The contact center customer experience includes social media interactions, real-time chat messaging, voice calls, and omnichannel self-service options. Providing a superior customer contact experience increases business growth, boosts customer retention, and improves company culture.
Read on to find out what a contact experience is and how to build one that serves customers and employees equally.
- What is a Contact Center?
- What is a Contact Center Experience?
- The Role of AI
- Why it Matters
- What Makes a Great Contact Center Experience
- Best Practices
- Essential Technologies
- Types of Contact Centers
- How to Choose the Right CCaaS Software
- FAQs
What is a Contact Center?
A contact center is a department or facility within an organization that manages customer inquiries through multiple channels, such as phone calls, live chats, social media, and email.
A contact center differs from a call center in that call centers are limited to voice calling and basic SMS, while contact centers add on digital communication channels like website chat, social media messaging, email, and video conferencing.
Additionally, contact centers leverage artificial intelligence much more than call centers. AI streamlines employee onboarding and training, boosts productivity, and uses forecasting methods to optimize agent schedules. AI-powered speech analytics pinpoint common customer service issues, monitor agent performance, and enhance the overall customer experience.
While call centers are focused on connecting customers to the right live agent, contact centers prioritize automated self-service and first contact resolution across voice/digital communication channels. Virtual agents, self-service chatbots with canned responses, and highly customizable routing strategies improve contact center CX.
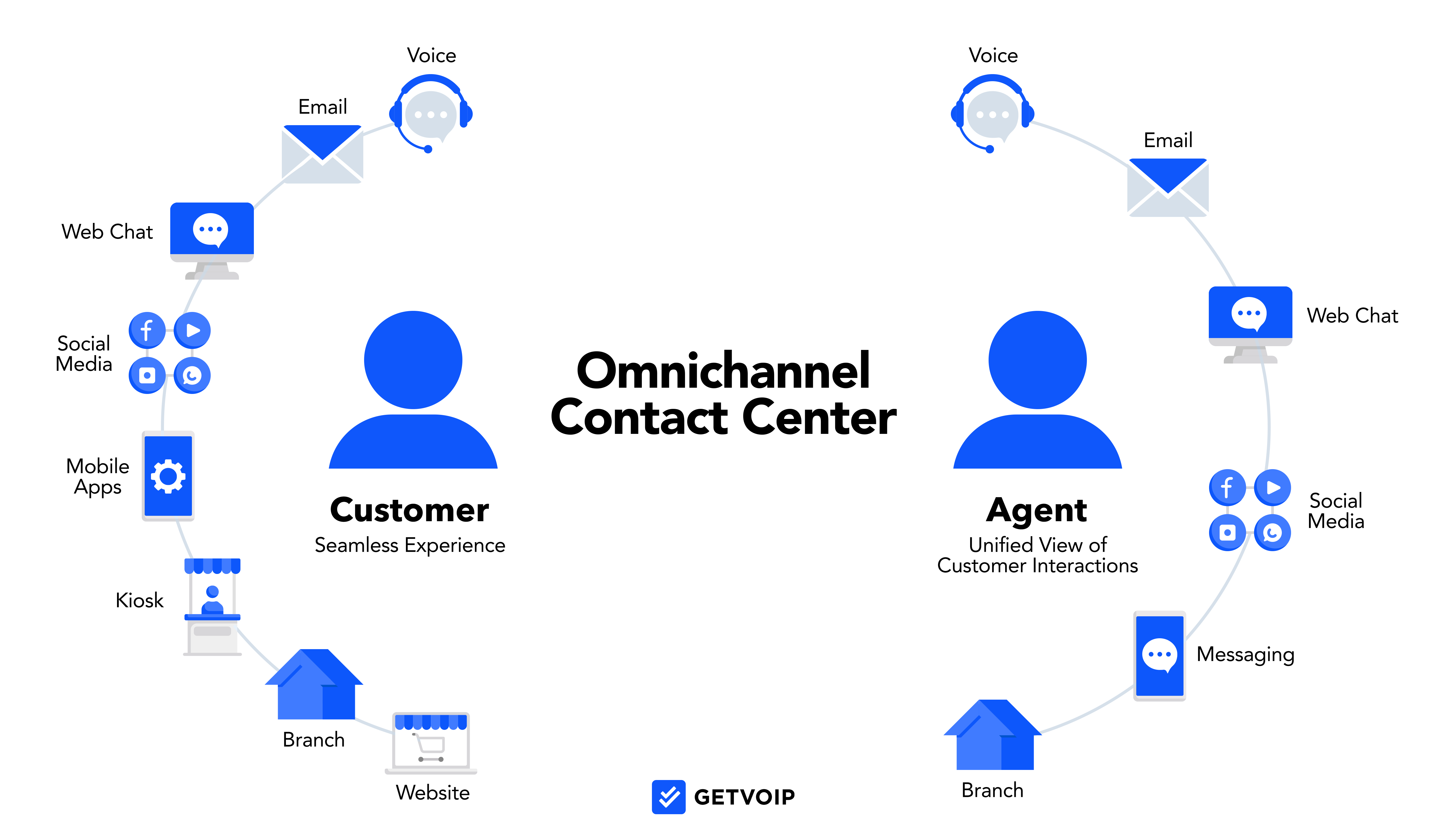
What is a Contact Center Experience?
The contact center experience is the complete series of interactions a customer has with your business, starting from the moment they contact your company and ending when their issue is entirely resolved and communication ends.
The contact center customer experience includes both automated and live customer:agent interactions, such as:
- IVA interactions and IVR menu selections
- Chat, email, and SMS interactions (including automated confirmations and SMS marketing)
- Waiting on hold and/or receiving a follow-up call/message
- Completing a customer survey at the end of an interaction
- Filling out an intake form
- Placing an order or scheduling a service appointment online
- Submitting a support ticket
- Interacting with a virtual agent or chat bot
The Role of AI in Contact Center Experience
AI has a role in nearly every aspect of the contact center from analytics to workforce management, but in recent years, AI has had increasing direct contact with customers. As consumers are becoming more comfortable interacting with AI, and AI advances in listening, speaking, and texting in natural language, it has become essential to the contact center experience.
Here are some of the ways AI shows up in contact center experience:
- Real-time agent assistance: AI monitors interactions between human agents and customers, offering suggested phrases or actions in real-time. For example, a real-time agent assistant provides notifications when an agent is speaking too fast, displays a caller's purchase history, or sends a link to a relevant knowledge base article while the agent is on the call.
- Intelligent routing and triage: Intelligent routing leverages AI to determine a caller's intent and then decide where the call should be routed. For example, an AI receptionist answers after hours calls and speaks with customers in natural language, conducting intake and answering FAQs.
- Sentiment analysis and quality monitoring: AI is used to determine customer sentiment and alert supervisors when a customer is becoming agitated or when an agent is out of compliance. For example, a quality management system automatically scores human agents for how well they follow a script.
- Personalized automation: Users design automation workflows so that when certain conditions are met, operations will be completed automatically and nothing slips through the cracks. For example, anytime an agent receives a compliance score under 80%, a supervisor will be notified.
- Smarter training/coaching: AI is used to streamline training by running simulations with new employees and then providing real-time coaching when they start taking live calls. For example, new agents can complete a training program with an AI trainer on their own time and on a rolling basis, with periodic supervisor check-ins.
Why Contact Center Experience Matters for Business
Businesses must prioritize a positive contact center experience to improve and maintain customer relationships, ensure customer loyalty, and increase sales.
Customers expect instant support and speedy response times across channels, which is another explanation for the explosive growth of contact center software.
Benefits to improving contact center experience include:
- Increased customer satisfaction and loyalty due to faster resolutions and immediate support
- Agents feel competent to resolve customer issues, resulting in higher retention rates
- Lower costs due to the ability to optimize available agents
- Insights from AI reporting to identify customer journey roadblocks and popular products/services
- Higher sales due to positive feedback, customer advocacy
What Makes a Great Contact Center Experience
A smooth, efficient contact center experience benefits agents and customers alike, but each group has a specific set of needs. While these needs vary depending on your industry, business goals, customer base, and company size, here are some general tips to keep in mind:
For Customers
- Personalization: Features like CRM software integration, shared omnichannel inboxes, multi-level IVR, and smart routing create a bespoke customer service and support experience
- Variety of channels: Contact centers offering a variety of communication channels (voice/video calls, SMS/MMS, live chat, etc.) let customers get help via their preferred channel and seamlessly switch between channels during an interaction if they are on-the-go
- Fast response: Businesses can shorten long wait times by monitoring on-hold times, ensuring adequate staffing during peak times and creating self-service options
- Efficient resolutions: Contact centers can ensure fast and efficient resolutions by recording interactions, analyzing the data for common customer complaints and agent training issues, and making adjustments accordingly
For Agents
- Automations: Contact center automations (SMS appointment reminders/shipping updates, customer callbacks, IVR, post-call summaries) greatly reduce after-call work for agents and decrease burnout
- Workforce Management: With AI-based/automated scheduling, employees can easily submit PTO requests and exchange shifts while performance gamification makes the work less tedious
- Thorough training: Robust agent training programs that include call recording playlists, one-on-one coaching, agent score sheets, and live call monitoring improve agent performance and create greater job satisfaction
- CCaaS software: A unified contact center software solution assists agents by automatically routing and transferring calls, recording calls, and organizing data so that agents can focus on conversations with customers
- CRM integrations: Integrating contact center software with a CRM platform like Salesforce lets agents view interaction and purchase history during live calls and provides vital contextual information
Best Practices for Creating a Good Contact Center Experience
- Implement omnichannel routing: Omnichannel routing allows customers to reach out to the company on the channel that is most convenient to them at the time, while agents have access to a complete interaction history regardless of the channel used.
- Conduct routine quality assurance assessments: Ensure agents are meeting and exceeding CX goals by evaluating communication quality with call recording, customer surveys, in-call coaching, and real-time/historical analytics
- Provide self-service options: 24/7 self-service tools like chat bots, online knowledge bases/forums, and IVAs reduce customer wait times and free up live agents
- Utilize employee performance gamification/recognition: Tools such as leaderboards and agent scoring not only improve productivity, but can increase employee retention rates and overall job satisfaction.
- Take advantage of AI features: AI tools are essential to uncover areas that need improvement in the contact center as well as relieving a lot of the pressure on agents.
- Integrate UCaaS features: Tools like video calls, team chat, etc. will prevent communication silos and unite remote teams
How to Measure the Effectiveness of a Contact Center
Continually measuring customer interactions and making data-informed improvements helps maintain efficiency and a positive contact center experience. Here are some important contact center metrics to be aware of:
Contact Center KPIs
- Conversion rate: The percentage of calls/interactions that result in a sale
- Call volume: The daily/weekly/hourly number of inbound calls
- Average call handle time (AHT): The amount of time an agent spends on all calls divided by the number of calls taken
- Agent retention: Measure the percentage of agents that stay with the company over a period of time
- QA Scores: Monitor whether agents are meeting compliance standards or going “off script”
- Call Abandonment Rate: The percentage of interactions that are abandoned by the customer before resolution
- First Contact Resolution Rate: The percentage of customer issues that are resolved in the first customer:agent interaction
- Cost per Contact: The total cost of running the contact center divided by the number of contacts handled.
- Customer Effort Score (CES): How much effort a customer had to expend to get their issue resolved. Typically asked as a post-call question.
- Customer Sentiment: A customer's attitude and emotion during an interaction (positive, negative, or neutral). Typically analyzed automatically during or after the interaction.
Customer Feedback
- Net promoter score (NPS): Customers rate their willingness to recommend the business on a scale of 1 to 10
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): Customers rate their experience by answering a direct question about how satisfied they are with service
- Customer surveys: Customers are given post-interaction surveys with specific questions. Answers can be open-ended or rating-based
Essential Technologies for Contact Centers
The most successful contact centers leverage a variety of technologies in order to optimize agent workforce, deliver more personalized customer service, cut back or even eliminate wait times altogether, and decrease employee burnout and turnover.
Tools that are powered by Generative AI, Natural Language Processing, and Agentic AI were once considered cutting-edge, but are now essential to stay competitive.
Here are the most essential technologies for contact centers:
- AI-powered chatbots/virtual agents: AI-powered chatbots communicate with customers via text using natural language, while virtual agents may use voice or text. They can answer questions and perform simple operations such as payment and scheduling. This feature routes routine requests and common questions away from live agents, reducing wait times, customer frustration, and agent burnout, while giving customers a 24/7 self-service option.
- IVR systems: IVR is a call routing system that uses menus, rules, conditions, and customer input to automatically route each incoming call to the best agent, department, or voice mailbox. An IVR system avoids the need for a receptionist. Intelligent IVR systems leverage AI to discern what a customer needs and will choose the best agent based on skillset, longest idle time, or other pre-determined factors.
- Speech and text analytics: Speech and text analytics leverage AI (and sometimes agentic AI) to monitor 100% of contact center communication and uncover insights that are meaningful for supervisors, admins, and owners. Speech and text analytics show customer intent, agent compliance, customer sentiment, FAQs, recurring problems, etc. This helps businesses address issues quickly.
- Quality management platforms: Quality management platforms keep track of local laws and regulations as well as company standards and procedures in order to help contact centers stay in compliance. Features of a quality management platform might include scorecards, call recording, screen recording, and automated scoring using natural language processing and understanding. The platform analyzes interactions for customer intent, sales opportunities, pain points, and sentiment in order to identify compliance risks.
- Conversation intelligence tools: This is an AI-powered platform that goes beyond recording and transcribing interactions, but reasons through and analyzes those interactions using agentic AI. With the data that the platform collects, it will automatically generate suggested next steps and action items, and in som cases, perform those actions as well.
- Knowledge base/self-service portals: This an interactive website where customers can search for the answers they need, make an appointment, or schedule a payment, without having to speak to a live agent. This is often preferable for customers, relieves stress on live agents, and allows the contact center to operate 24/7.
- Workforce management tools: These are tools that automate agent scheduling taking into account agent skills, preferences, and availability. Workforce management tools eliminate hours of works for supervisors and are less frustrating for employees. Workforce management features may include shift swapping capabilities, time off requests, gamification, etc.
- Smart callback technology: Smart callback technology gives customers the option to request a call back from the company so they don't have to continue waiting on hold. They system will conduct an automatic intake gathering basic information from the customer and automatically assigning the call to an appropriate agent.
- Experience orchestration: Experience orchestration personalizes and coordinates customer interactions across all channels. The tool leverages AI to make decisions based on customer behavior in real time. This allows contact centers to provide extremely tailored customer service to every customer regardless of what channel they use.
Types of Contact Centers
Contact centers span across many industries and often become a necessity when a company reaches a certain size. There are different types of contact centers that serve different purposes.
Let's take a look at different types of contact centers:
- Inbound vs. Outbound vs. Blended: Inbound contact centers only take incoming communication and do not make calls. An example of an inbound contact center would be a customer service team. An outbound contact center primarily makes outgoing calls and/or sends texts to consumers. An example of an outbound contact center would a sales department. A blended contact center does both. An example of a blended contact center would be a doctor's office that both takes calls from patients and makes outbound follow up calls.
- Multi-channel vs. Omnichannel: Multi-channel contact centers are reachable by customers on multiple channels, but the channels are kept separate. Omnichannel contact centers use software to ensure that context is kept whenever customers switch channels. For example, a customer calls with a question, then emails with a follow-up question, then uses a self-service portal to make a return, then follows up with another call. In an omnichannel system, the agent speaking to the customer would have a complete interaction history.
- Cloud-Based vs. On-Premises: Cloud-based contact centers use a SaaS provider that manages the entire system and stores all data in the cloud. There are much lower upfront costs , new features are rolled out regularly, and the system is flexible and scalable. On-premise contact centers purchase and install their own hardware. Although more expensive, on-premise solutions are more customizable and secure and offer complete control, best for government.
- Virtual vs. Hybrid: Virtual contact centers employ 100% remote employees, this cuts overhead costs dramatically and agents can be hired from anywhere in the world. Hybrid contact centers allow agents to work remotely part of the time, or allows some employees to work remotely all of the time. Hybrid models are more complex and expensive, but can foster team building and are good for contact centers that have a physical space to utilize.
How to Choose the Right CCaaS Software
Each contact center software provider has different strengths and weaknesses, and it’s important to select one that will fit the needs of the business.
Things to consider when choosing a CCaaS provider include:
- Available integrations: Ensure the contact center integrates with your existing software, including customer relationship management (Salesforce, Zendesk), file storage (Google Docs, box) and collaboration tools (Slack, Zoom, Teams)
- Available communication channels: Not every customer will utilize every communication channel, but it is essential to determine which channels are important to your customers and ensure that your CCaaS platform includes them
- Pricing and options: When considering which providers fit into your company’s budget, consider which features you will need and whether those features are included in a bundled plan or must be purchased as an add-on
- Scalability: Make sure that you will be able to scale when the time comes without incurring extra costs
- Security and network reliability: To avoid costly data breaches or service interruptions, ensure your chosen CCaaS provider has two-factor authentication, encryption, a minimum 99.9% uptime guarantee, etc.
- Onboarding and customer support: Consider the installation process, average resolution time, customer support hours/channels, and evaluate paid support plans



