Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP) provides crystal-clear HD audio by transmitting data packets from caller to recipient.
Fundamentally, VoIP works by breaking down vocal sounds and audio into smaller data packets that travel over the Internet and reassemble at the destination.
Usually, these packet transmissions are sent without a hitch.
However, when traveling over the Internet, there’s always a chance these data packets can get lost or degraded.
Minimizing this loss is crucial, as it results in miscommunication and frustration that damage customer experience and the business’s reputation. Worse still, when Unified Communications (UC) software experiences high packet loss, it can lead to reduced security, faulty file transfers, and increased jitter.
Read on to learn how to fix packet loss by identifying common causes and solutions to the issue.
- What is Packet Loss?
- How to Fix Packet Loss
- What Causes Packet Loss?
- How to Detect Packet Loss
- Tools to Fix Packet Loss
What is Packet Loss?
Packet loss is when data packets fail to successfully transmit over the Internet from sender to receiver. In VoIP, lost packets delay communication, create garbled sounds, and can even scramble and reorder parts of the conversation.
IT professionals consider 1-2% of packet loss as an “acceptable rate” for VoIP, as such low levels shouldn’t affect SIP or hosted PBX call quality.
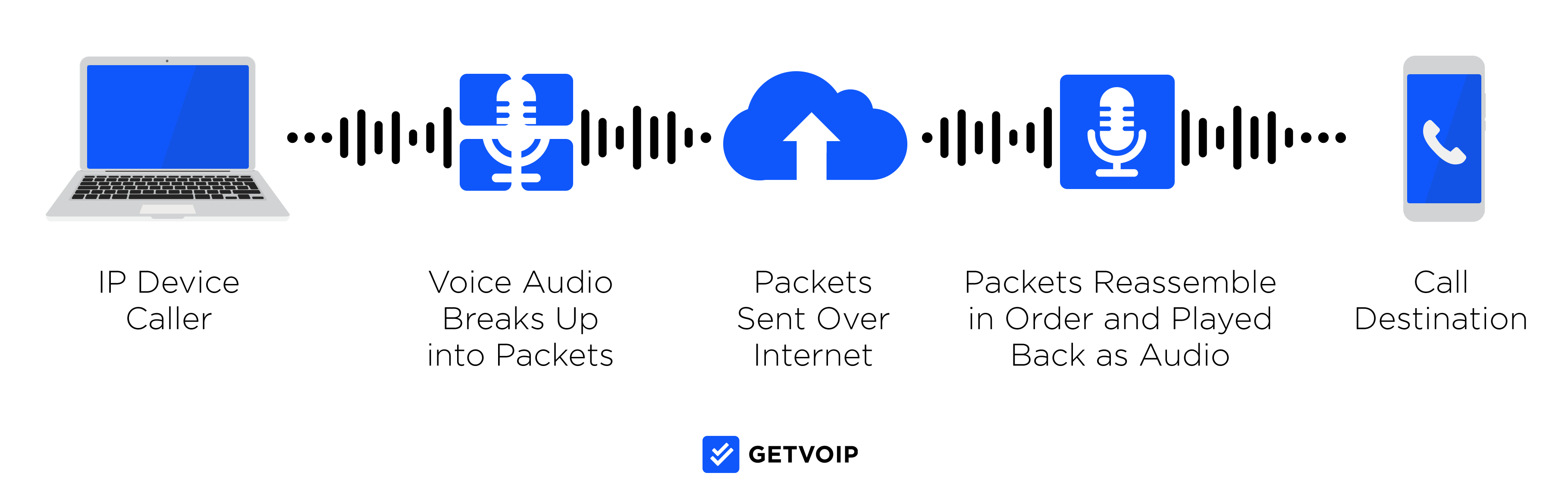
What are Data Packets?
Technically, everything you send over the Internet is a data packet–emails, voice communication, video calls, and more.
Calls from VoIP phone systems begin as recorded sounds. These sounds are broken up into smaller, more manageable pieces of data and transmitted over the Internet as packets. These packets are usually encrypted and reduced in size to ensure faster transfers.
When the information is sent, it automatically detects and travels via the most efficient path. Sometimes, however, the information does not make it to the intended destination successfully.
The further the data must travel, the higher the chance of errors during the transmittal.
How To Fix Packet Loss in Six Steps or Less
Use the following 6 steps to troubleshoot packet loss:
- Examine Physical Connections
- Check For Software Updates
- Upgrade Your Hardware
- Check Your Wi-Fi Connection
- Address Bandwidth Congestion
- Address Network Security Vulnerabilities or Attacks
1. Examine Physical Connections
First, make sure your Ethernet cord is physically plugged into your router, and that visible cables are properly and completely inserted into their corresponding ports. Replace worn-out cables to establish a clearer connection path.
When purchasing future Ethernet cables:
- Choose the proper category of wire. A Cat 5 is typically strong enough for a small business, but if using more than a 1 Mbps Internet connection, you'll need a higher category.
- Check the jacket on the wire for durability that won’t easily abrade
- If running several cables together, use a cable shield to prevent signal interference
2. Check For Software Updates
When software hasn’t been recently updated, it can inefficiently consume data, causing packet loss and other performance issues.
Keep all software updated, especially VoIP and UCaaS applications. After the update, restart the application and reboot your hardware.
If the software still has known bugs, you may have to wait for the development team to release a solution to the issue. If there’s no immediate fix, consider an alternative software solution that doesn’t cause packet loss.
3. Upgrade Your Hardware
Outdated hardware–including routers, switches, computers, and phones–causes packet loss, so make sure you’re working with new equipment whenever possible.
Most modern routers provide sufficient bandwidth speeds for multiple simultaneous VoIP users, but we recommend updating your VoIP network router at least every 3-5 years. You’ll know it’s time to upgrade your hardware when it consistently malfunctions, displays “error” messages, suddenly shuts down, or just stops working as normal.
Having a dedicated IT team to keep up with server and VoIP hardware minimizes packet loss.
4. Check Your Wi-Fi Connection
A weak Wi-Fi connection may be the reason for packet loss. If your signal is lacking or dropping out, reset the router or the device to see if it gets stronger. Move your device closer to the router, aiming for no obstacles in between.
If needed, set your device to access another Wi-Fi network or, preferably, use a wired connection instead.
5. Address Bandwidth Congestion
Bandwidth congestion occurs when your local network has more data traffic than it can handle, slowing transmission speeds. This frequently occurs when too many users simultaneously engage in data-heavy activities on the same network.
Activities that consume a lot of data:
- VoIP calls
- Video conferencing
- Streaming video
- Gaming
If you have multiple users sharing a router or local network, alleviate network congestion by reducing the number of users simultaneously engaging in these activities. If needed, ask those using mobile devices to use cellular data, or add another router to support the heavy data consumption.
6. Address Network Security Vulnerabilities or Attacks
Network attacks and hacking can cause packet loss and other serious issues.
If you suspect an attack, inspect IP logs for unfamiliar addresses or traffic flooding on the network. Block these IP addresses to stop the attack and allow the traffic on the network to return to normal.
In most cases, it’s best to get a professional involved when privacy and security are at stake. They can also help you to address security vulnerabilities to prevent future attacks.
What Causes Packet Loss?
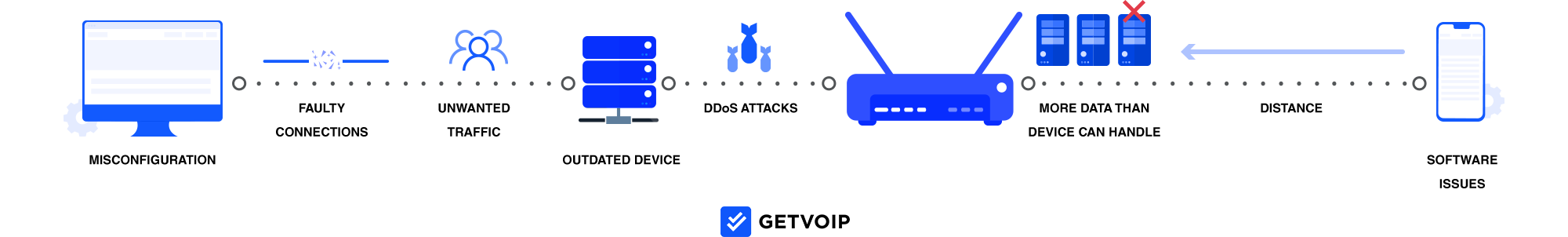
Below are the six most common causes of packet loss:
- Bandwidth Congestion
- Faulty Networking Wires
- Faulty or Insufficient Hardware
- Software Issues
- Wi-Fi Networks
- Network Attacks
1. Bandwidth Congestion
Bandwidth congestion, or network congestion, is the reduction in VoIP call quality and overall speed of transmission that occurs when your Internet bandwidth can’t handle the amount of current data it’s asked to process.
Think of it as a digital traffic jam during the busiest time of the day.
Your data experiences delays getting to its intended destination because heavy traffic causes some information packets to be left behind so the network can “catch up.”
Typically, these packets will automatically resurface when the network congestion decreases, but sometimes the packets can permanently be lost in the shuffle.
How to Detect It: A network with a high amount of congestion experiences high latency, increased jitter, and higher-than-normal packet loss rates. Use an Internet speed test to make sure your latency and jitter are below 150 and 30 ms, respectively. If your latency and jitter measure significantly higher than these levels, you might have too many users engaging in high-bandwidth activity simultaneously on your network.
2. Faulty Networking Wires
If you’re working on a wired network, damaged Ethernet cables can cause packet loss.
These physical wires handle a lot of traffic. If they have deteriorated, data can’t be efficiently sent, leading to packet loss. Damaged or improperly connected cables increase the electrical signals that travel along with the data you’re sending, compounding the issue.
Dirty fiber connectors are also a significant source of packet loss.
How to Detect It: Physically check your cables thoroughly and ensure there is no visible exterior damage. Examine the network connection points to confirm they are secure.
3. Faulty or Insufficient Hardware
VoIP Hardware like Internet routers and firewalls are crucial to sending information across the Internet, and any outdated or faulty network devices could lead to packet loss.
This often happens when a company expands without upgrading the hardware needed to manage the now-increased data volume.
In an Internet connection, duplex communication allows for the connected devices to send and receive data. When two connected devices are operating in different duplex modes, the link isn’t as efficient.
This usually means that one device is working at a half-duplex setting and the other is functioning in a full-duplex mode.
When a device is half-duplex, signals travel both ways, but can only travel in one direction at a time. When one device is experiencing full-duplex functionality and the other is experiencing half-efficiency, packet loss occurs.
How to Detect It: When you have an issue with a specific piece of hardware, some computers display an error message, alerting you that the device is not working as intended. Monitor any pieces of hardware–especially older ones–to ensure proper performance. Any malfunctions should also be noted in device hardware logs.
4. Software Issues
Business communication software like VoIP applications and UCaaS platforms are an integral part of transferring data, but the software can cause packet loss when not working correctly.
When software hesitates because of a programming error, unexpected behavior can occur on your network. This is often because of software bugs or software that requires an update.
How to Detect It: If your connection seems slow, check to see if a specific application is using a lot of bandwidth even when not in use. A computer’s Task Manager/Activity Monitor tool shows how apps are currently communicating with the network, with app communication history from the last 30 days. This makes it easy to compare app usage with your latency issues.
5. Wi-Fi Networks
Wi-Fi often degrades the quality of the information packets sent across the network, simply because the Internet connection is not as strong as it should be.
Packet loss can result from a weak WiFi connection, devices placed too far away from the router, or obstacles like walls blocking the wireless connection. Wireless networks tend to suffer more setbacks and interference than wired connections.
How to Detect It: Check the Wi-Fi connection strength for each device on your network. If the Wi-Fi signal does not have full bars, you may need to move closer to the router, upgrade your router, move closer, or reduce the number of devices on your network.
6. Network Attacks
There are countless reasons to take VoIP security seriously, but few people consider that cyber threats like Denial of Service (DoS) attacks can cause network packet loss amongst other problems.
DoS attacks intentionally overload your network, leading to an increase in packet loss and network vulnerability. Packet loss creates what’s called a low-priority backdoor, which is a hole that makes it easy for hackers to circumvent security measures and sneak in malicious code that can compromise private data.
Businesses of any size are vulnerable to DoS attacks and other threats, especially if there are existing packet loss issues.
How to Detect It: Monitor your network traffic and determine if there is additional, unfamiliar activity on the network. When network attacks occur, your network becomes much slower than normal. Files and websites are slow to open, and VoIP calls experience jitter and stuttering.
How to Detect Packet Loss
Now that you know the root causes of packet loss and how to detect specific issues, let’s discuss how to use your system’s Operating System (OS) to determine whether or not you are experiencing packet loss.
Below, we’ll outline how to detect packet loss on Mac, Linux, and Windows systems.
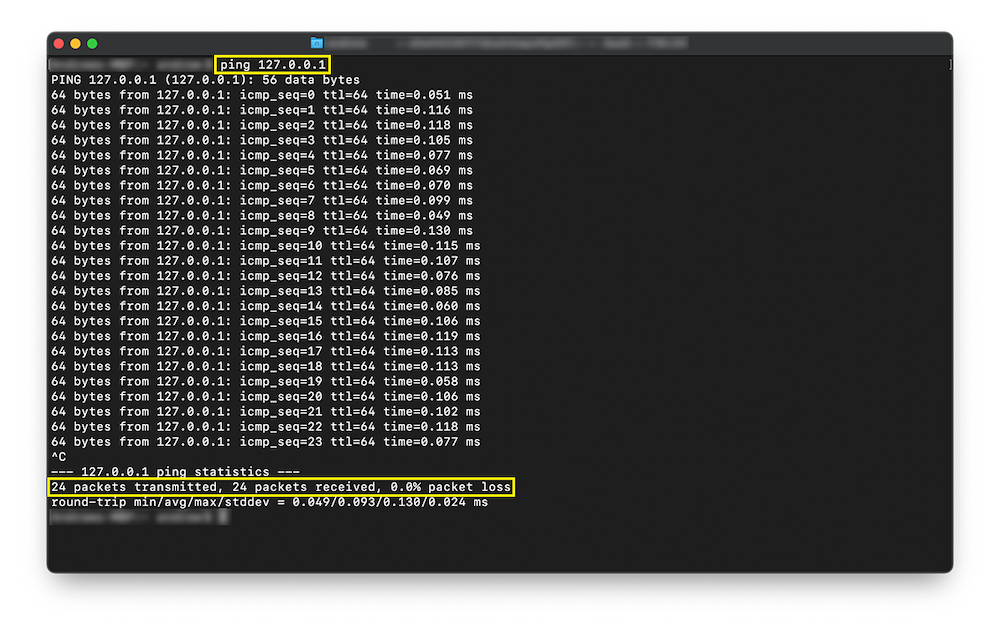
macOS Packet Loss
To see if you’re experiencing packet loss on macOS, follow the below steps.
1. Click on Finder → Applications → Utilities
2. Open the Utilities folder and select “Terminal”
3. Type in the command: Ping 127.0.0.1 and press “Enter”
4. Let the process run for a few moments, then press “Control C” to stop the test.
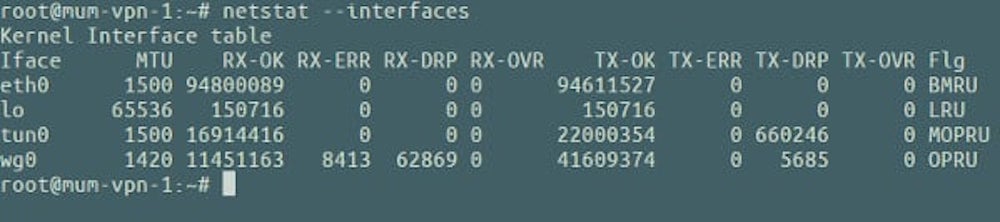
5. Review the statistics at the bottom of the page (See image below)
Linux Packet Loss
1. To see if you’re experiencing packet loss in Linux:
2. Press “Control T” to open the Terminal
3. Type in the command: Ping 127.0.0.1 and press “Enter”
4. Review the statistics displayed at the end of the test (See image below)
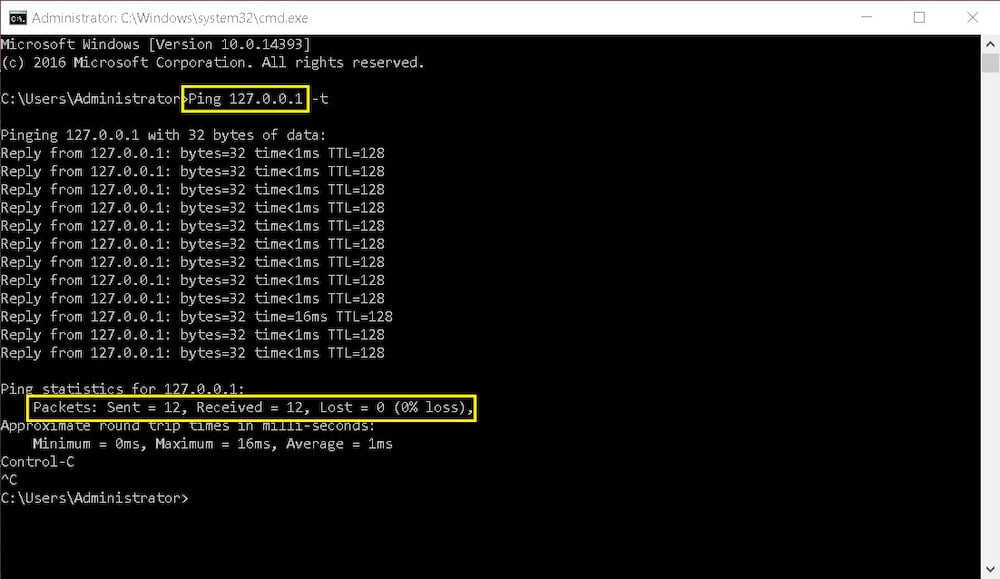
Windows Packet Loss
To see if you’re experiencing packet loss in Windows:
1. Open the “Run” application by pressing the “Windows Key” + “R”
2. Type “cmd” into the “Open” box and press “OK”
3. In the terminal, type the command: Ping 127.0.0.1 -t and press “Enter”
4. Once at least 10 packets have been processed, press “Control” + “C” to stop the test
5. Examine the results (See image below)
Best Tools To Fix Packet Loss
Quality of Service (QoS) and Network Monitoring software solutions provide you with real-time data and alerts about packet loss, network performance, server activity, and other essential security and activity updates.
Below, we’ll explore some of the most popular platforms.
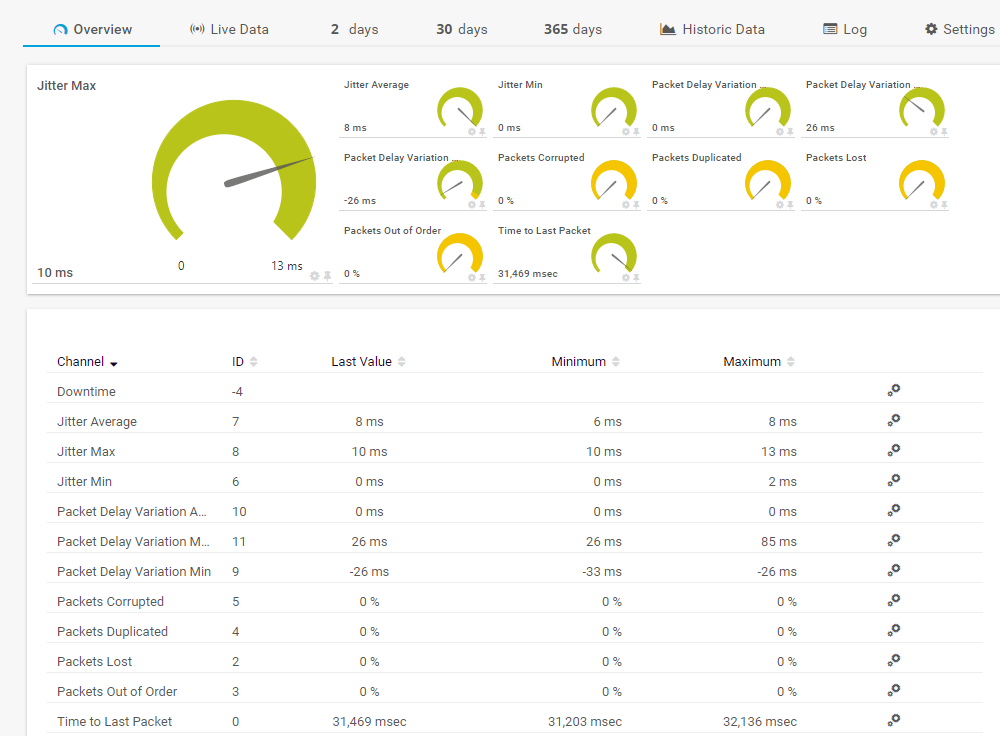
Paessler PRTG: For Comprehensive “Best Overall” Monitoring
The Paessler PRTG Network Monitor is one of the best monitoring tools on the market today, providing a comprehensive real-time overview of your entire IT infrastructure.
Users can configure custom notifications on desktop computers and mobile apps for iPhone and Android, allowing them to receive monitoring alerts for network events:
- Percentage-based packet loss and packet sniffing
- Bandwidth use and potential bottlenecks
- Network traffic, security, speed, optimization, and activity
- Firewall status
- Jitter levels
- Wi-Fi signal strength
- Quality of Service
Standout Features
- Multi-OS compatibility: PRTG is compatible with a wide variety of operating systems and technologies (Windows, Linux/Unix, macOS, REST APIs, etc.)
- Custom maps and dashboards: Choose from more than 300 monitoring metrics to create custom maps and dashboards, monitoring data performance across devices
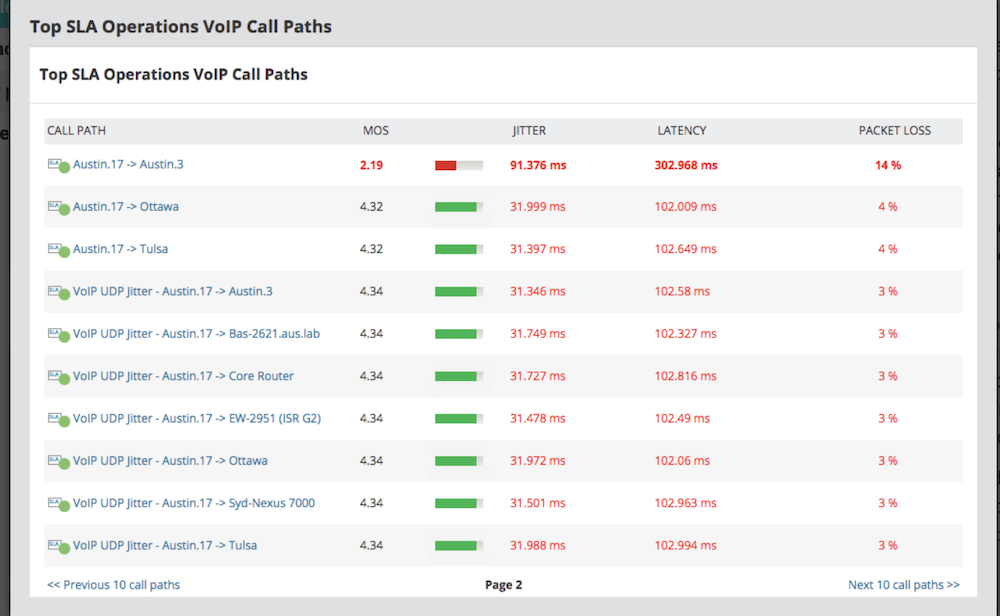
SolarWinds: For Multi-Vendor Quality of Service Monitoring
SolarWinds VoIP and Network Quality Manager (VNQM) tool provides detailed real-time insights and updates on network performance thanks to its advanced packet loss monitoring.
The platform provides call path details and call signaling data, examining performance metrics that signal packet loss or a decline in overall call quality.
These metrics include:
- Percentage-based packet loss monitoring
- Jitter
- Latency
- Mean Opinion Score (MOS) to measure call quality
- Protocol
- Devices
- Codec
- Reason for call termination
- Call duration
- Call locations
- Origin/Destination IP Addresses
Standout Features
- PerfStack dashboard: This patented comprehensive dashboard compares packet loss data to SIP trunk activity, network status, and VoIP performance, providing a comprehensive overview of your system through real-time and historical data
- Custom alerts: Like Paessler PRTG, SolarWinds users can also configure custom alerts/notifications based on high-priority QoS issues
ManageEngine OpManager: For Scalable, Affordable Monitoring
ManageEngine OpManager is a continuous network monitoring software that works across devices, networks, WAN links, access points, and more. It doesn’t just pinpoint network issues–it also includes troubleshooting capabilities and configuration management.
OpManager monitors over 2,000 network performance metrics, including:
- Packet loss by percentage
- Latency, speed, and network traffic
- Performance bottleneck analysis
- Network devices (routers, wireless LAN controllers, servers, switches, firewalls, etc.)
- Errors and discards
- WAN performance
- Memory and CPU
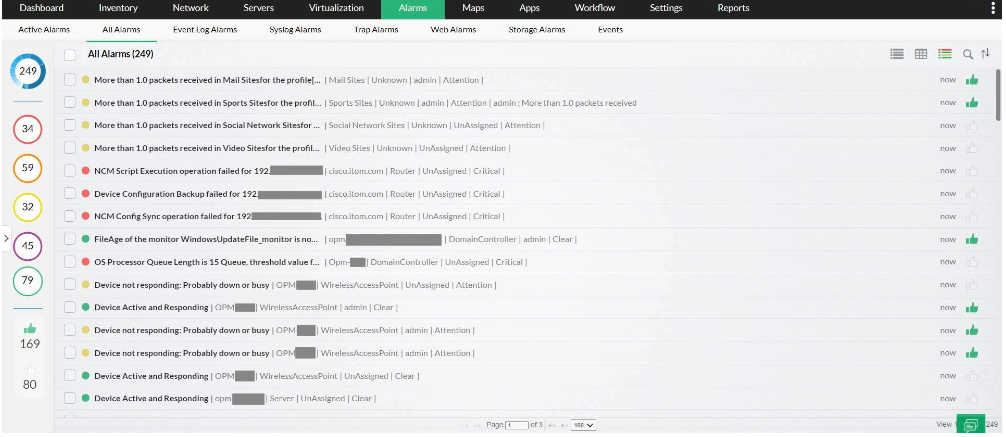
manage-engine alerts
Standout Features
- Custom dashboards: Build customized multi-view dashboards with over 200 widgets, and notifications (called “Alarms”) are triggered when preset metrics dip below a specified threshold.
- Flexible pricing: Though integrated network monitoring software is available, OpManager is unique in that it offers three separate plans, each with a different level of monitoring and designed with affordability in mind.
Nagios Core: For Free Open-Source Basic Network Monitoring
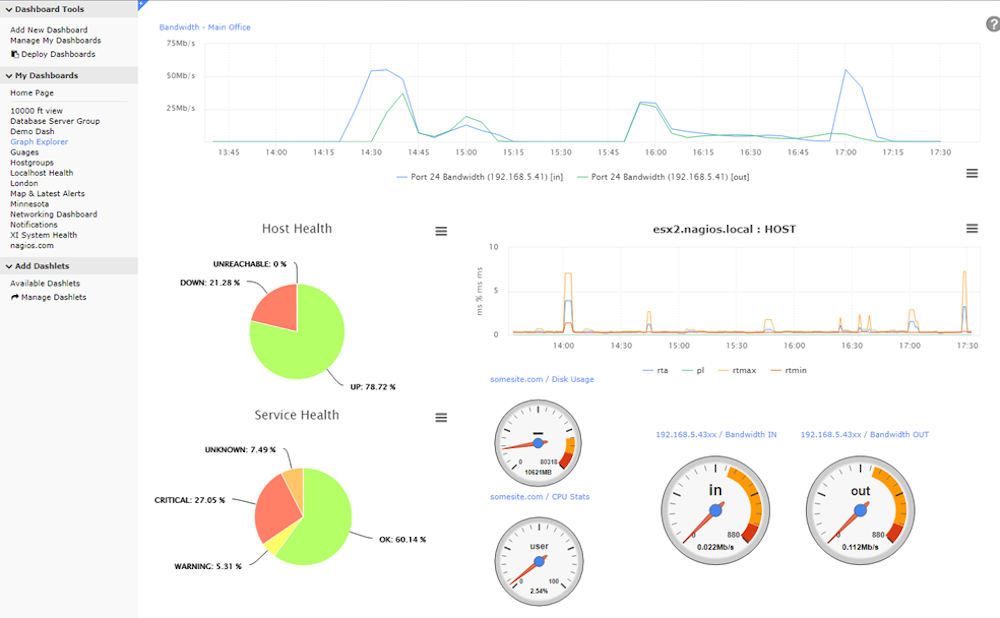
Nagios is a big name in IT infrastructure, and its free, open-source network monitoring platform, Nagios Core, is quite popular.
Though originally designed for Linux, Nagios Core now works with additional operating systems like macOS and Windows. Over 50 plugins are available for download, and further customization is available by downloading front-ends and Core add-ons from the developer community.
Nagios Core monitors metrics like:
- Packet loss
- Network traffic
- Jitter
- Latency
- Protocols
- Servers
Standout Features
- Free and customizable option: Nagios is a free, open-source tool, which means it’s a highly customizable solution. However, it will likely require some basic programming knowledge or an IT team to set up and successfully use. Those without technical knowledge should opt for Nagios XI, the company’s paid network monitoring software.
- Wide visibility: Dashboards provide a unified view of your whole IT infrastructure, quickly detecting outages and aging hardware or software
Don’t Let Packet Loss Hurt Your Business
VoIP is a superior calling solution to PSTN networks, but it’s critical to maintain your Internet resources and reduce the impact of packet loss. In addition to careful diagnosis, follow the preventative steps we’ve outlined in this post to reduce packet loss, including investing in the right tools.
Look for the right VoIP software with strong security features like automatic updates, real-time network monitoring, and end-to-end encryption to keep your business communication running smoothly.