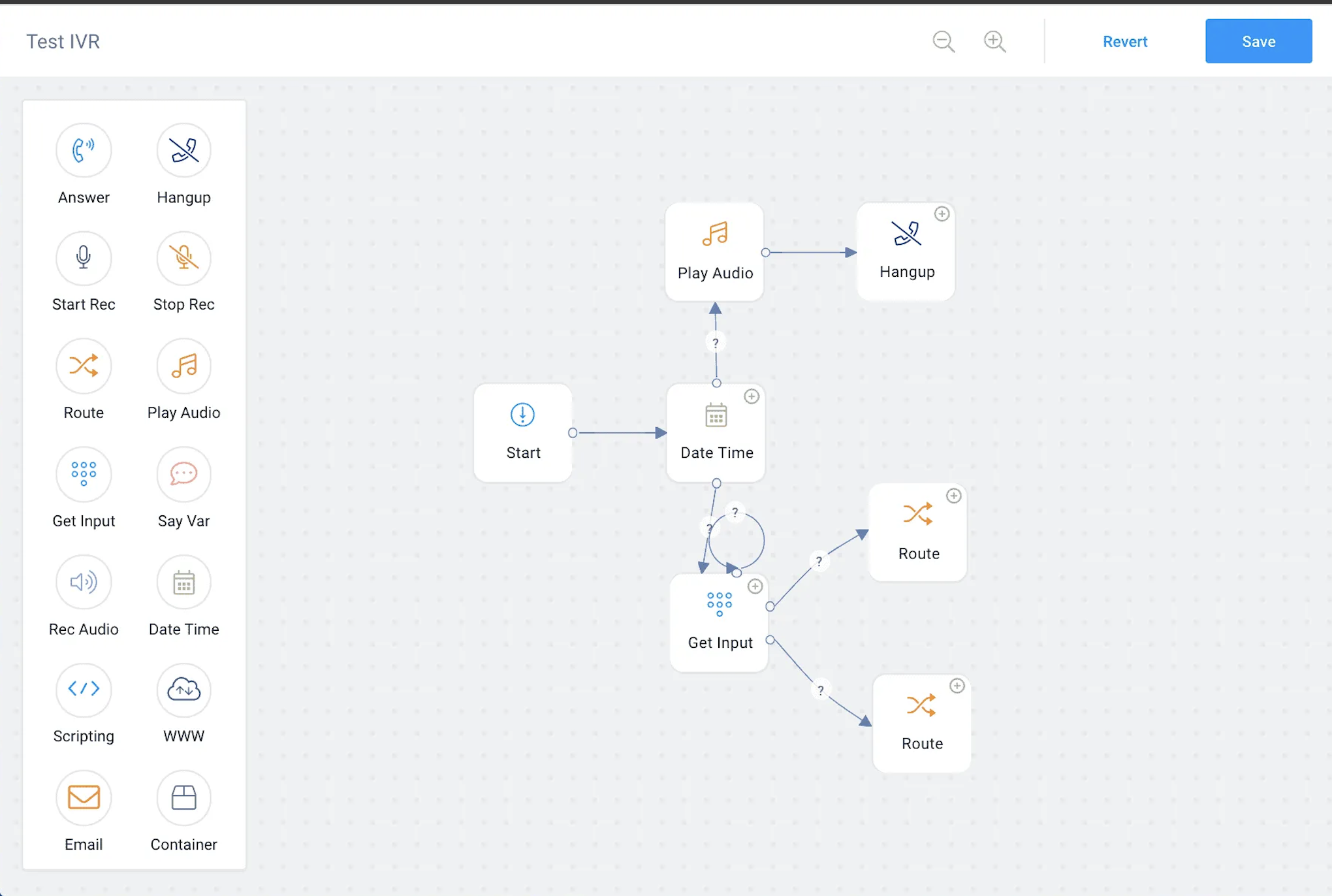
Features such as interactive voice response (IVR), call routing, call scripts, CRM and knowledge base integration, and analytics further optimize call center call flows.
Although the specifics on creating a call will vary amongst providers, here are the basic steps to creating a call flow:
- Step 1: Create a name for your call flow to distinguish it from other call flows
- Step 2: Use text-to-speech or upload a recording to add a call greeting/welcome message
- Step 3: Create your IVR menu to determine call menu options by uploading audio file prompts that explain menu options and instruct callers who to dial if there’s an invalid option or timeout
- Step 4: Set up rules to govern how calls will be handled. For each menu option chosen, you can select ring duration, whether the call will afterward be transferred to a department, agent, outside phone number, or voicemail box, and more
- Step 5: Determine how post-call documentation will be handled and train agents
How to Optimize a Call Flow
Tips for optimizing call flows using contact center software include:
- Update Call Flows Regularly: As your company grows, you can make real-time, automatic, or post-call edits to the call flow based on insight from analytics and customer survey responses, new product launches, sudden customer issues, changes in personnel, etc.
- Implement Omnichannel Customer Support: While call flows help reduce call hold and call wait times, implementing additional communication channels such as SMS, email, and social media decreases agent workloads, shows omnichannel communication history, and lets customers choose how they connect with your business
- Integrate CRM Software: CRM integrations give agents full contextual information and past interaction history for each customer or prospect they’re talking to, leading to better customer service and faster resolutions
- Leverage Analytics: Contact center reporting and analytics tools offer deep insights into how current call flow path effectiveness and the most popular IVR options, ensuring admins can continuously optimize call flow experience and route calls more efficiently
Call Flow FAQs
Below, we've answered the top Call Flow FAQs.



