HD Voice strengthens call clarity, prevents miscommunication, and improves overall customer experience on 4G, 5G, and VoIP networks.
High-definition voice calls also reduce the number of IT support requests and make conference calls more productive.
But how does HD Voice work, and what should users consider before implementing it?
This article will outline HD Voice, including how it works, network requirements, key benefits, and factors to consider before implementing HD Voice.
We’ll also introduce top VoIP providers that offer HD Voice calling.
- What is HD Voice?
- How Does it Work?
- Requirements
- Benefits of HD Voice
- How to Switch
- VoIP with HD Voice
- FAQs
What is HD Voice?
High-definition (HD) voice calling is audio technology that delivers clearer voice calling and a higher overall phone call quality by using a wideband signal to transmit high- and low-frequency sounds.
Most VoIP and mobile phone providers support HD Voice, as it can transmit over the internet, 5G, 4G LTE, and even Bluetooth–this means you can access it on your mobile device, business VoIP system, and home VoIP system.
Paired with noise cancellation technology in call center headsets or headphones, high-definition voice provides VoIP audio that captures the speaker’s natural sound, clearly distinguishing it from other speakers and background noises.
How Does HD Voice Work?
HD voice calling works by compressing and transmitting a high frequency-range analog signal with a high sample rate and bitrate.
High bitrates of 85-100 Kbps mean clearer audio that mimics face-to-face conversation.
This increased call clarity is thanks to codecs, the computer code technology that determines the quality of sound transmission. A combination of the words compress and decompress, codecs take an analog sound and convert it into a digital data format so that it can be decompressed by the receiving codec in another device.
Codec software exists in desktop and mobile devices and can transmit wideband audio frequencies via the internet, Bluetooth, traditional PSTN landline, as well as 4G LTE networks using voice over LTE (voLTE). This is why Apple iPhones, Android phones, Samsung, AT&T, Verizon, and many other smartphone and mobile providers–in addition to VoIP providers–support HD voice.
While codecs compress all sorts of media–like videos into .mov files and images into .jpeg files–audio codecs determine the sound transmission’s signal frequency, sample rate, and bitrate, which are all critical components of the high-definition sound quality.
Audio Signal Frequency in HD Voice
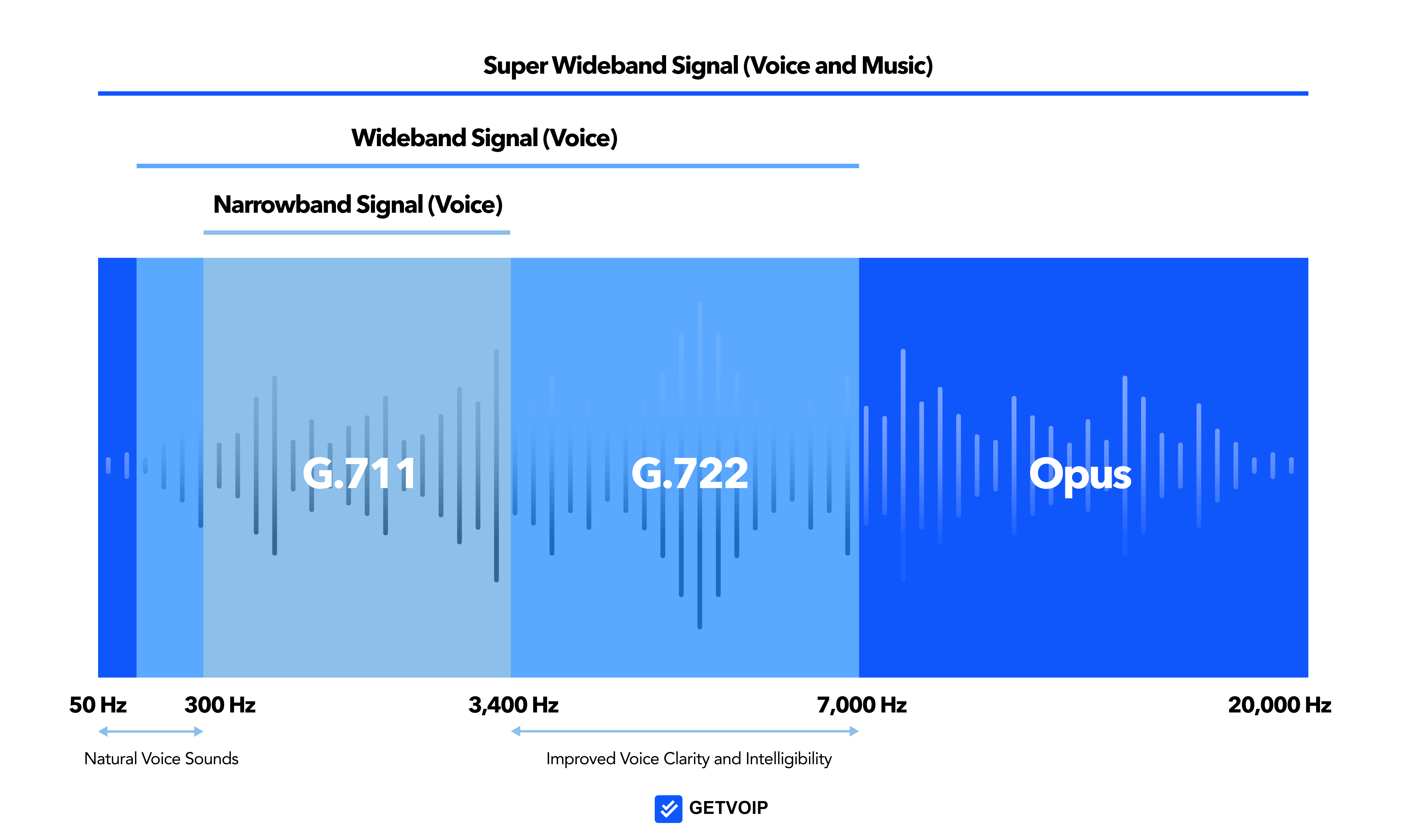
Traditional, narrow-band audio transmits only the mid-range frequencies of a speaker’s voice, while higher-tech wideband audio technology–like in HD calling–transmits a wider-range frequency that captures more speech tones.
While the human voice frequency ranges from 50 to 7,000 Hz, a traditional PSTN phone connection with narrowband audio transmits voice frequencies between 300 and 3,400 Hz–cutting out the speaker’s lowest and highest pitches, leading to fuzzier, duller sound quality.
In contrast, codecs in HD Voice-capable devices – with wideband audio – transmit audio frequencies between 50 and 20,000 Hz, covering many of the human voice's natural higher and lower sounds, leading to clearer, more realistic-sounding audio over mobile and VoIP headphones, hardphones, and softphones.
Sample Rate in HD Voice
Sample rate is the number of audio samples the codec takes per second in order to compress and transmit the most accurate frequency possible. The higher the sample rate, the better the audio quality.
While traditional PSTN codecs have a sample rate of around 8,000 samples per second, HD voice codecs have a sample rate of 16,000 or even up to 48,000 samples per second–leading to tremendously more accurate sound.
Bitrate in HD Voice
Bitrate measures the speed of audio data transfers made via uploads and downloads – in other words, bitrate shows the amount of audio data transferred per second.
Bitrate is measured in kilobits per second (Kbps). While a high bitrate generally means better quality, larger amounts of data demand more network bandwidth. Some network connections with lots of simultaneous calls prefer to use codecs with lower bitrates to conserve bandwidth.
Both traditional PSTN and modern HD Voice codecs have bitrates around 64 Kbps, while many carriers today support the G.729 codec with an 8 Kbps bitrate. Opus, a state-of-the-art codec, has a flexible bitrate that can range from 6-510 Kbps, depending on user demands and network crowdedness.
Comparing Popular HD Voice Codecs
Here are today’s most popular codecs and their key features:
- G.711: Used by traditional PSTN networks and many modern-day VoIP providers, this codec has narrowband sound quality and a high bitrate
- G.729: Supported by some VoIP providers, this codec has narrowband sound quality but a low bitrate–a great option if the network shares many devices
- G.722: Relatively modern, this wideband codec transmits a high sample rate and high bitrate
- AMR-WB (G.722.2): An update on the regular G.722, this wideband codec is supported by most mobile carriers and transmits a high frequency, high sample rate, and a low bitrate
- Opus: The current gold standard of codec technology, this codec delivers super-wideband signal that transcends regular voice tones, with flexible sample rate and bitrate that can be very small or very large
| Codec | Signal | HD | Sample Rate | Bandwidth Used | Bitrate |
| G.729 | 300-3400 Hz narrowband | No | 8,000 samples per second | 24-30Kbps | 8 kbit/s |
| G.711 | 300-3400 Hz
narrowband |
No | 8,000 samples per second | 80-90 Kbps | 64 kbps |
| G.722 | 50-7000 Hz | Yes | 16,000 samples per second (16,000 Hz) | 80-90 Kpbs | 64 Kbps |
| AMR-WB (G.722.2) | 50-7000 Hz | Yes | 16,000 samples per second
(16,000 Hz) |
30 Kbps | 24 Kbps |
| Opus | 50-20,000 Hz | Yes | 8,000-48,000 samples per second | 10-550 Kbps | 6-510 Kbps |
Requirements for HD Voice
Before integrating HD Voice, consider if your setup meets the following bandwidth and hardware requirements.
High-Speed Internet with Sufficient Bandwidth
Since HD Voice’s higher bitrate uses more data than a standard-quality phone call, make sure your internet connection provides enough bandwidth to support all the network’s high-definition phone calls.
Regardless of which codec your VoIP devices use, you should reserve at least 100 Kbps of data per VoIP call.
20 agents require at least 2,000 Kbps for simultaneous calls, plus further bandwidth for file sharing, emailing, texting, and video.
Most internet connections today support a bandwidth between 20,000 and 1,200,000 Kbps (200-1200 Mbps), and most high-quality routers support anywhere between 40,000 and 80,000 Kbps–so a good router and internet provider will support dozens of HD Voice calls within a network.
HD Voice-Supporting Codec
In order to make an HD call on a 4G, 5G, or VoIP network, your provider must support one of the following codecs: G.722, AMR-WB (G.722.2), Enhanced Voice Service (EVS), or Opus. Luckily, most providers support several of these codecs.
Handset or Device with Noise Cancelling Technology
For an optimal high-definition voice calling experience, mobile and VoIP hardware devices like headsets, hard phones, or mobile devices should have noise-canceling technology, which detects and eliminates call background noise, so callers receive a more distinguishable voice signal.
Noise cancellation is supported by nearly all of today’s VoIP hardware providers, including Ooma, Avaya, Yealink, Cisco, Polycom, and more.
Benefits of HD Voice Calling
Here are some of our favorite HD Voice benefits:
Clearer Sound
HD Voice wideband codecs catch several hundred Hz of natural voice sounds left out by narrowband voice signal, on both the low and high ends. This means HD Voice callers receive a fuller sound that mimics natural conversation.
More Effective Conference Calls
HD Voice’s clearer intelligibility is a major benefit for conference calls with large parties.
During HD Voice conference calls, when multiple users speak at once, it’s easier to distinguish each individual’s voice and what each participant says, reducing the need for repetition – and lowering frustration levels.
Accurate Voicemail Transcriptions
A popular feature among VoIP users, voicemail transcriptions can sometimes frustrate users with inaccurate transcription, which occurs more often when the incoming speech is fuzzy or unclear.
HD Voice’s increased clarity makes it easier for Natural Language Technology (NLT) to distinguish the speaker’s words and transcribe the voicemail accurately.
Improved Customer Experience
Customers expect fast service. When poor call quality forces agents and customers to repeat themselves, both parties become frustrated, harming relationships and the customer’s perception of your company.
HD Voice demonstrates professional-grade customer-facing technology that reduces the need for repetition. This means quicker, more efficient calls, higher first-call resolution rates, and an improved CSAT score.
Optimal Bandwidth Usage
All phone numbers and devices in a VoIP call must use the same codec, and most network providers support multiple codecs. When a call connects, the mobile or VoIP phone system automatically utilizes the most optimal codec shared by both parties and supported by bandwidth.
Multiple team members sharing an internet connection and VoIP provider can use different codecs for simultaneous calls, taking advantage of as much network bandwidth as possible.
No Additional Setup
Since mobile devices and VoIP PBX systems already contain the codecs and noise-cancellation materials for HD Voice, your phone system automatically provides the highest audio quality possible during every call–no need to install or enable anything.
If you want to disable HD Voice, you can switch to your phone carrier network on your VoIP or mobile provider’s Settings page.
What to Consider Before Switching to HD Voice Calling
Before selecting an HD Voice service provider, consider the following:
Provider-Supported Codecs
While nearly all phone service providers offer HD Voice and a G.711 narrowband codec, many offer even stronger options, like G.722 and Opus codecs.
Select a company with codecs that fit your network's bandwidth demands while providing the highest frequency and sample rate possible.
Call and Data Volume
Use your network's call and data volume to calculate how much bandwidth you will need to support all callers simultaneously using HD Voice, Also consider other bandwidth-heavy applications like video conferencing, streaming, gaming, and cloud-based apps.
In your router’s Settings menu, view the following information for individual devices or the entire network:
- The router’s connected devices
- IP Address
- Upload speed
- Download speed
- Total data used
If your network already uses most of your bandwidth before adding HD Voice, you may need to remove devices, applications, or strengthen your network via an added router.
Price
Nearly all VoIP and mobile providers offer HD Voice technology as part of their standard voice plans. However, each pricing plan has unique features and tiers.
When selecting a VoIP provider, in addition to the provider’s codec and HD Voice offerings, consider the features they offer alongside HD Voice–video conferencing, texting, auto attendants, and other features.
VoIP Providers with HD Voice Calling
The table below lists some of our favorite HD-Voice VoIP providers.
| Provider | Pricing for Packages with HD Voice | HD Voice Ready Phones | Supported HD Voice Codecs | More Info |
| RingCentral | All RingEX plans, ranging from $20 to $35 monthly per user | RingCentral Phone (softphone), RingCentral Phone for mobile, Yealink, and Polycom phones. | Opus, G.722, G.711 | RingCentral Reviews |
| Nextiva | All Business Communication and Contact Center plans, ranging from $18.95 to $32.95 monthly per user | Nextiva desk phones, cordless phones, Nextiva for mobile and softphone, Blackwire headsets and all Yealink, Polycom, and Cisco phones | G.711 | Nextiva Reviews |
| Zoom Phone | All Zoom Phone plans, ranging from $10 to $20 monthly per user | Zoom Phone for mobile, Yealink, Polycom, and AudioCodes phones, all conference phones and headsets | Opus, G.722, G.711 | Zoom Reviews |
| Dialpad | All Business Communications plans, ranging from $15 to over $25 monthly per user | All Polycom devices, Dialpad on mobile, and Dialpad softphone | Opus, G.722, G.711, G.729, | Dialpad Reviews |
| 8x8 | All Business Communication plans, ranging from $15 to $44 monthly per user | 8x8 for mobile or softphone, Cisco, Yealink, Polycom, and Jabra phones or headsets | G.722, G.711, G.729 | 8x8 Reviews |
HD Voice is a major step forward from traditional PSTN phone systems, alleviating the frustration of fuzzy, low-quality calls.
VoIP with HD Voice not only provides clearer audio quality on mobile, desktop softphone, or desk phone–it’s also more affordable than most traditional phone systems, easy to set up, and will help your company take advantage of all available network bandwidth.
To learn more, check out our list of today’s top business VoIP providers.
HD Voice Calling FAQs
We’ve answered some commonly asked questions about HD Voice.



