If your company works in a field that utilizes patient data, there are compliance HIPAA security rules that you must follow. Two acts protect electronic health records. HIPAA, which was established during the Clinton administration, was designed to patients with a reliable digital system of healthcare, even when they were between jobs. The HITECH act, which was instituted during the Obama administration was designed to shore up weaknesses in HITECH and facilitate digital record adoption by healthcare organizations.
Both of these acts protect the health data of Americans by establishing rules for the management of sensitive information. Since both acts state that organizations must fill out business agreements to manage American health information, even offshore organizations are liable. It’s not enough to protect secure customer data like call recordings and records by encrypting it while it’s at rest – organizations must also protect the data as it’s transmitted. Compliance is the only way to avoid steep penalties.
Both HIPAA and HITECH are also designed to bring customers extra convenience. The acts allow patients to review their health information at their convenience with a provided user ID. Electronically protected health information (ePHI) is sensitive data, and being compliant will protect you and your employees from future liability.
Compliance also ensures medical information is digitally shareable with both healthcare professionals and patients. Validated services for the sharing of medical information over digital platforms are called telehealth services, and these communications technologies protect voice, data, and any images from data breaches.
- What is HIPAA?
- What is HITECH?
- How Does HITECH-HIPAA Compliance Impact Businesses?
- Safeguards to Encrypt Medical Records
- Encrypted Data Protects Organizations
- Ways to Encrypt Data
- What are the Best Practices for Encryption?
- Why Should You Encrypt Your Data?
- Staying HITECH and HIPAA Compliance Saves Money
What is HIPAA?
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act was the initial attempt by congress to help individuals maintain their health records and insurance between jobs. The initial act was passed in 1996 and received updates in 2003 and 2005. In addition to making it easier to maintain health insurance for employees and former employees, HIPAA is also an act that protects information by employing technologies like virtual private networks (VPN) and transport layer security (TLS) encryption.
- VPN: Virtual private networks encrypt confidential data as it travels on and off the network.
- TLS: Transport layer security is a protocol that uses ciphers to encrypt patient data. Some algorithms that generate ciphers are less secure than others.
HIPAA directly affects health plans, healthcare providers, and healthcare clearinghouses. The act initially didn’t cover the business associates of these organizations. Any information that is being accessed on mobile devices must use user IDs for healthcare holders and patients. Data breaches tend to happen at the device level, and encryption protocols and network-level encryption techniques ensure that patient and company devices won’t cause vulnerabilities. "Bring your own device" policies must require the installation of encryption software.
HIPAA breaches can be costly – in May of 2019, Touchstone Medical Imaging was charged a penalty of three million dollars for using a third-party data center that exposed the electronic health records (HER) of more than 300,000 patients.
What is HITECH?
The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act was initially designed to provide healthcare organizations and their associates with monetary reasons to update their patient data. The HITECH architects recognized that there needed to be stronger protections in an era where there was an increased exchange of electronic health information. HITECH was initially passed during the Obama administration in 2009.
Healthcare organizations that go digital with their data receive cash rewards from the government, but all affected organizations are responsible for the safe handling of the protected health records of patients. There are four levels of violations for healthcare companies and their associated partners that reflect the level of liability in breaches. At the maximum level, the penalty for a single security breach is $1.5 million. It’s essential to understand that HITECH places the onus of responsibility on the shoulders of both the organization and its employees and holds them liable for willful neglect.
How Does HITECH-HIPAA Compliance Impact Businesses?
Your business needs to ensure complete compliance if you work, even tangentially, with patient medical data. This includes direct data or even call recordings that may have information about patient health plans or medical history. For example, merely using a widely-used app like Facetime will expose your company to penalties if any aspect of patient medical data is discussed using the platform. Using any software that isn’t validated for telehealth by HIPAA or HITECH is a major federal regulation violation.
In 2013, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) issued an updated version of the HITECH-HIPAA Omnibus Rule that effectively expanded the number of businesses affected by both acts. While this was a few years back, it’s entirely possible that a business could be swimming in HITECH-HIPAA waters and not know that they are subject to the policies of these healthcare compliance acts.
So, if you fall into the classification of HIPAA-covered entities, which means that you’re either a healthcare organization, a healthcare clearinghouse, health plan administrator, or a business associate of any of those organizations, then you’ll need to ensure precise compliance or be liable. By law, business associates must sign a business associate agreement (BAA) so that they understand that they are accountable for faulty ePHI data management.
Data breaches are happening at an increasing rate, but with the right level of encryption and the correctly-selected communications provider, you will be able to protect yourself and your data. Every year, the secretary of the HHS issues guidance to affected healthcare entities – keeping up with this will alert you of any changes to federal policies that may have changed.
In the realm of unified communications, there is a wide variety of technologies that can send data. This will include company SMS, electronic forms, and video conferencing software. Each of these transmits relevant data over internet communications channels, which means that every aspect of the communications technology will have to be completely compliant. Here are a few of the UC features that must be encrypted to protect patient healthcare data:
- Texts
- Voice Calls
- Call Recordings
- Faxes
- Voicemails
- Video Conferences
- Chats
- File Sharing
Encryption at Every Stage
Additionally, encryption needs to happen when the data is at rest as well as when it’s in transit.
At Rest
This is when data is stored in a static location, like on a server. Data at rest is just being kept for future use, and encryption is used to ensure that VoIP hackers using backdoors that may have arisen due to packet loss won’t be able to access data that’s being stored. Attackers value this kind of data since it tends to be more complete.
In-Transit
In-transit data has a direct impact on VoIP phone service and UC since this type of encryption happens as the data is broken into packets and sent to its destination. In-transit data encryption isn’t just for information traveling over an internet connection, sometimes, this is encryption also is used for data being transmitted over a local area network (LAN) or a wide-area network (WAN).
Safeguards to Encrypt Medical Records
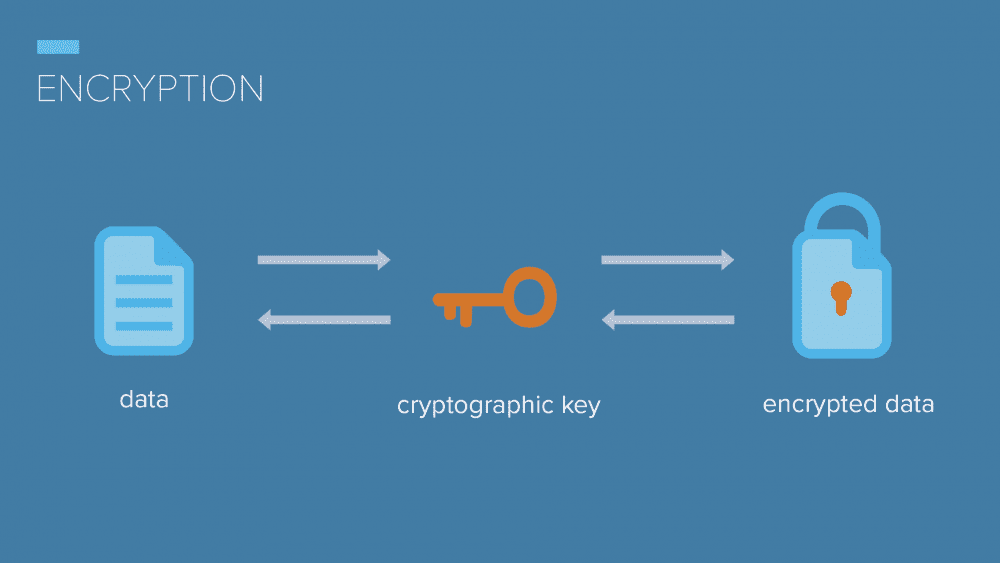
When it comes to the protection of patient information, HIPAA security rules dictate the implementation of several critical safeguards. The types that are prescribed by federal law include technical, physical, and administrative safeguards. The security management process is complex, but with the right implementation, your organization will have a high level of protection.
Technical Safeguards
The HIPAA and HITECH acts state that technical safeguards are "the technology and the policy procedures for its use that protect electronic protected health information and control access to it."
The implementation of these safeguards will depend on the size and industry of the organization. For this reason, your organization will need to identify any risks or vulnerabilities that may be present in their patient data management.
You will be required to implement some access control methodology, introduce activity logs and audit controls. In addition to this, you'll be expected to introduce some means of ePHI authentication so that any altered or destroyed data is detectable. To facilitate higher security, automatic log-off of devices with HITECH-HIPAA data is also a safeguard that can ensure that any data on physical devices is protected. Even those that are granted facility access won't be able to access devices with protected data.
Physical Safeguards
HIPAA regulations also dictate some of the methodologies in which your organization will need to add a physical layer to your ePHI security measures. For example, you'll need to strictly control facility access so that only authorized agents are granted physical access to servers and devices that contain sensitive data.
Workstation positioning and secure usage is also a safeguard that you will have to implement. For example, objects like barriers around workstations will need to be utilized. HIPAA rules also dictate how ePHI functions are to be performed on these devices.
Devices that have had patient info on them can be a security risk, even after they are no longer being actively used. HIPAA guidelines state that an inventory of ePHI hardware must be kept and maintained. Additionally, a copy of any ePHI must be made before moving a workstation. Proper data management when moving electronic media like key drives must also be observed.
Finally, since enterprise mobility allows for remote storage and access patient data from smartphones and mobile devices, safeguards must be used for these items as well. Your company must develop policies that detail how patient data is removed from these devices when the user leaves the organization or the device is upgraded or reused. Proper device handling procedures that follow these guidelines will prevent direct-access security incidents.
Administrative Safeguards
The final safeguards that will need to be implemented so that you are adhering to HIPAA privacy rules pertain to ePHI data administration. These will entail policies and procedures that combine the requirements of both the privacy and security rules of HITECH-HIPAA.
Based on federal regulations, you'll be required to conduct regular risk assessments to identify all points of contact with patient data. Any area that utilizes ePHI will need to be assessed. If there are points where a data breach is possible, it must be identified and any vulnerabilities shored up.
This risk assessment phase must be repeated at regular intervals. In addition to this, if there are employees who have violated any policies related to this data, then there must also be a sanctioning policy to address and reduce the chance of incidents.
Also to prevent breaches, regular training will need to be scheduled to further reduce the chance of a data breach incident. Topics of the training can include how to react to a potential data breach and how to identify malicious software. You'll have to document any training used as an administrative safeguard against attacks and breaches.
You'll also need to develop, test, and implement a contingency plan. This is to protect data in the event of an emergency, which may be a data breach or natural disaster. Proper planning ensures that lapses in the business processes are addressable and procedures can continue without placing the data at further risk. During emergency mode, backups will need to be available for use and policies to help restore any lost data.
Modern business oftentimes requires the help of third-parties. HIPAA and HITECH dictate that business partners are liable for data breaches, but organizations must also restrict data access to third parties that do not require it. This includes subcontractors, software vendors, and parent organizations. Also, BAA agreements will need to be signed for any third party that is being granted access.
Finally, when a security incident is detected, it will need to be reported. Sometimes, security incidents don't always indicate a breach, but in all situations, these must be reported so that the incident is contained and the data is retrieved. This will allow for the proper parties to perform a risk assessment and determine if data has been stolen or lost. Proper reporting allows for better disaster recovery and can facilitate better risk analysis.
The HIPAA breach notification requirements state that businesses must immediately disclose that a breach of protected medical data has occurred. According to HIPAA, a breach is defined as "generally, an impermissible use or disclosure under the Privacy Rule that compromises the security or privacy of the protected health information." In the situation of a breach, you must report this to affected individuals and the Secretary of the HHS. Federal policy may even dictate that a breach must be reported to the media as well.
Encrypted Data Protects Organizations
Non-compliance not only exposes patient data, but a practice of using unencrypted communications erodes stakeholder confidence and will damage the reputation of your organization. With a single HITECH violation costing millions, it’s also relatively easy for non-compliant organizations to be driven out of business because of unsecured information.
For compliance, all phones and external devices must include authentication with a user ID and all call data must be recorded and kept securely using at rest encryption. This will protect your organization's data should a laptop or phone be stolen. In addition to call records that store voice information, all administrative functions performed during a call with a patient requires recording. This is called storing the metadata.
Since these acts affect businesses and their associates, VoIP phone service and UC providers must be HIPAA compliant. This also means that service providers that delete recording data after a few months cannot be used. Additionally, any provider that has low caps on storage must be avoided since call recordings and metadata can use up significant space on servers.
Ways to Encrypt Data
Data encryption isn’t just for businesses that want to be HIPAA and HITECH compliant, any small and midsize business (SMBs) that deal with personally identifiable information (PII) will need to utilize encryption methodologies. This includes encryption practices for both at rest and in-transit data. Data breaches that aren’t healthcare-related may go without regulatory punishment, but data breaches of this type can still open up your organization to breach-related lawsuits.
How Do You Encrypt Data on PC?
For Mac systems, software like FileVault and GNU Privacy Guard can be used to encrypt computers so that the data is HIPAA and HITECH compliant. For Windows machines, solutions like BitLocker and Veracrypt are useful options.
When data is encrypted, it is broken down into a random collection of characters that will need to be unlocked using a key or a cipher. The primary way for a malicious party to unlock the encrypted data is to have the decryption key, which should only be in the hands of IT staff and trusted employees. Fortunately, when it comes to data at rest, most hardware platforms are designed with the smooth implementation of encryption features so that your company can protect its information.
How Do You Encrypt Data on Mobile Devices?
Mobile platforms like Android and iOS have built-in encryption. For iPhones, a simple trip to settings, then Touch ID and Passcode, and Passcode Options will allow you to select a numeric or alphanumeric code for the device. For Android, the process can be completed by navigating to Settings, then to Security, then to Encrypt Phone, and finally, you’ll need to set a numeric code. On Android, the process is extensive and may take up to an hour – be sure to keep your phone plugged in.
How Do You Encrypt Data in Transit?
Secure sockets layer (SSL) is also a means to protect your data as it’s moving from device to device. If you’ve ever seen the words “secure” next to the URL on a website, this is SSL tunneling at work. SSL is used explicitly for browser and cloud solutions to provide a layer of encryption for file transfers.
All of these encryption methods will protect your data as it sits on hard drives, but for HITECH-HIPAA compliance, your data will need to be protected as it’s being transmitted. Providers like 8x8, Mitel, RingCentral for Healthcare, and Zoom all provide in-transit encryption for their subscribers and also have BAA agreements. Providers such as these are all very valuable for their ability to encrypt your data while it’s in transit, which is when some protected information is most vulnerable.
Also, cloud encryption gateways are a cloud security proxy that works at the application level. These solutions encrypt and tokenize data on an item-by-item basis. These work as great in-transit solutions and they are configurable so that the organization can change the algorithm for encryption on the fly. You’ll be able to choose a higher level of encryption or opt to go with a slightly less stringent level of encryption to preserve the file format and any sorting associated with the files.
Best Practices for Encryption
To protect yourself and your organization's ePHI data, there are a few steps that you will need to take. Here’s a quick list of HITECH-HIPAA-friendly encryption best practices.
Invest In High-End Encryption Software
HIPAA violations destroy small businesses, so investing in a more fully-featured encryption solution that will adhere to national standards for security is well worth the expense. A good solution will encrypt quickly, and many have tools that will help solve any issues that may crop up. For example, if there’s an error, a good encryption tool will alert you and deliver a solution that you can use to bring the system up to security standards. Also, quality software will create logs so that administrators will be able to review the status of encrypted data.
Manage Keys Intelligently
According to the documentation provided by the HHS, all protected health information (PHI) must be completely indecipherable without a dedicated key system. HIPAA requirements state that data must be encrypted using algorithms and the key must not be on the same device where the patient information is stored.
Encryption keys provide you with a means of quickly decrypting any data that may be stored on your drives or servers. The HHS demands a high level of security for these keys and states that you must not store the keys on the same device that houses the encrypted data. Proper key management requires that you keep these keys safe since losing them means that you will lose your data. It’s a good idea to use a storage provider so that you have a secure method of retrieval when the data is needed.
Test Security Daily
As the business owner and the primary stakeholder, you’re going to want to have a secure centralized management process for all encrypted data. This means that it’s a good idea to seek out encryption solutions that allow you to utilize a web-based dashboard that will provide metrics detailing what’s been happening with your encrypted data. With one, you'll be able to keep up to date on security measures and the status of encrypted identifiable health information on servers and associated devices. This includes alerts about updates, device configuration, and logs.
Implement User Authentication
From the very beginning, HIPAA has required that organizations utilize user authentication for access to ePHI data. Most companies use usernames and passwords, but there are new technologies that bolster security when working with sensitive data. With the right tools, the risk of unauthorized access is greatly reduced within patient information systems. For example, implementing technologies like cryptographic tokens and biometrics are surefire ways to ensure that only authenticated users will have access control to their encrypted data.
Why Should You Encrypt Your Data?

Now that you know how to start encryption and some of the best practices, let’s take a look at a few critical reasons to encrypt your data.
Protects the Company from Liability
Don’t get caught with a multimillion-dollar fine. Encryption will protect your data from security the breaches that threaten your business. It’ll also protect you from liability; patients with stolen data have filed breach of privacy lawsuits, especially if multiple patients are affected by a data breach. Encryption is a much cheaper alternative.
Simplifies New Tech Implementation
Technology constantly updates, and new technologies for encryption release continuously. Provider-based encryption has the benefit of being updated automatically by their staff. When updates and new technology become available, your organization upgrades to provide a higher level of ePHI security. Even software that’s installed on-premise can be quickly updated by IT staff to add an extra layer of data protection. This is especially true for VoIP providers that have a cloud-based structure.
With the increase of automated systems and conversational AI, customer information collected needs to be protected.
Ensures Archived Call Recording Data
Data collected with call recordings can protect your company because it has useful information that benefits your organization should a patient decide to take you to court. Under HIPAA and HITECH, most call recording data is kept indefinitely, so it’ll be available for meaningful use when it’s needed.
Staying HITECH and HIPAA Compliant Saves Money
Whether your organization works directly in healthcare or you merely have clients that are healthcare providers, you must be HITECH-HIPAA compliant. The right encryption solution for your communications and stored data will provide you with a security framework that will protect you from fines and lawsuits. Patients and customers have a right to privacy, so converse with your IT organization to determine if you’ve taken all of the necessary steps to fully encrypt your relevant data.
You might consider premium encryption to be an unnecessary expense, but spending a few extra dollars for heightened HITECH-HIPAA compliance will prevent your business from becoming the latest data breach horror story.
For extra information about logging your calls for better compliance, take a look at our guide to call logging features to look out for when selecting a solution.

![How to Encrypt HITECH and HIPAA Compliant Data [Guide] How to Encrypt HITECH and HIPAA Compliant Data [Guide]](https://getvoip.com/uploads/hipaa-compliant-700x406.jpg)

